Abstract
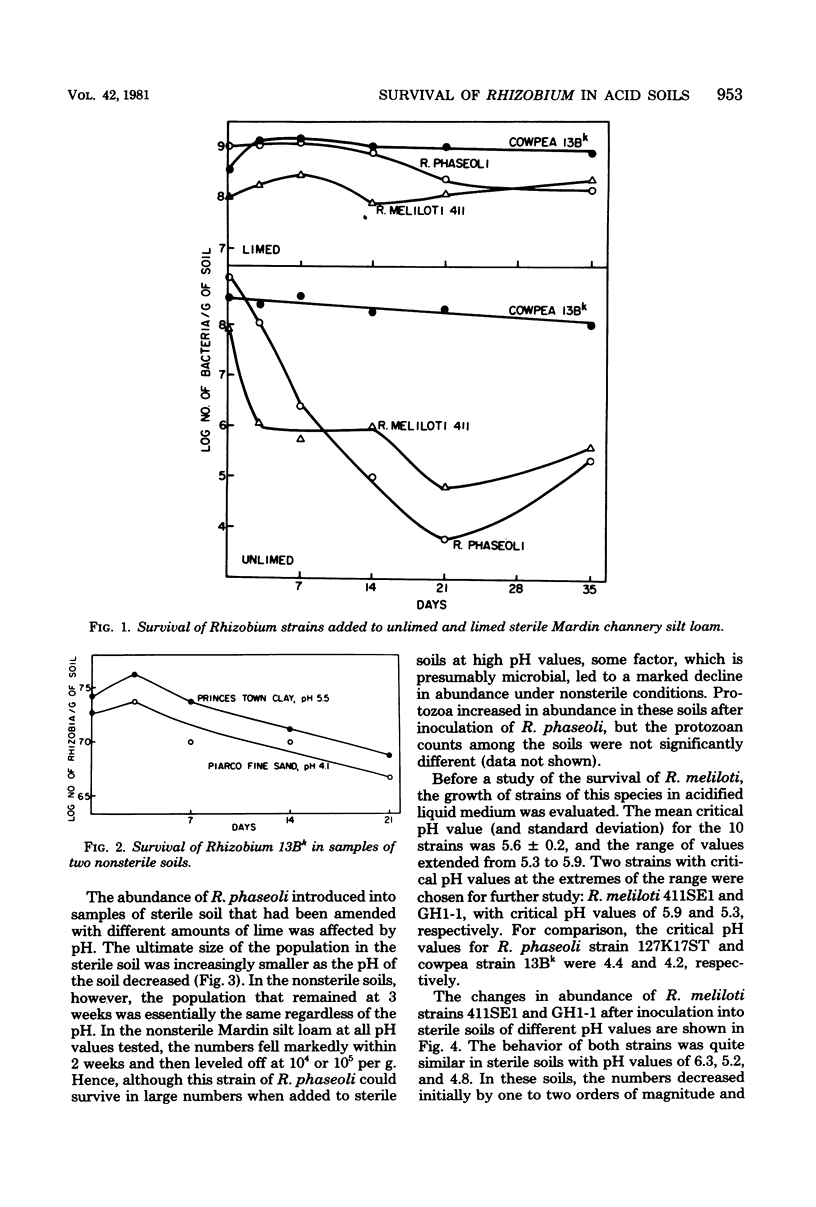
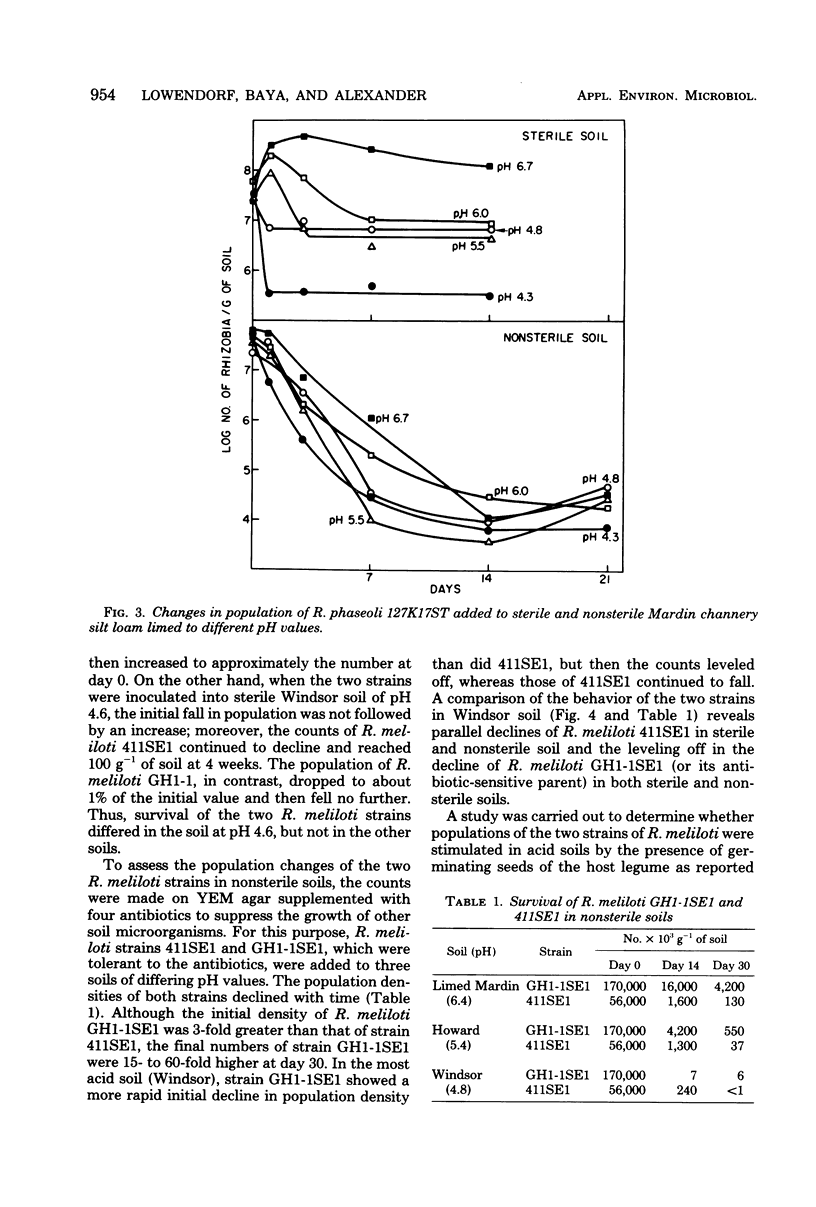
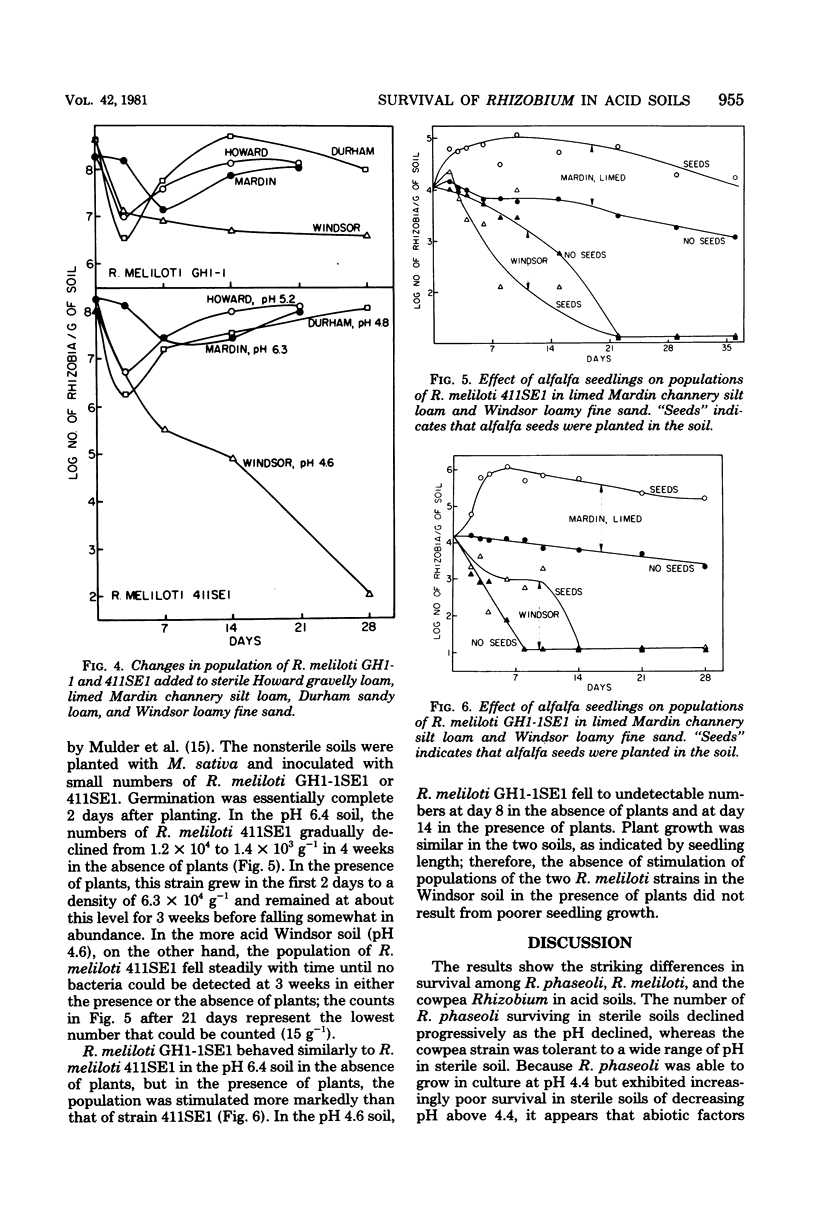
A Rhizobium strain nodulating cowpeas did not decline in abundance after it was added to sterile soils at pH 6.9 and 4.4, and the numbers fell slowly in nonsterile soils at pH 5.5 and 4.1. A strain of R. phaseoli grew when added to sterile soils at pH 6.7 and 6.9; it maintained large, stable populations in soils of pH 4.4, 5.5, and 6.0, but the numbers fell markedly and then reached a stable population size in sterile soils at pH 4.3 and 4.4. The abundance of R. phaseoli added to nonsterile soils with pH values of 4.3 to 6.7 decreased similarly with time regardless of soil acidity, and the final numbers were less than in the comparable sterile soils. The minimum pH values for the growth of strains of R. meliloti in liquid media ranged from 5.3 to 5.9. Two R. meliloti strains, which differed in acid tolerance for growth