Abstract
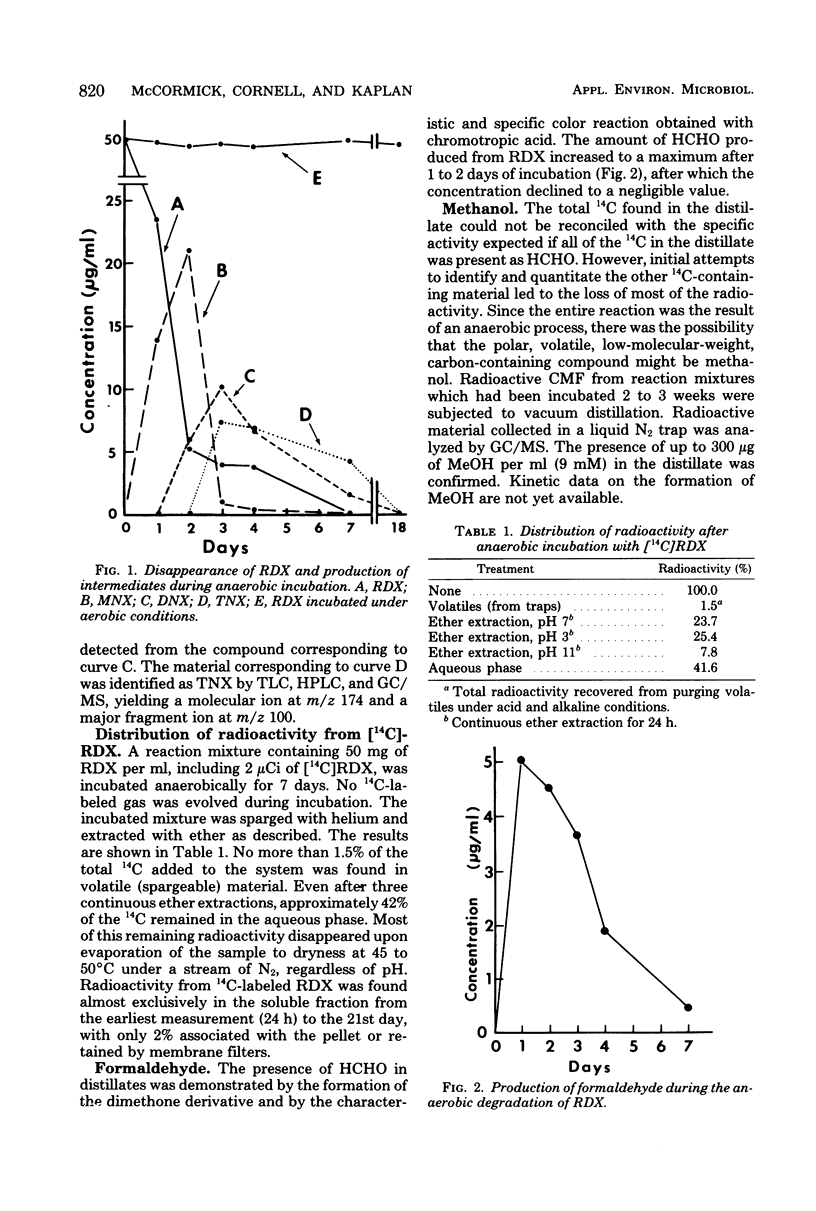
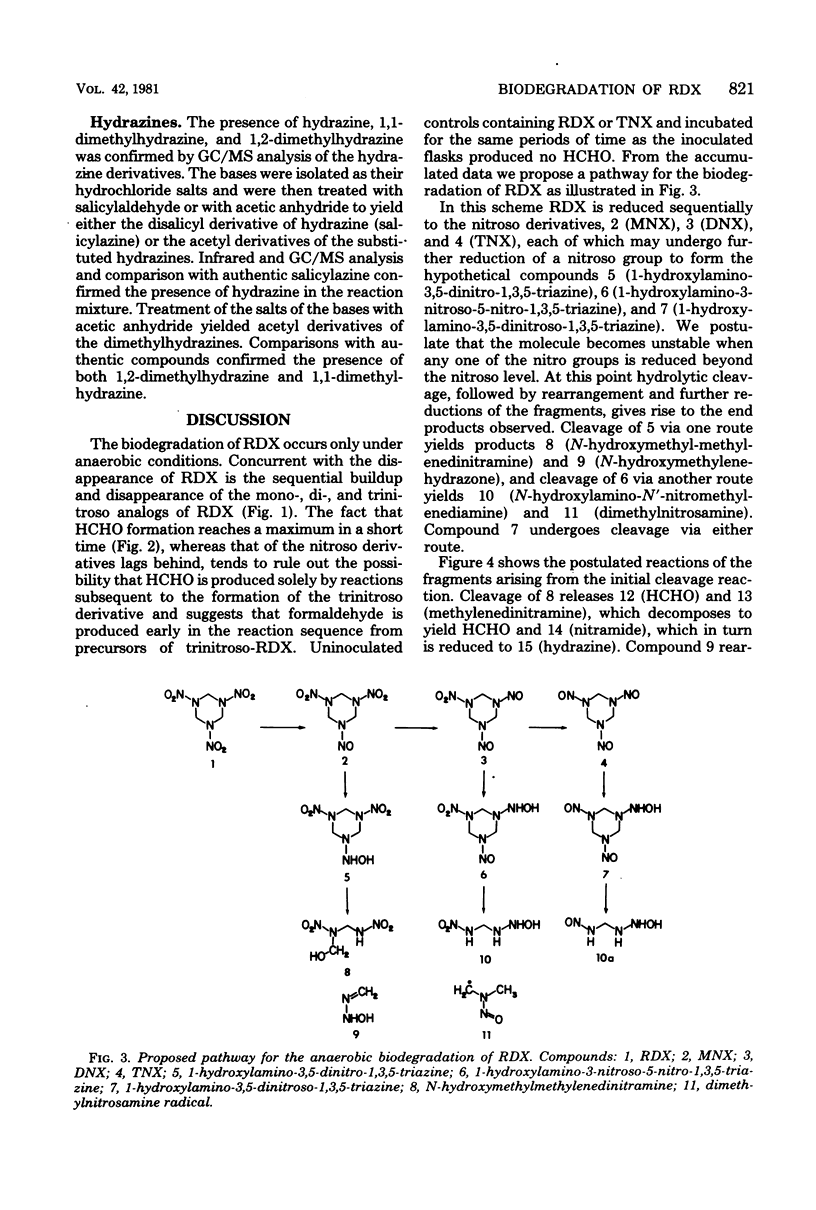
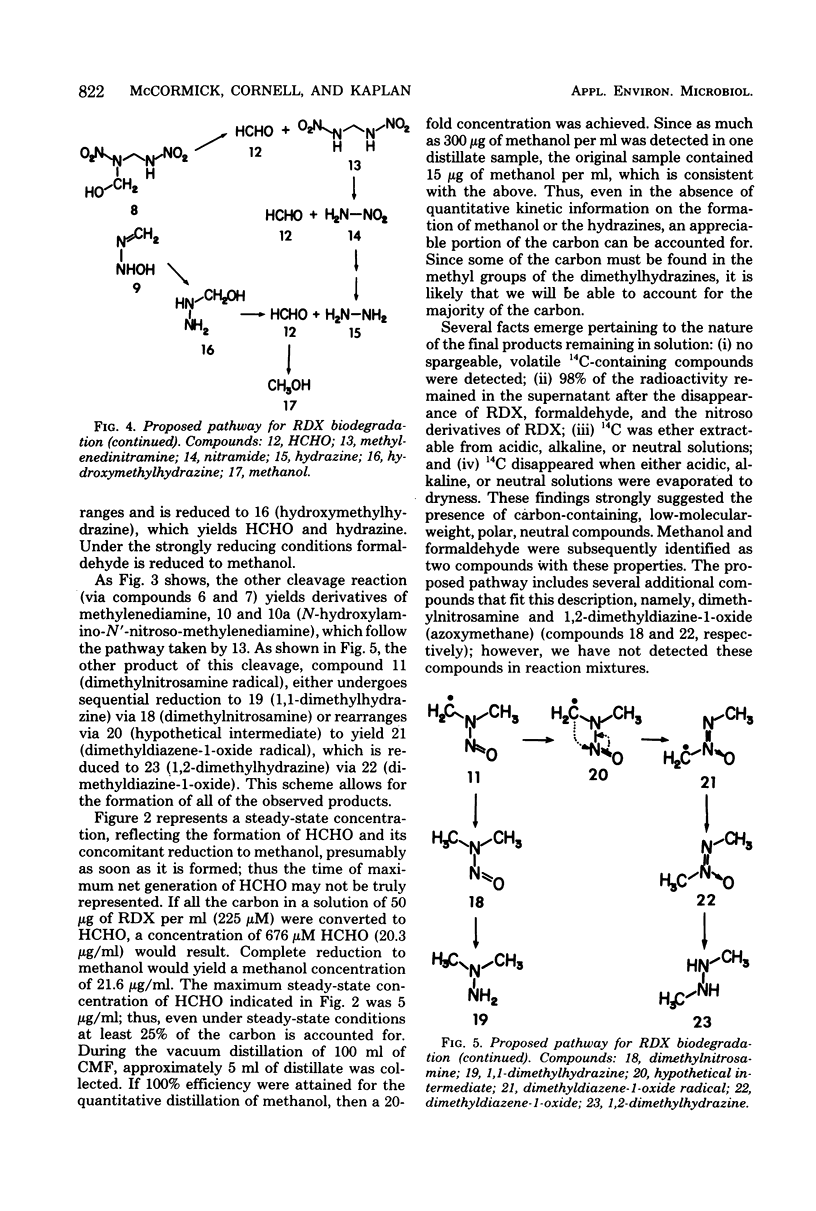
Biodegradation of the explosive hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) occurs under anaerobic conditions, yielding a number of products, including: hexahydro-1-nitroso-3,5-dinitro-1,3,5-triazine, hexahydro-1,3-dinitroso-5-nitro-1,3,5-triazine, hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitroso-1,3,5-triazine, hydrazine, 1,1-dimethyl-hydrazine, 1,2-dimethylhydrazine, formaldehyde, and methanol. A scheme for the biodegradation of RDX is proposed which proceeds via successive reduction of the nitro groups to a point where destabilization and fragmentation of the ring occurs. The noncyclic degradation products arise via subsequent reduction and rearrangement reactions of the fragments. The scheme suggests the presence of several additional compounds, not yet identified. Several of the products are mutagenic or carcinogenic or both. Anaerobic treatment of RDX wastewaters, which also contain high nitrate levels, would permit the denitrification to occur, with concurrent degradation of RDX ultimately to a mixture of hydrazines and methanol. The feasibility of using an aerobic mode in the further degradation of these products is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fiala E. S. Investigations into the metabolism and mode of action of the colon carcinogens 1,2-dimethylhydrazine and azoxymethane. Cancer. 1977 Nov;40(5 Suppl):2436–2445. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197711)40:5+<2436::aid-cncr2820400908>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway J. A., Buck C. R. Absence of health hazards associated with RDX manufacture and use. J Occup Med. 1977 Apr;19(4):269–272. doi: 10.1097/00043764-197704000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider N. R., Bradley S. L., Andersen M. E. Toxicology of cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine: distribution and metabolism in the rat and the miniature swine. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;39(3):531–541. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skopek T. R., Liber H. L., Krolewski J. J., Thilly W. G. Quantitative forward mutation assay in Salmonella typhimurium using 8-azaguanine resistance as a genetic marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):410–414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


