Abstract
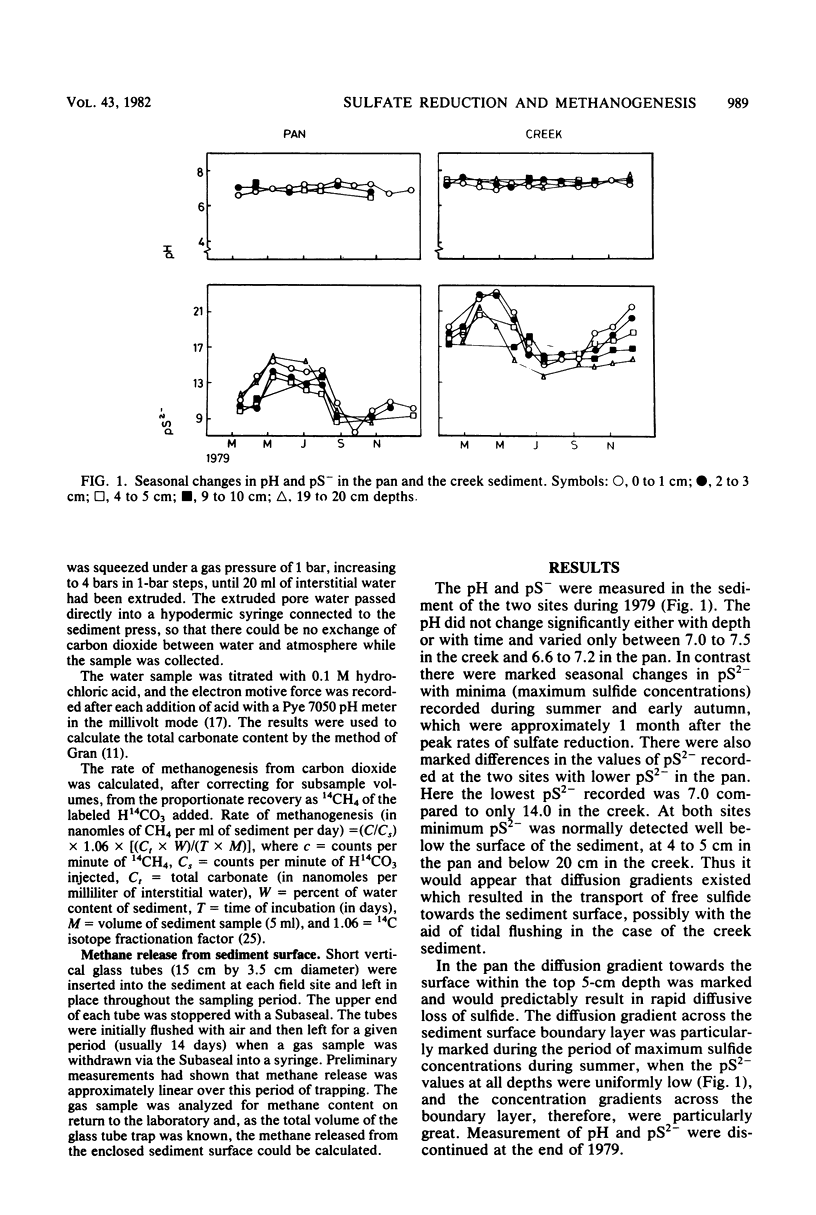
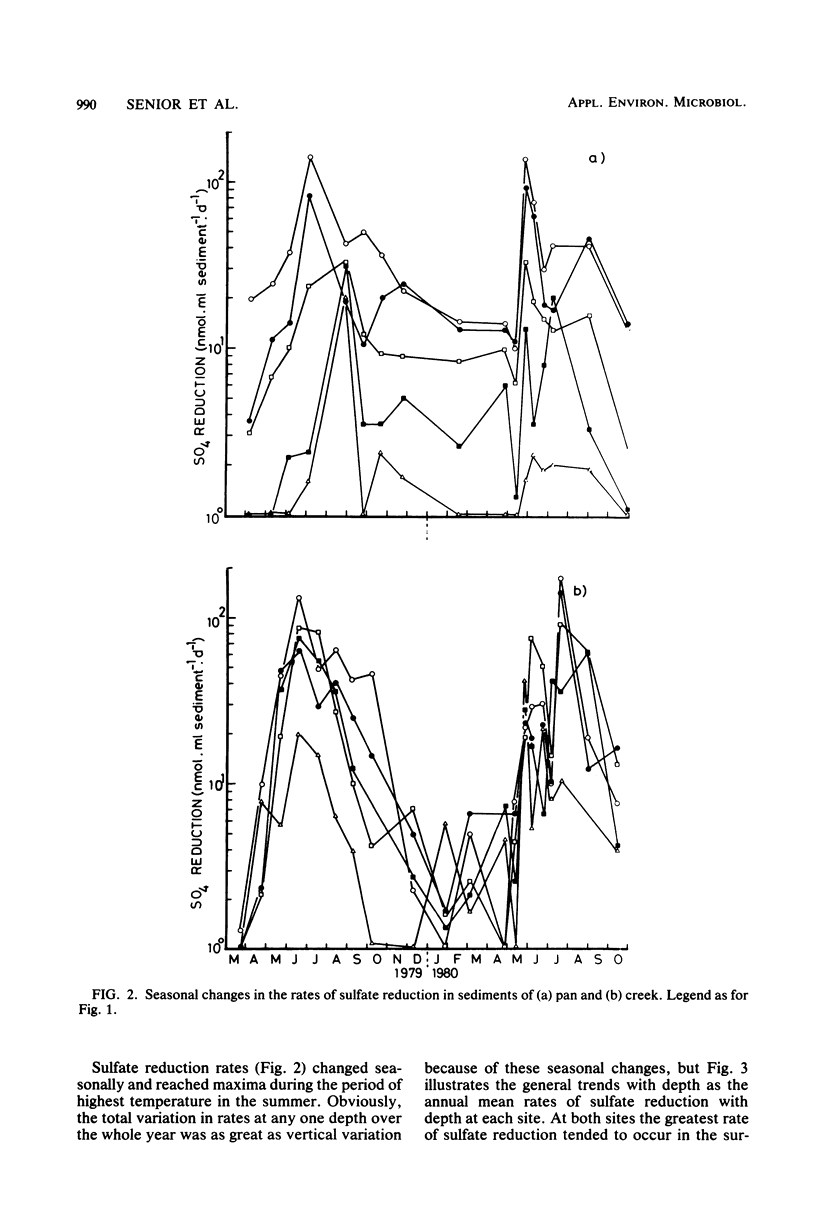
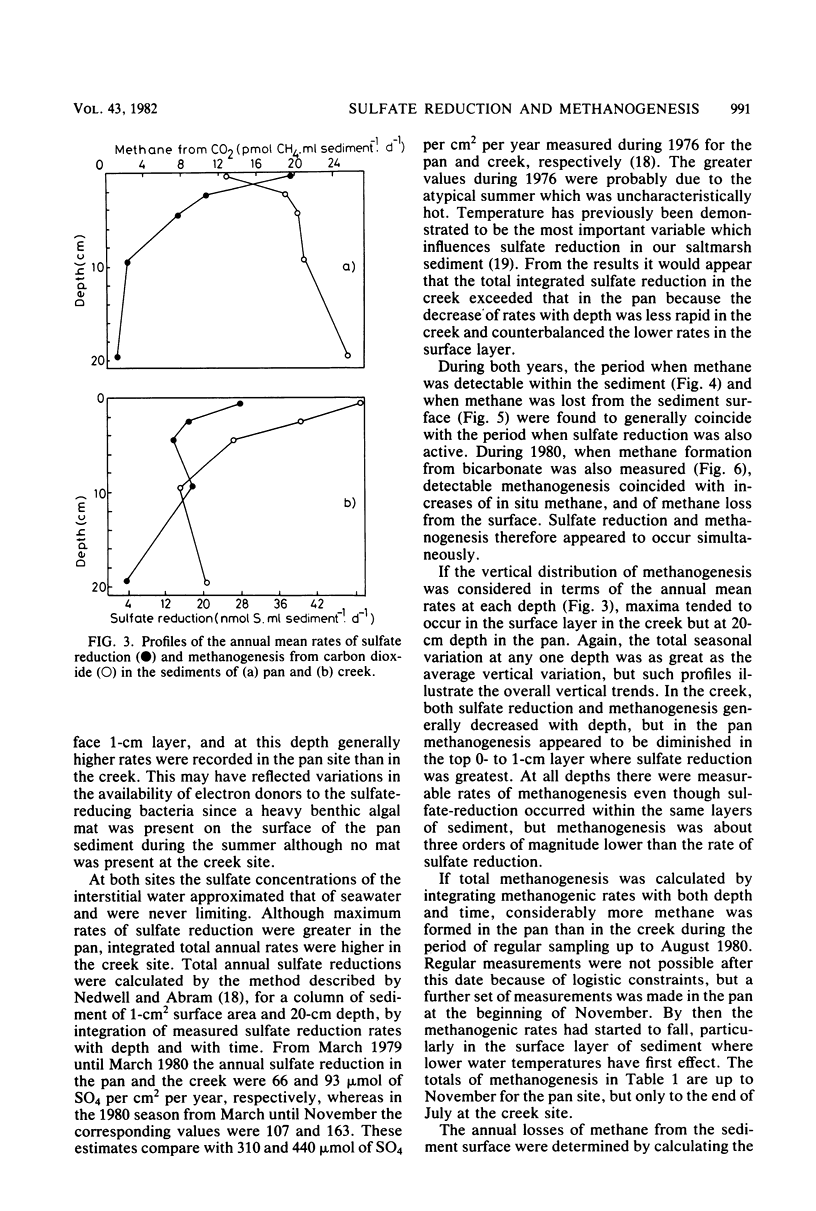
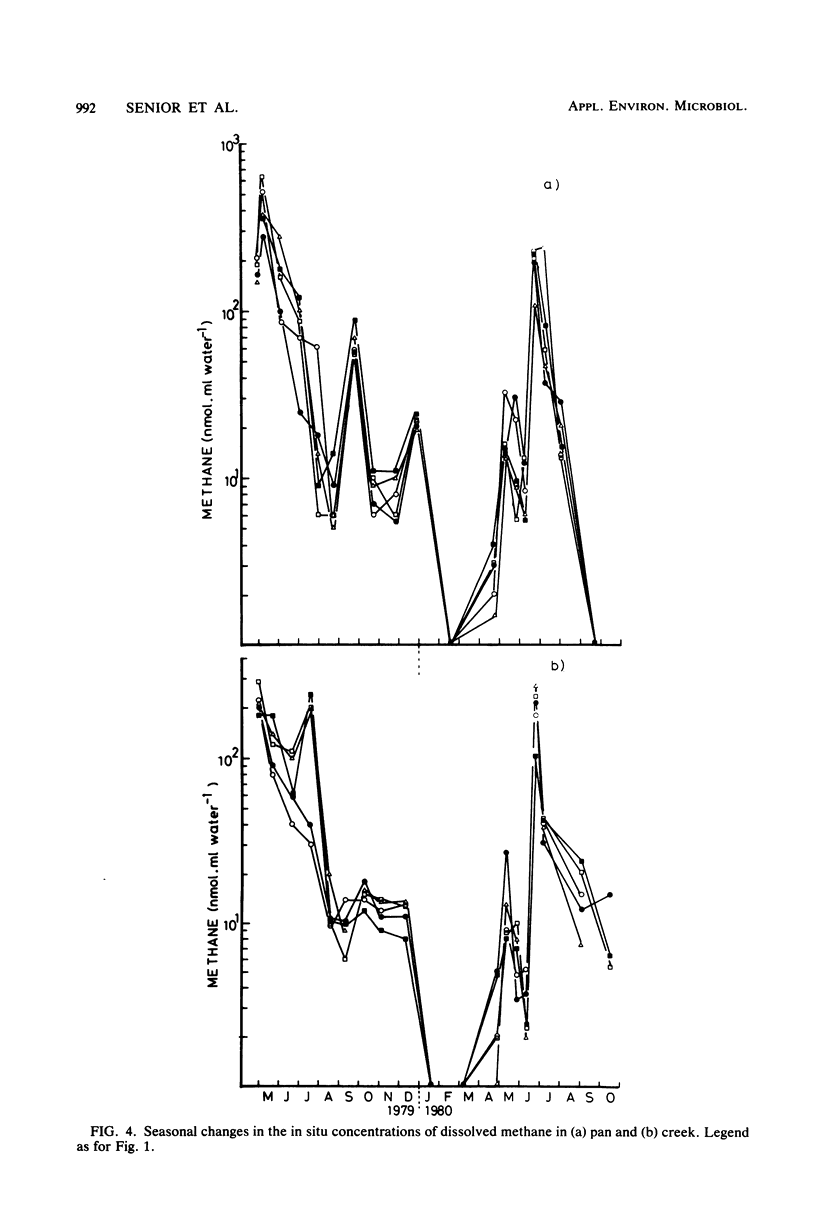
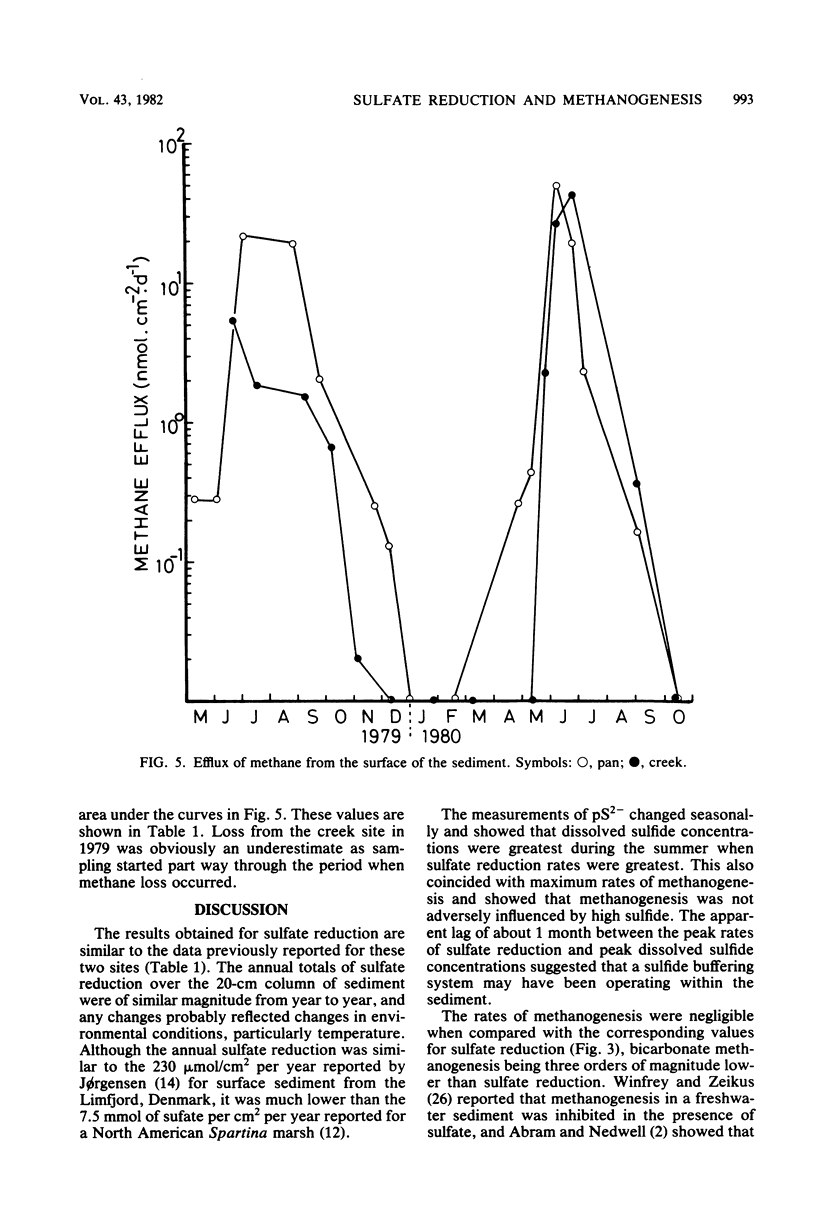
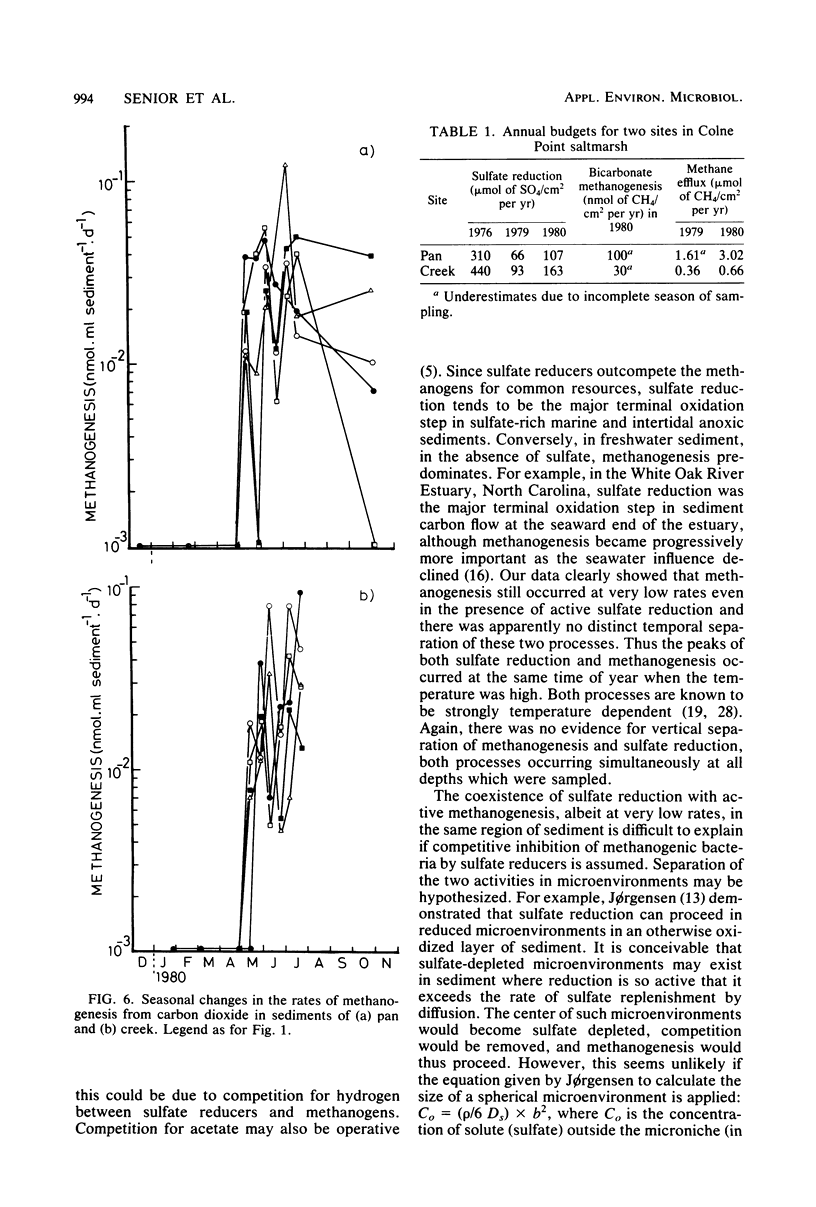
The rates of sulfate reduction, methanogenesis, and methane loss were measured in saltmarsh sediment at monthly intervals. In addition, dissolved methane and sulfate concentrations together with pS2− and pH were determined. Methane formation from carbon dioxide, but not from acetate, was detected within the same horizon of sediment where sulfate reduction was most active. Sulfate reduction was about three orders