in culture, did not differ in numbers or decline when added to sterile soils at pH 4.8, 5.2, and 6.3. The population size of these two strains was reduced after they were introduced into nonsterile soils at pH 4.8, 5.4, and 6.4, and the number of survivors was related to the soil pH. The R. meliloti strain that was more acid sensitive in culture declined more readily in sterile soil at pH 4.6 than did the less sensitive strain, and only the former strain was eliminated from nonsterile soil at pH 4.8; however, the less sensitive strain also survived better in limed soil. The cell density of the two R. meliloti strains was increased in pH 6.4 soil in the presence of growing alfalfa. The decline and elimination of the tolerant, but not the sensitive, strain was delayed in soil at pH 4.6 by roots of growing alfalfa.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Danso S. K., Habte M., Alexander M. Estimating the density of individual bacterial populations introduced into natural ecosytems. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;19(11):1450–1451. doi: 10.1139/m73-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danso S. K., Keya S. O., Alexander M. Protozoa and the decline of Rhizobium populations added to soil. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jun;21(6):884–895. doi: 10.1139/m75-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habte M., Alexander M. Further evidence for the regulation of bacterial populations in soil by protozoa. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jun 20;113(3):181–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00492022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méndez-Castro F. A., Alexander M. Acclimation of Rhizobium to salts, increasing temperature and acidity. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1977 Jul-Sep;18(3):155–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


