Abstract
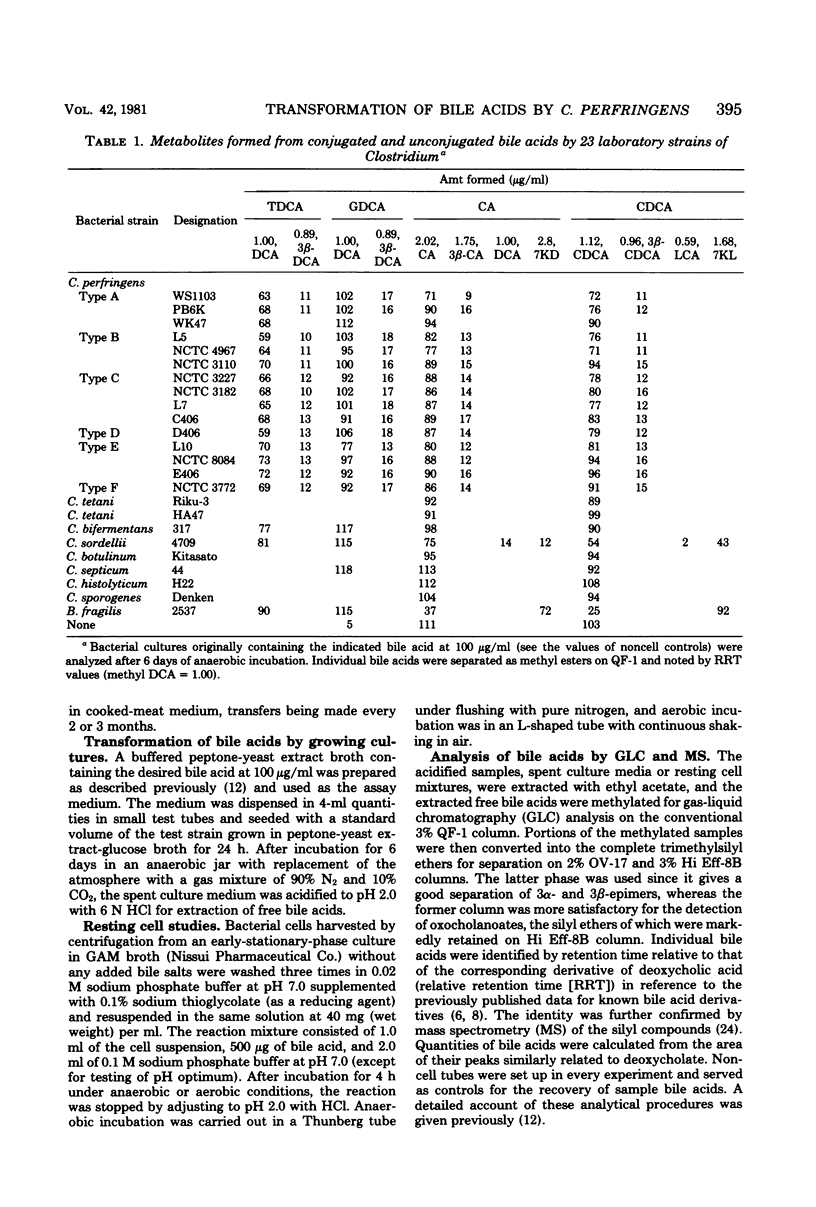
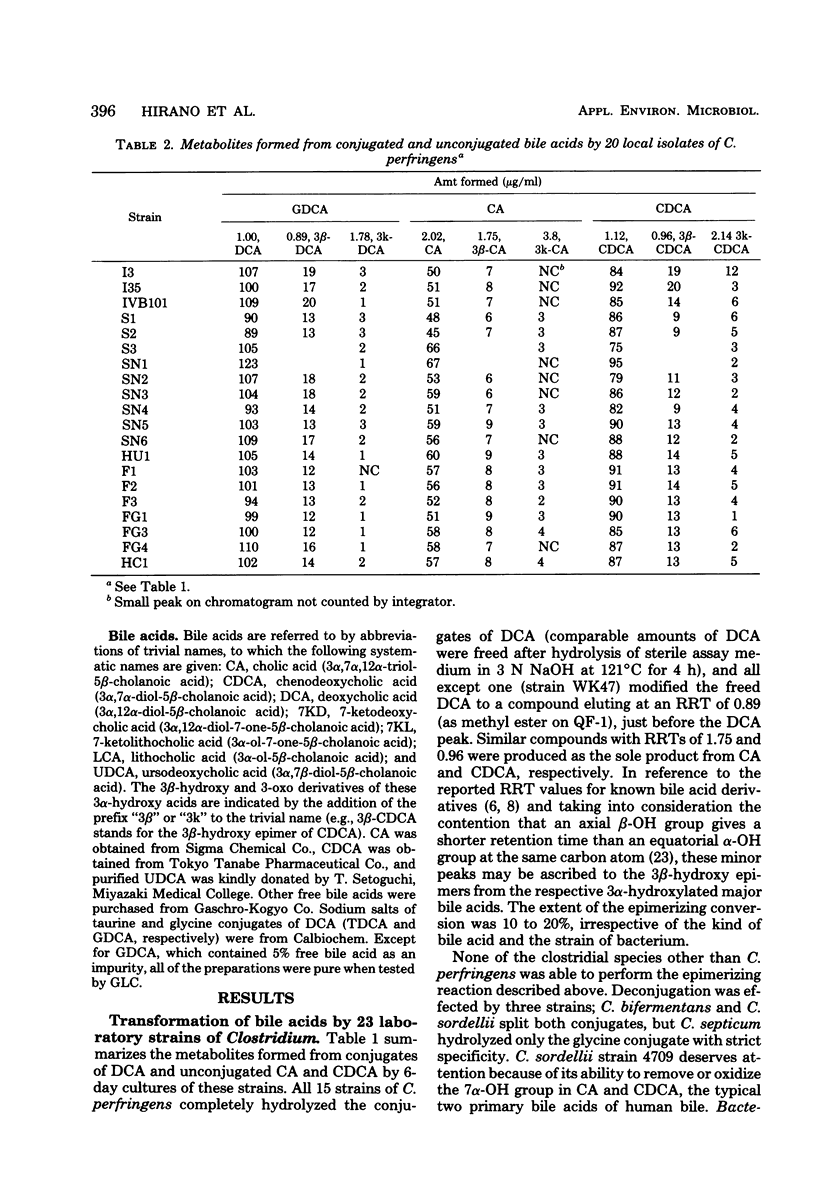
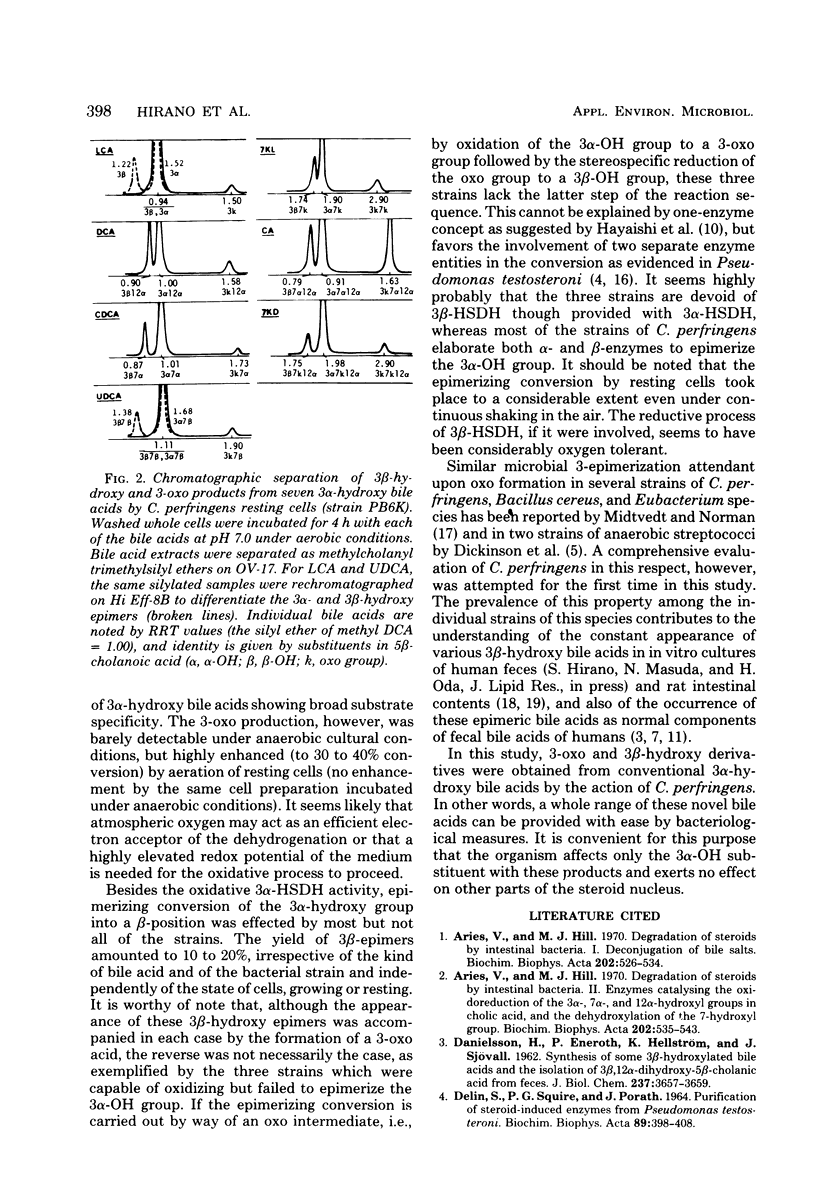
Thirty-five strains of Clostridium perfringens were examined for their ability to transform bile acids, both in growing cultures and by washed whole cells. All of the strains oxidized the 3 alpha-hydroxy group to an oxo group, and all except three converted the same alpha-hydroxy group into a beta-configuration. The oxidative 3 alpha-dehydrogenation was barely detectable under anaerobic cultural conditions but was clearly demonstrated in an aerated system using washed whole cells, with a pH optimum between 7.0 and 9.0. The epimerizing reaction amounting to 10 to 20% conversion was observed in anaerobic cultures and also with resting cells, irrespective of oxygen supply. Both reactions were carried out with seven conventional 3 alpha-hydroxy bile acids, thus producing a series of 3-oxo and 3 beta-hydroxy derivatives that could be examined for gas-liquid chromatographic and mass spectrometric behavior. No evidence for the occurrence of 7 alpha- and 12 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities among the test strains was found. A highly potent deconjugating hydrolase was elaborated by all of the strains.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aries V., Hill M. J. Degradation of steroids by intestinal bacteria. I. Deconjugation of bile salts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):526–534. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aries V., Hill M. J. Degradation of steroids by intestinal bacteria. II. Enzymes catalysing the oxidoreduction of the 3 alpha-, 7 alpha- and 12 alpha-hydroxyl groups in cholic acid, and the dehydroxylation of the 7-hydroxyl group. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIELSSON H., ENEROTH P., HELLSTROM K., SJOVALL J. Synthesis of some 3beta-hydroxylated bile acids and the isolation of 3beta, 12alpha-dihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid from feces. J Biol Chem. 1962 Dec;237:3657–3659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELIN S., SQUIRE P. G., PORATH J. PURIFICATION OF STEROID-INDUCED ENZYMES FROM PSEUDOMONAS TESTOSTERONI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Sep 18;89:398–408. