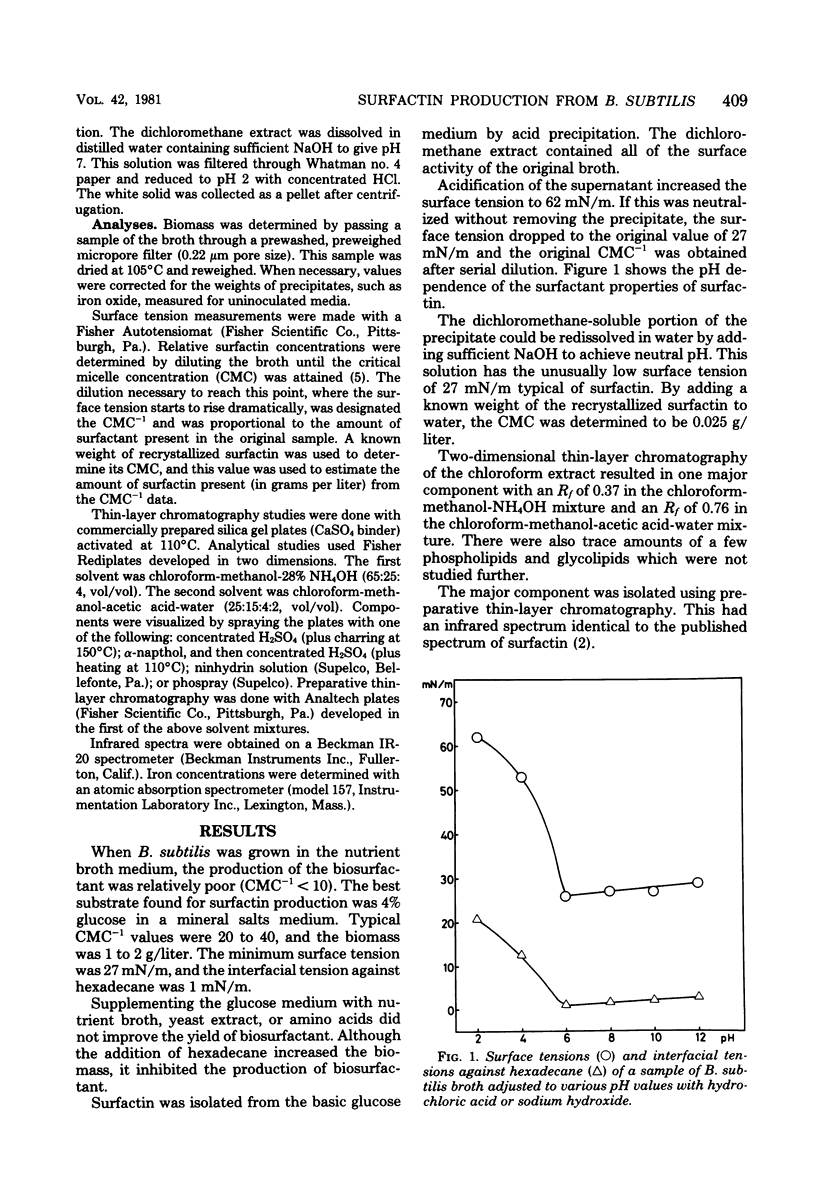
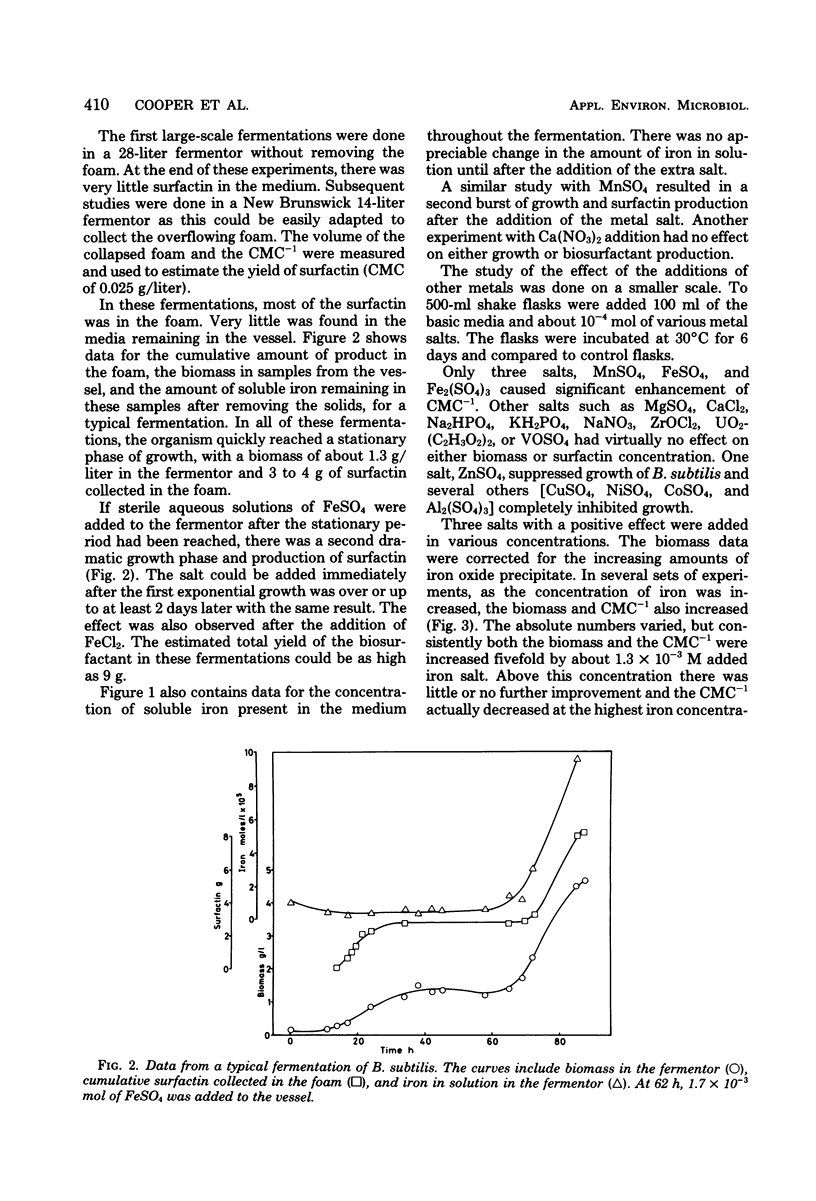
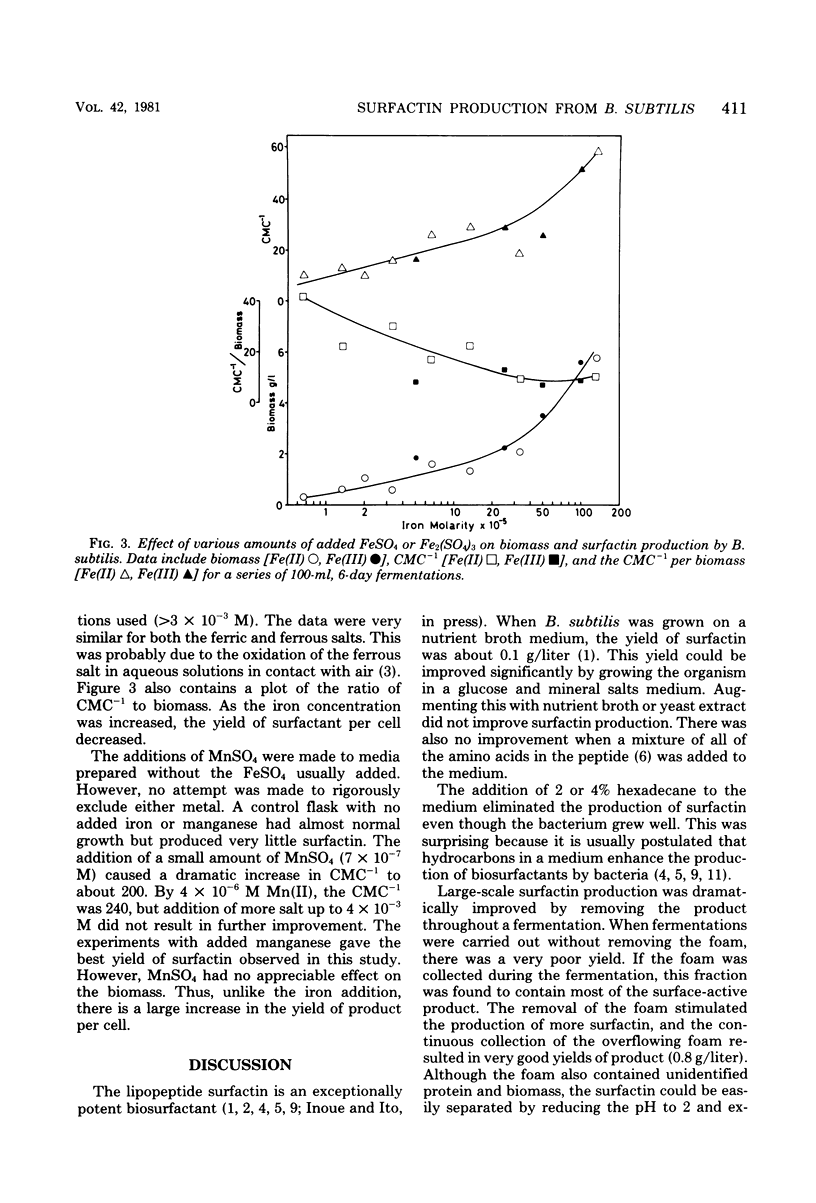
Abstract
The lipopeptide, surfactin, is produced by Bacillus subtilis. A study has been made on large-scale production of this surfactant. A good yield was obtained from a glucose substrate fermentation by continuously removing the product by foam fractionation. The surfactin could be easily recovered from the collapsed foam by acid precipitation. The yield was also improved by the addition of either iron or manganese salts. Hydrocarbon addition to the medium, which normally increases biosurfactant production, completely inhibited surfactin production by B. subtilis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arima K., Kakinuma A., Tamura G. Surfactin, a crystalline peptidelipid surfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis: isolation, characterization and its inhibition of fibrin clot formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 May 10;31(3):488–494. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S. Nature and properties of a cytolytic agent produced by Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jun;61(3):361–369. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-3-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. G., Zajic J. E., Gerson D. F. Production of surface-active lipids by Corynebacterium lepus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):4–10. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.4-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald C. R., Cooper D. G., Zajic J. E. Surface-Active Lipids from Nocardia erythropolis Grown on Hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):117–123. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.117-123.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Perry A., Gibson D. T., Gutnick D. L. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: specificity of hydrocarbon substrate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):409–413. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.409-413.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Zuckerberg A., Rubinovitz C., Gutnick D. L. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: isolation and emulsifying properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):402–408. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.402-408.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajic J. E., Guignard H., Gerson D. F. Properties and biodegradation of a bioemulsifier from Corynebacterium hydrocarboclastus. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1977 Sep;19(9):1303–1320. doi: 10.1002/bit.260190905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


