Abstract
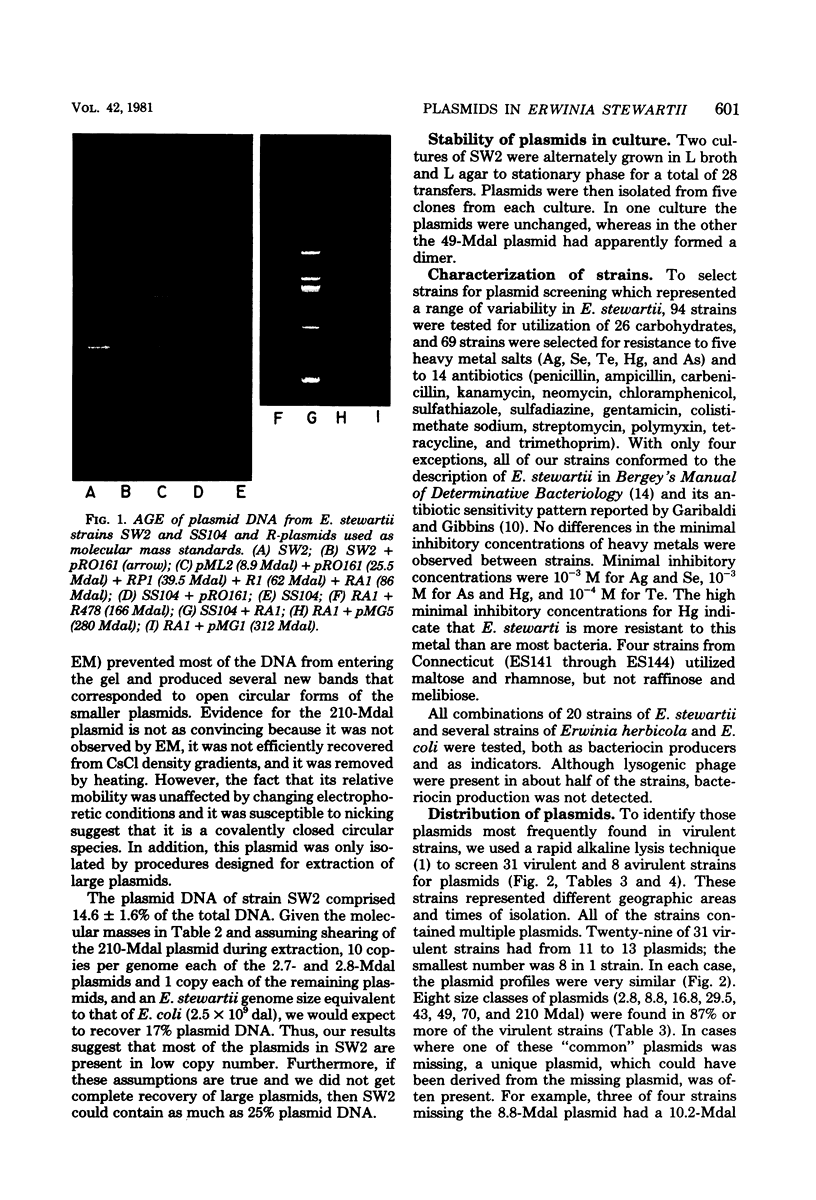
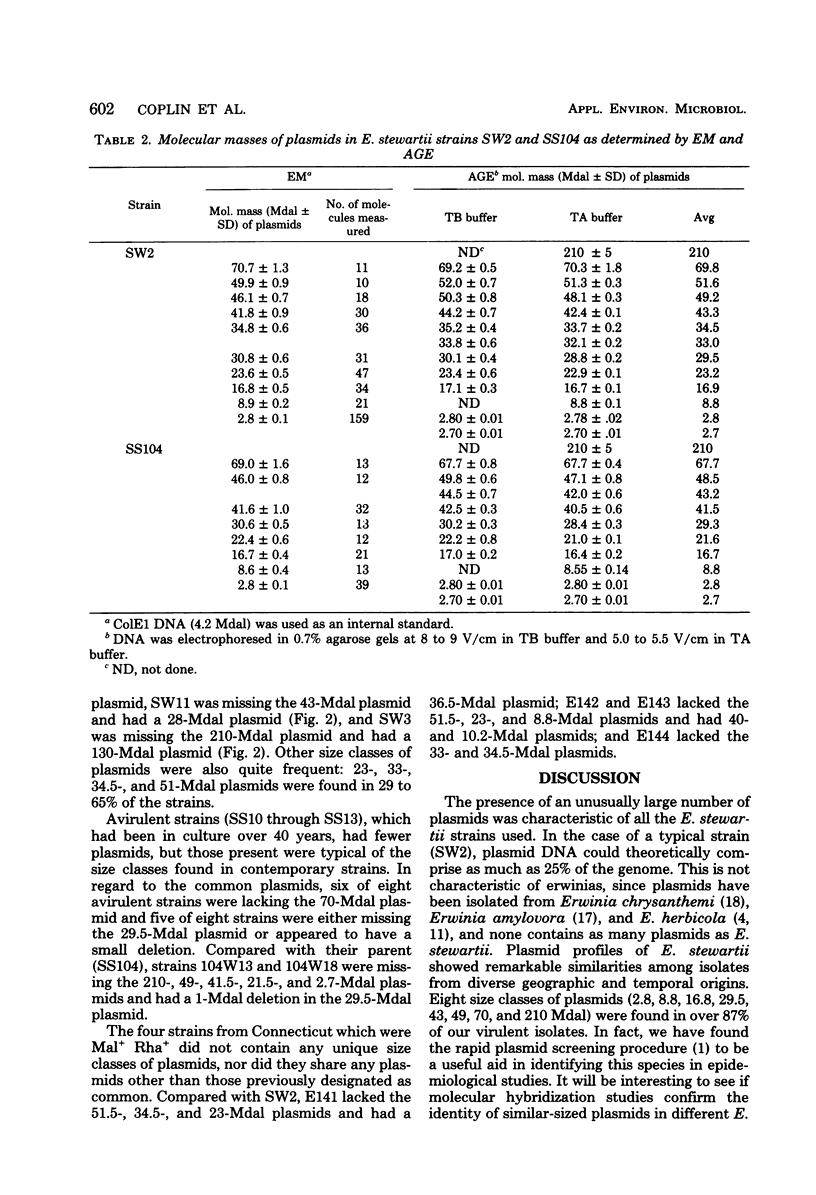
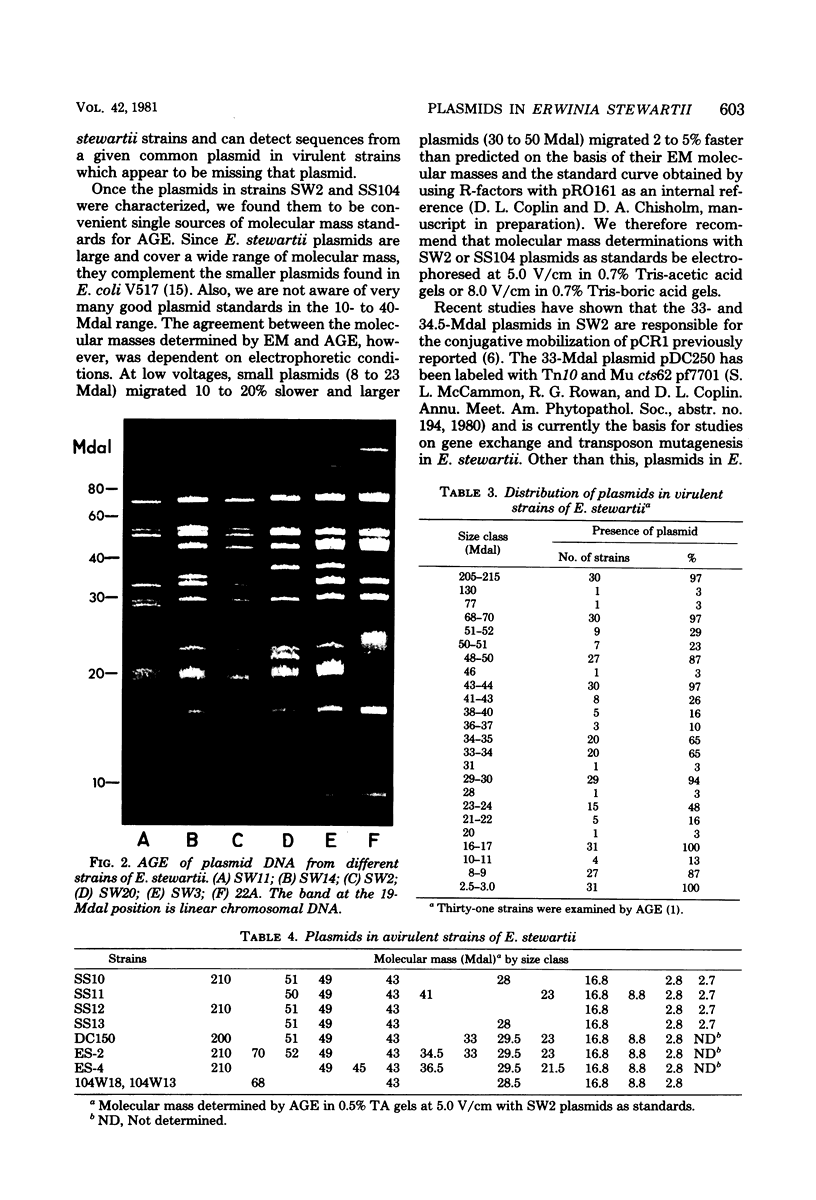
Plasmids in 39 strains of Erwinia stewartii were examined by agarose gel electrophoresis. Most virulent strains had from 11 to 13 plasmids ranging in molecular mass from 2.8 to 210 megadaltons and contained plasmids of 210, 70, 49, 43, 29.5, 16.8, 8.8, and 2.8 megadaltons. Plasmids in strains SW2 and SS104 were characterized by both electron microscopy and agarose gel electrophoresis and may be useful as convenient references for sizing plasmids by electrophoresis. Specific size classes of plasmids could not be associated with antibiotic and heavy metal resistance, carbohydrate utilization, bacteriocin production, or pathogenicity to corn. However, avirulent strains tended to have fewer plasmids than virulent strains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw-Rouse J. J., Whatley M. H., Coplin D. L., Woods A., Sequeira L., Kelman