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. B., Gustafsson B. E., Norman A. Determination of bile acid conversion potencies of intestinal bacteria by screening in vitro and subsequent establishment in germfree rats. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(5):691–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eneroth P., Gordon B., Ryhage R., Sjövall J. Identification of mono- and dihydroxy bile acids in human feces by gas-liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):511–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floch M. H., Gershengoren W., Freedman L. R. Methods for the quantitative study of the aerobic and anaerobic intestinal bacterial flora of man. Yale J Biol Med. 1968 Aug;41(1):50–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYAISHI O., SATO Y., JAKOBY W. B., STOHLMAN E. F. Reversible enzymatic oxidation of bile acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Jun;56(2):554–555. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEFTMANN E., WEISS E., MILLER H. K., MOSETTIG E. Isolation of some bile acids and sterols from the feces of healthy men. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Oct;84:324–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90597-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Nakama R., Tamaki M., Masuda N., Oda H. Isolation and characterization of thirteen intestinal microorganisms capable of 7 alpha-dehydroxylating bile acids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):737–745. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.737-745.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS P. I., TALALAY P. Induction and purification of alpha- and beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):661–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald I. A., Bishop J. M., Mahony D. E., Williams C. N. Convenient non-chromatographic assays for the microbial deconjugation and 7alpha-OH bioconversion of taurocholate. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):530–535. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.530-535.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Forrest T. P., Costain G. A., Rao B. G. Identification of 7alpha-, 12alpha-dihydroxy-3-oxo cholanoic acid as the major degradation product from cholic by C. perfringens. J Steroid Biochem. 1978 Apr;9(4):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(78)90630-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Meier E. C., Mahony D. E., Costain G. A. 3alpha-, 7alpha- and 12alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities from Clostridium perfringens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 19;450(2):142–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Norman A. Adsorption of bile acids to intestinal microorganisms. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(2):202–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Norman A. Anaerobic, bile acid transforming microorganisms in rat intestinal content. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;72(2):337–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb01347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Norman A. Bile acid transformations by microbial strains belonging to genera found in intestinal contents. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;71(4):629–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb05183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair P. P., Gordon M., Gordon S., Reback J., Mendeloff A. I. The cleavage of bile acid conjugates by cell-free extracts from Clostridium perfringens. Life Sci. 1965 Oct;4(19):1887–1892. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair P. P., Gordon M., Reback J. The enzymatic cleavage of the carbon-nitrogen bond in 3-alpha, 7-alpha, 12-alpha-trihydroxy-5-beta-cholan-24-oylglycine. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 10;242(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. G. Enumeration of Clostridium welchii in the faeces of varying sections of the human population. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Sep;64(3):367–374. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


