Abstract
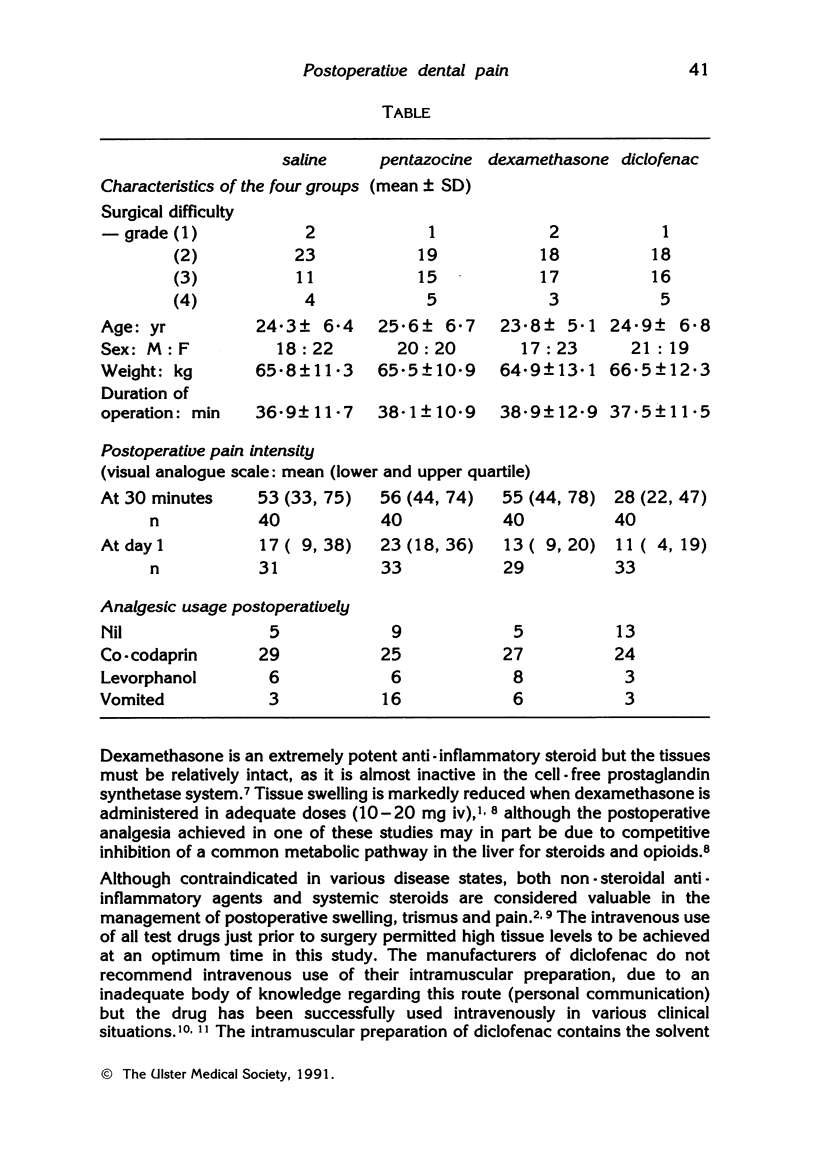
Intravenous dexamethasone and diclofenac were evaluated in a double blind randomised trial, relative to an opioid (pentazocine) and placebo (saline), in 160 patients undergoing extraction of impacted lower third molar teeth. Test drugs were administered intravenously before surgery to provide postoperative analgesia. Following the operation, pain was assessed using a 10 cm visual analogue scale. Patients who received diclofenac reported significantly less pain than others 30 minutes after surgery (p less than 0.05). Pain scores on the day following surgery were also significantly lower in the diclofenac group compared to the opioid and placebo groups (p less than 0.05) but not less than those who received dexamethasone--possibly indicating a long term advantage of the anti-inflammatory drugs. Vomiting was a problem in the opioid group.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell W. I., Watters C. H. Venous sequelae following i.v. administration of diclofenac. Br J Anaesth. 1989 May;62(5):545–547. doi: 10.1093/bja/62.5.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke R. S. Nausea and vomiting. Br J Anaesth. 1984 Jan;56(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/bja/56.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne R. A., Campbell R. A., Cooper S. A., Hall D. L., Buckingham B. Suppression of postoperative pain by preoperative administration of ibuprofen in comparison to placebo, acetaminophen, and acetaminophen plus codeine. J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;23(1):37–43. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1983.tb02702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ElHag M., Coghlan K., Christmas P., Harvey W., Harris M. The anti-inflammatory effects of dexamethasone and therapeutic ultrasound in oral surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1985 Feb;23(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0266-4356(85)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins and the mechanism of analgesia produced by aspirin-like drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;49(1):86–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Nakamura M., de Abreu Castro M. S. The hyperalgesic effects of prostacyclin and prostaglandin E2. Prostaglandins. 1978 Jul;16(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R., Gryglewski R., Herbaczyńska-Cedro K., Vane J. R. Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on prostaglandin biosynthesis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):104–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio238104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman B., McKay R. J. Steroids and postoperative analgesia. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1985 Nov;13(4):395–398. doi: 10.1177/0310057X8501300412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesenti A., Riboni A., Basilico E., Grossi E. Antipyretic therapy in ICU patients: evaluation of low dose diclofenac sodium. Intensive Care Med. 1986;12(5):370–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00292928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Arx D. P., Simpson M. T. The effect of dexamethasone on neurapraxia following third molar surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989 Dec;27(6):477–480. doi: 10.1016/s0266-4356(89)80005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


