Abstract
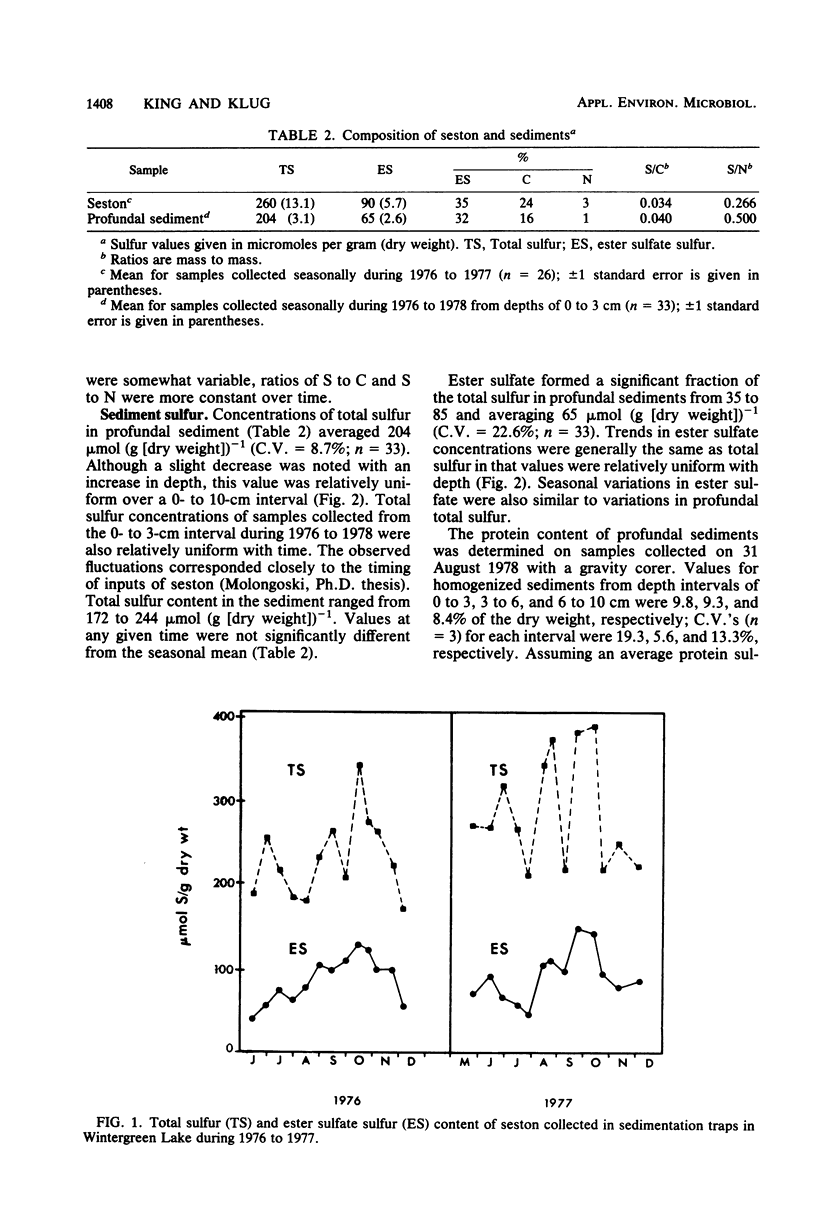
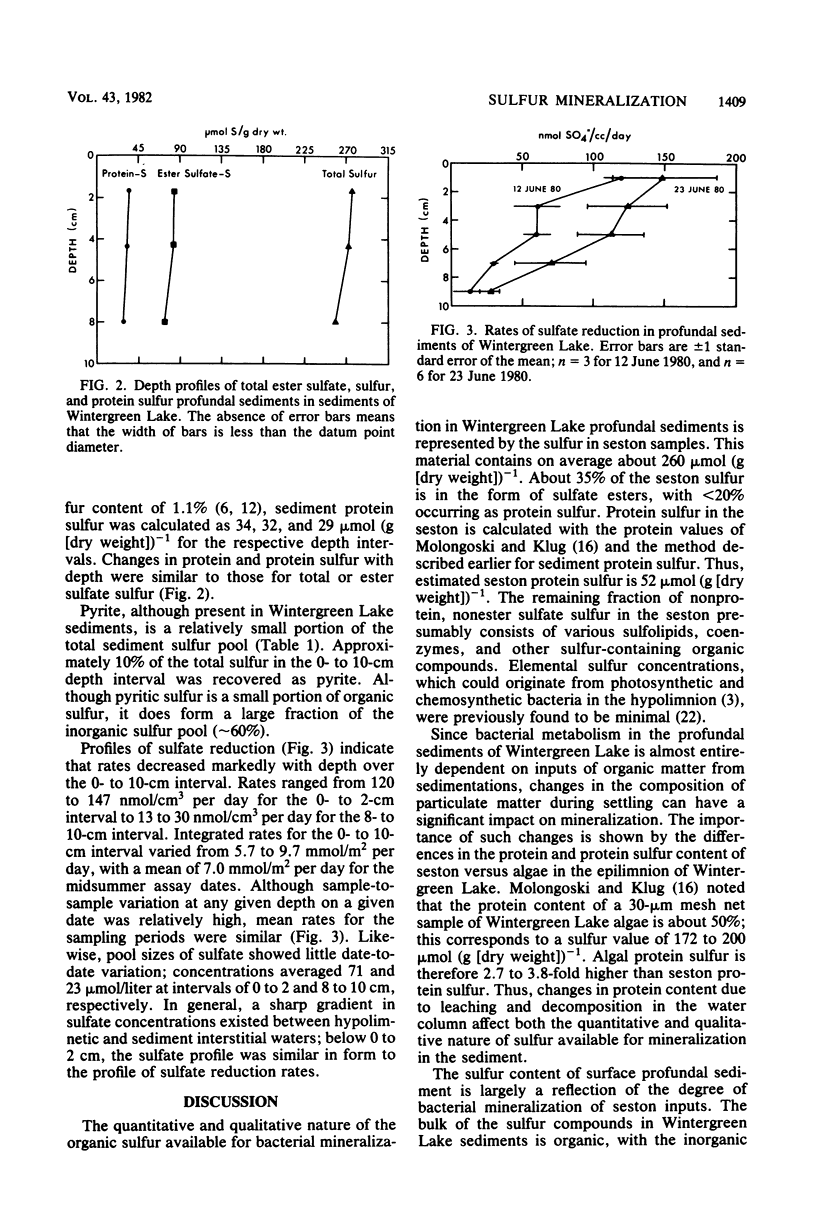
The net mineralization of organic sulfur compounds in surface sediments of Wintergreen Lake was estimated from a mass-balance budget of sulfur inputs and sediment sulfur concentrations. The net mineralization of organic sulfur inputs is <50% complete, which is consistent with the dominance of organic sulfur (>80% of total sulfur) in sediment. Although sediment sulfur is predominantly organic, sulfate reduction is the most significant process in terms of the quantities of sulfur transformed in surface sediments. Rates of sulfate reduction in these sediments average 7 mmol/m2 per day. On an annual basis, this rate is 19-fold greater than net rates of organic sulfur mineralization and 65-fold greater than sulfate ester hydrolysis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell D. E., Tiedje J. M. The structure of anaerobic bacterial communities in the hypolimnia of several Michigan lakes. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):377–385. doi: 10.1139/m75-052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casagrande D., Siefert K. Origins of sulfur in coal: importance of the ester sulfate content of peat. Science. 1977 Feb 18;195(4279):675–676. doi: 10.1126/science.195.4279.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jukes T. H., Holmquist R., Moise H. Amino acid composition of proteins: Selection against the genetic code. Science. 1975 Jul 4;189(4196):50–51. doi: 10.1126/science.237322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. M., Klug M. J. Sulfhydrolase activity in sediments of wintergreen lake, kalamazoo county, michigan. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):950–956. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.950-956.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Klug M. J. Intermediary metabolism of organic matter in the sediments of a eutrophic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):552–560. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.552-560.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Klug M. J. Electron donors utilized by sulfate-reducing bacteria in eutrophic lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):116–121. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.116-121.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Klug M. J. Reduction of sulfur compounds in the sediments of a eutrophic lake basin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1230–1237. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1230-1237.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


