Abstract
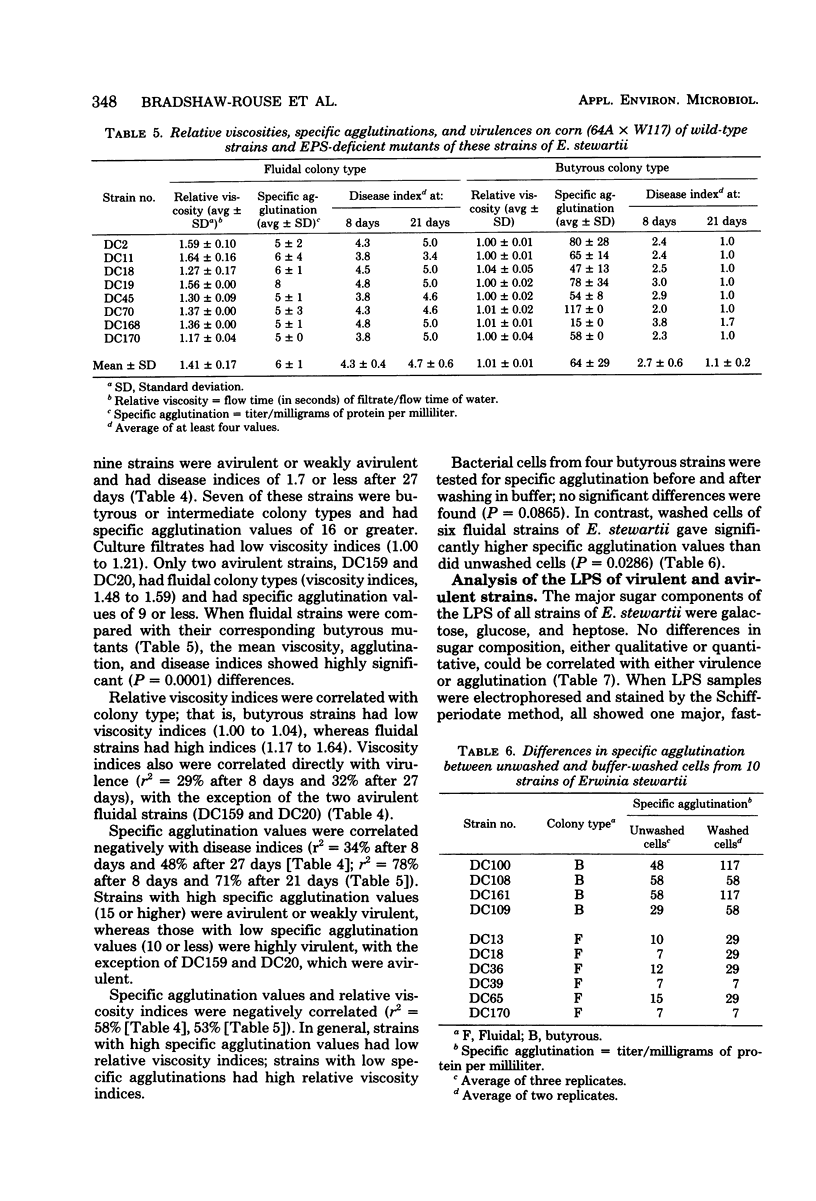
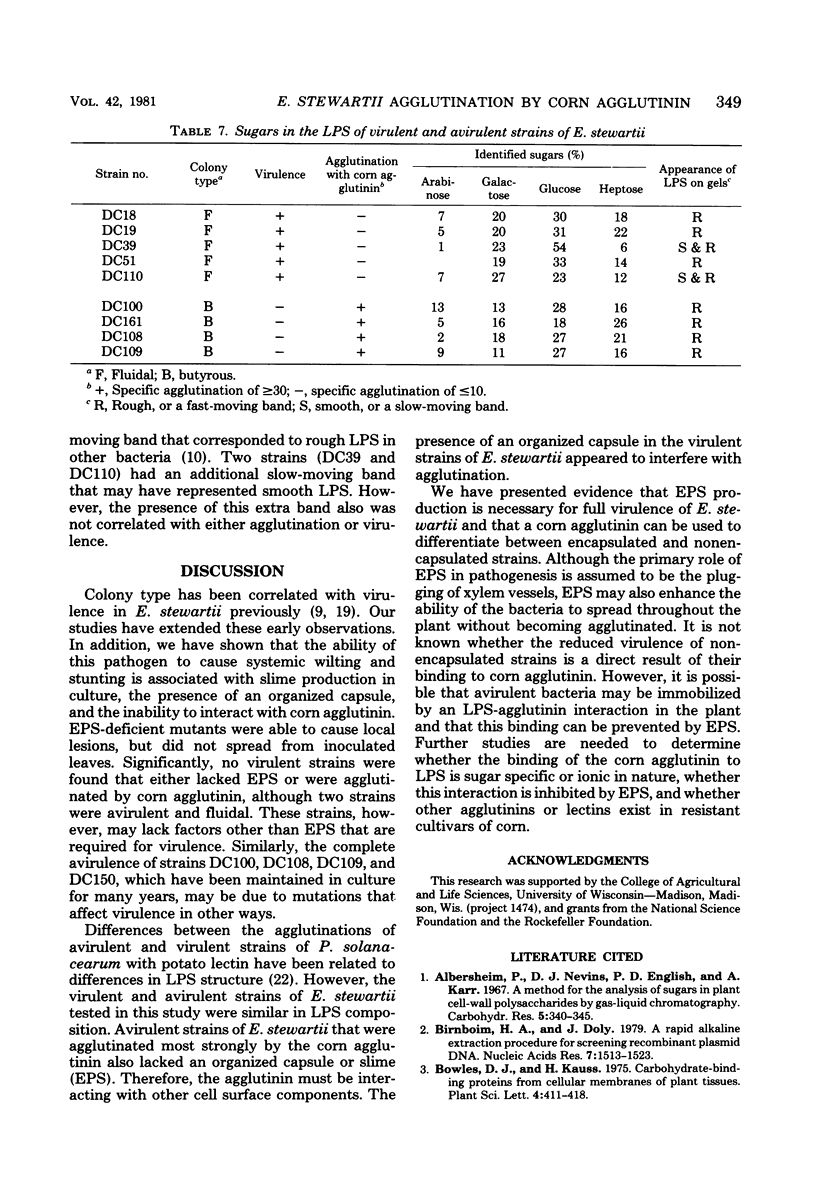
A bacterial agglutinin was extracted from ground corn (WI hybrid 64A × W117) seed with phosphate-buffered saline (pH 6.0) and precipitated with (NH4)2SO4 at 70% saturation. The activities of this agglutinin against 22 strains of Erwinia stewartii (agent of bacterial wilt of corn) that varied in virulence were determined. Specific agglutination (agglutination titer per milligram of protein per milliliter) values were correlated negatively with virulence ratings. Strains with high specific agglutination values (15 or higher) were avirulent or weakly virulent; strains with low specific agglutination values (10 or lower) were highly virulent, with two exceptions. Avirulent strains produced butyrous colonies and released only small amounts of extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) into the medium, and the cells lacked capsules; virulent strains produced fluidal colonies and released large amounts of EPS, and the cells were capsulated. There was a strong correlation between the amount of EPS produced by each strain (as determined by increase in viscosity of the medium) and the specific agglutination