A. Agglutination of Erwinia stewartii Strains with a Corn Agglutinin: Correlation with Extracellular Polysaccharide Production and Pathogenicity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):344–350. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.344-350.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier T. C., Nester E. W. Isolation of covalently closed circular DNA of high molecular weight from bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1976 Dec;76(2):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90338-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garibaldi A., Gibbins L. N. Induction of avirulent variants in Erwinia stewartii by incubation at supraoptimal temperatures. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Aug;21(8):1282–1287. doi: 10.1139/m75-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbins L. N., Bennett P. M., Saunders J. R., Grinsted J., Connolly J. C. Acceptance and transfer of R-factor RP1 by members of the "herbicola" group of the genus Erwinia. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):309–316. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.309-316.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten J. L., Vidaver A. K., Koski R. K., Semancik J. S. RNA polymerase activity associated with bacteriophage phi 6. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):464–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.464-471.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver A. K., Mathys M. L., Thomas M. E., Schuster M. L. Bacteriocins of the phytopathogens Pseudomonas syringae, P. glycinea, and P. phaseolicola. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jun;18(6):705–713. doi: 10.1139/m72-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hondel C. A., Keegstra W., Borrias W. E., van Arkel G. A. Homology of plasmids in strains of unicellular Cyanobacteria. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]