of magnitude greater than annual methanogenesis. The two processes were not separated either spatially or temporally, but occurred within the same layer of sediment at the same time of the year. Their coexistence did not seem to be the result of sulfate-depleted microenvironments within which methanogenesis could occur, but the methanogenic bacteria persisted at very low rates of activity within the same environment as the sulfate reducers.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abram J. W., Nedwell D. B. Hydrogen as a substrate for methanogenesis and sulphate reduction in anaerobic saltmarsh sediment. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):93–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00689357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abram J. W., Nedwell D. B. Inhibition of methanogenesis by sulphate reducing bacteria competing for transferred hydrogen. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):89–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00689356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banat I. M., Lindström E. B., Nedwell D. B., Balba M. T. Evidence for coexistence of two distinct functional groups of sulfate-reducing bacteria in salt marsh sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):985–992. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.985-992.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappenberg T. E. Interrelations between sulfate-reducing and methane-producing bacteria in bottom deposits of a fresh-water lake. I. Field observations. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(2):285–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00394387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C. A., Chynoweth D. P. Comparison of in situ and in vitro rates of methane release in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):287–293. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.287-293.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Zeikus J. G. Effect of sulfate on carbon and electron flow during microbial methanogenesis in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):275–281. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.275-281.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. S. Microbial formation of methane. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;6:107–146. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Winfrey M. R. Temperature limitation of methanogenesis in aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jan;31(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.1.99-107.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