value; in contrast, lipopolysaccharide compositions were similar in all strains. When cells of six fluidal strains were washed by repeatedly centrifuging and resuspending them in buffer, they were agglutinated more strongly by corn agglutinin than were unwashed cells. When avirulent cells were washed, their specific agglutination values did not increase significantly. Eight EPS-deficient mutants of E. stewartii, selected for resistance to the capsule-dependent bacteriophage K9, had lower virulence but higher specific agglutination than did their corresponding wild-type parents. Production of EPS appears to be essential for virulence; EPS may prevent agglutination of bacteria in the host, thus allowing their multiplication.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
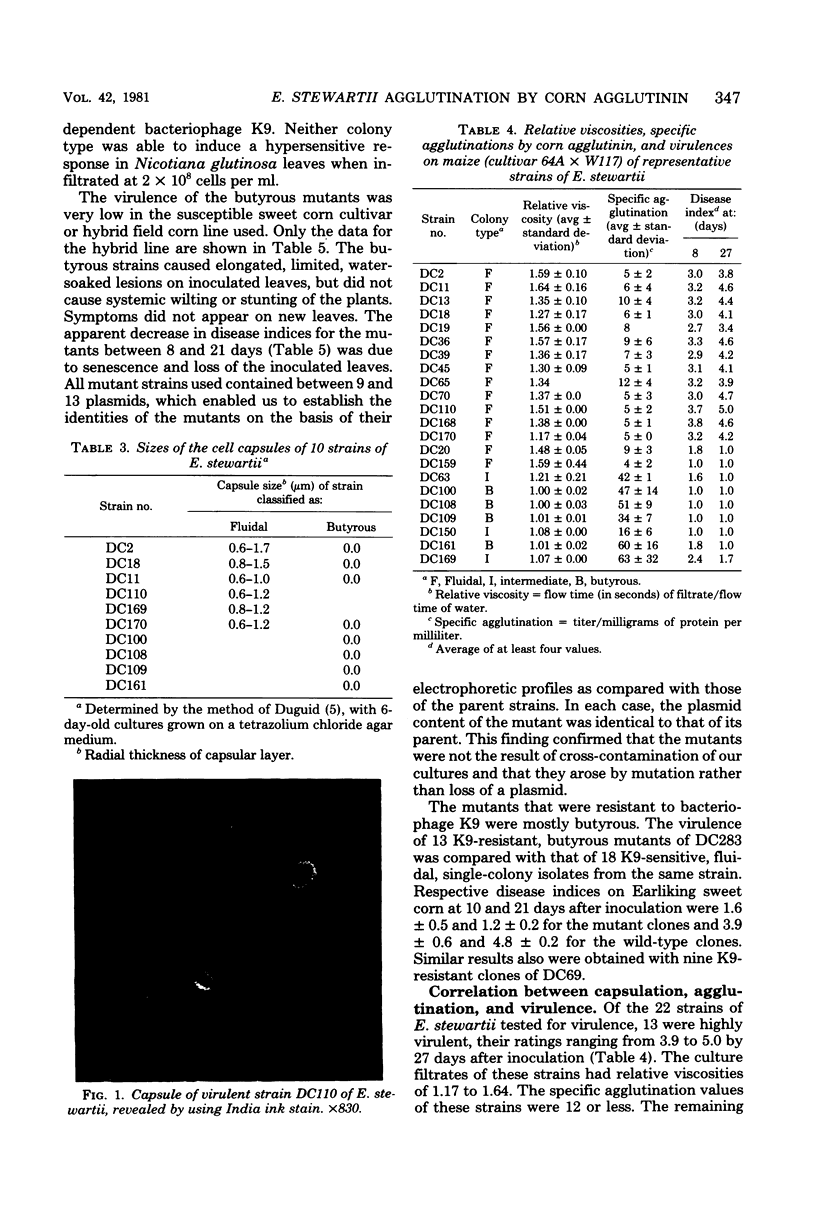
- DUGUID J. P. The demonstration of bacterial capsules and slime. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;63(4):673–685. doi: 10.1002/path.1700630413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanoff S. S., Riker A. J., Dettwiler H. A. STUDIES ON CULTURAL CHARACTERISTICS, PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOGENICITY OF STRAIN TYPES OF PHYTOMONAS STEWARTI. J Bacteriol. 1938 Mar;35(3):235–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.35.3.235-253.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Reske K., Jann K. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides. Analysis of polysaccharide chain lengths by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., ADAMS J. N., TING R. C. Transduction of lactose-utilizing ability among strains of E. coli and S. dysenteriae and the properties of the transducing phage particles. Virology. 1960 Nov;12:348–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whatley M. H., Bodwin J. S., Lippincott B. B., Lippincott J. A. Role of Agrobacterium cell envelope lipopolysaccharide in infection site attachment. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1080–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1080-1083.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whatley M. H., Hunter N., Cantrell M. A., Hendrick C., Keegstra K., Sequeira L. Lipopolysaccharide Composition of the Wilt Pathogen, Pseudomonas solanacearum: CORRELATION WITH THE HYPERSENSITIVE RESPONSE IN TOBACCO. Plant Physiol. 1980 Mar;65(3):557–559. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]