Abstract
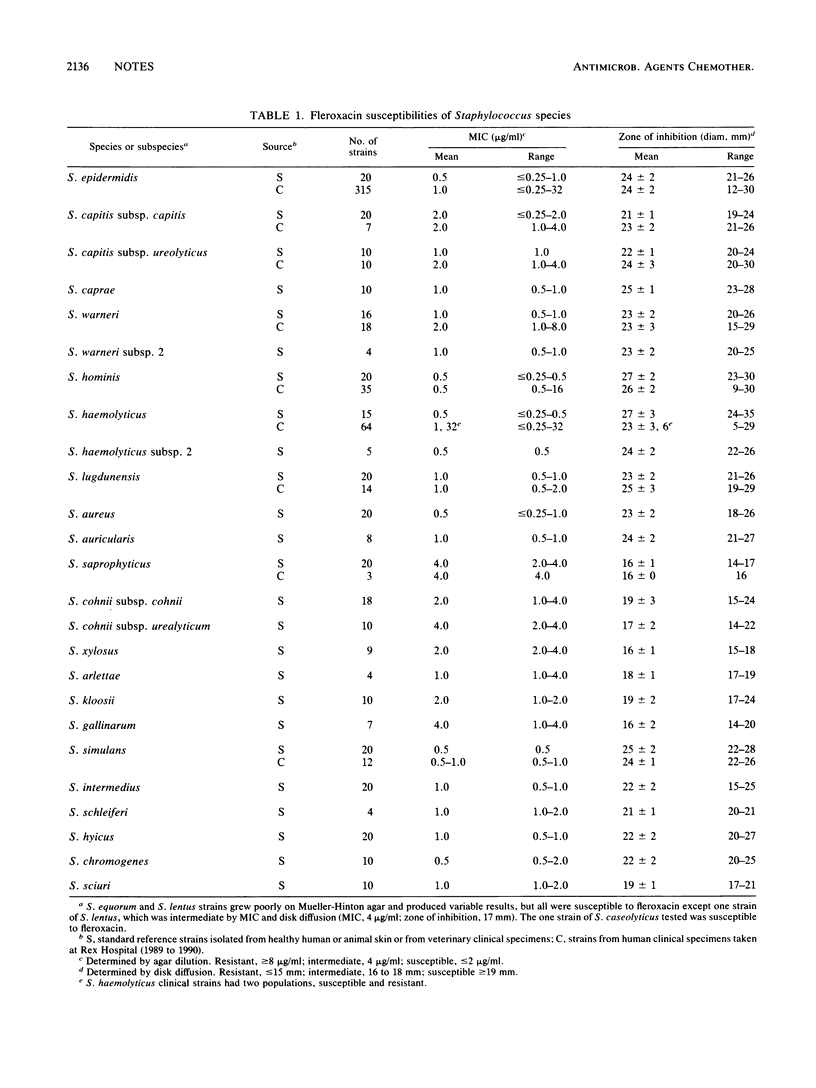
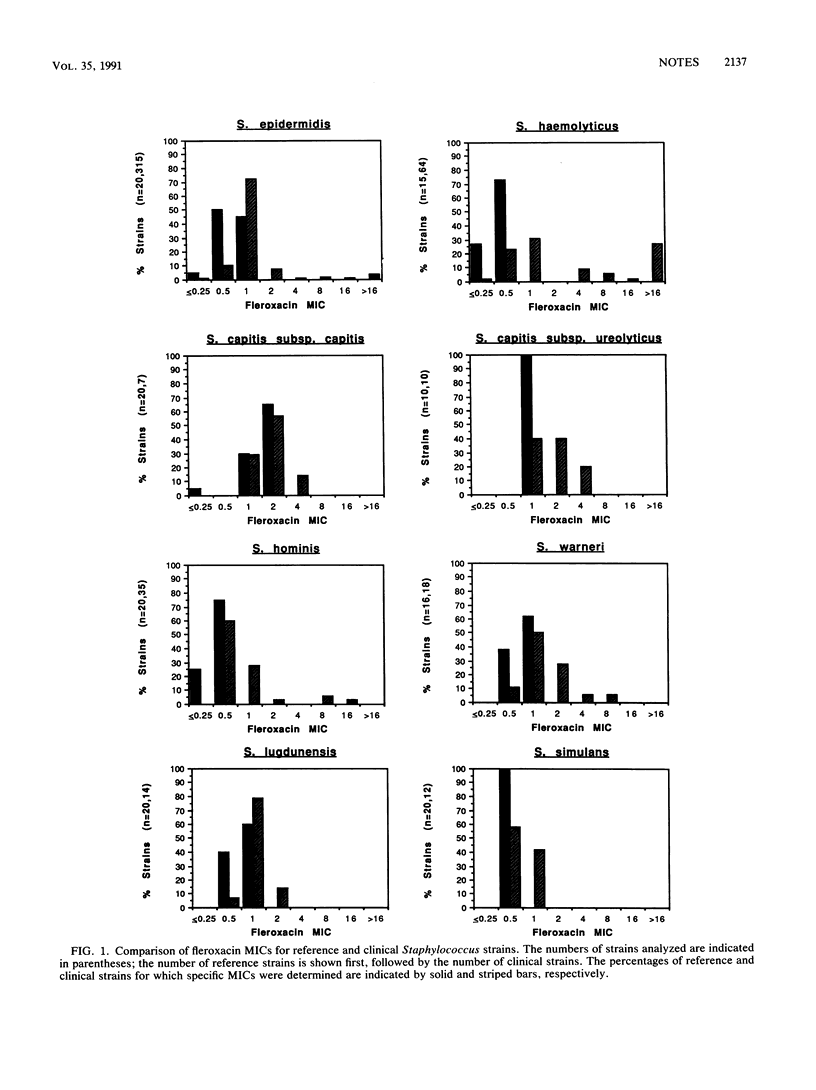
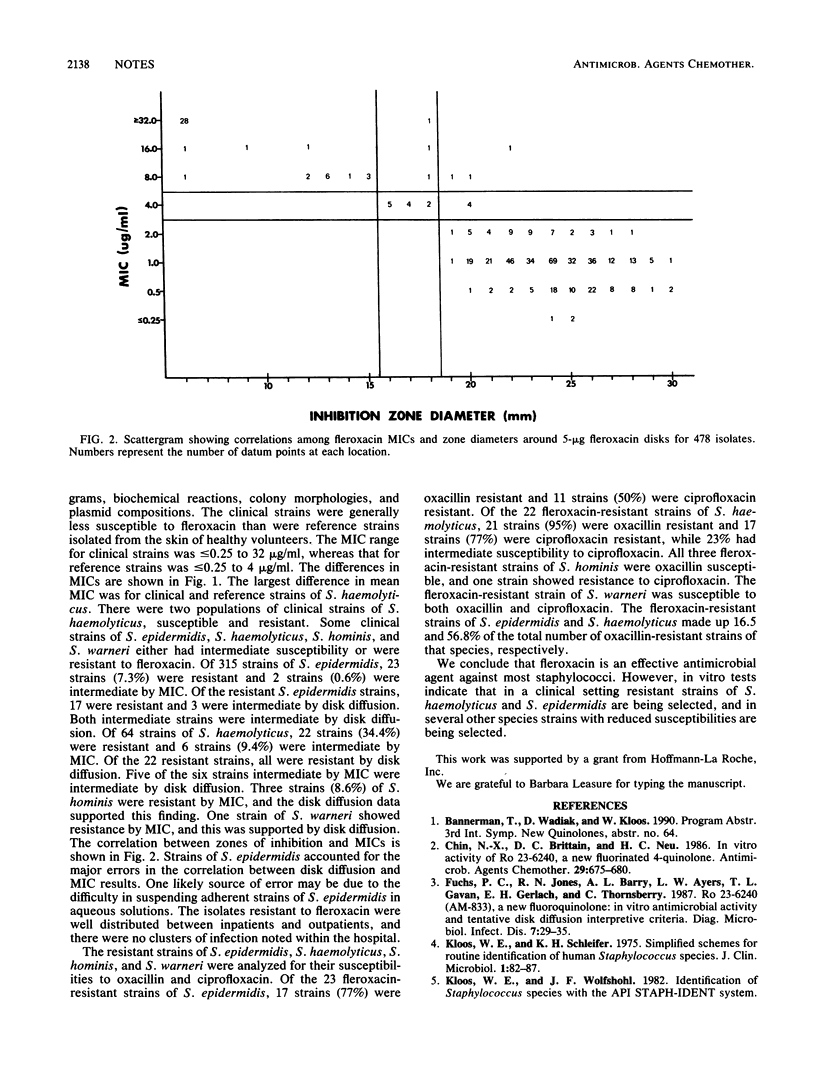
Twenty-four Staphylococcus species or subspecies were examined for their susceptibilities to the fluoroquinolone fleroxacin (Ro 23-6240) by disk diffusion (5-micrograms disk) and by agar dilution for the determination of MICs. Resistant strains were further tested for their susceptibilities to oxacillin and the fluoroquinolone ciprofloxacin. Reference strains of the novobiocin-resistant species (Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Staphylococcus cohnii, Staphylococcus xylosus, Staphylococcus arlettae, and Staphylococcus gallinarum) had an intrinsic intermediate susceptibility (MIC, 4 micrograms/ml) to fleroxacin. Fleroxacin resistance was not observed in the reference strains of the novobiocin-susceptible species (MIC, 0.5 to 2.0 micrograms/ml). Clinical isolates of coagulase-negative species were generally less susceptible to fleroxacin than were reference strains. Seven percent of the Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical strains were resistant (MIC, greater than or equal to 8 micrograms/ml) to fleroxacin. Of these strains, 77% were resistant to oxacillin and 50% were resistant to ciprofloxacin. Thirty-four percent of the Staphylococcus haemolyticus clinical strains were resistant to fleroxacin, and 9% had intermediate susceptibility. Of the resistant strains, 95% were resistant to oxacillin and 77% were resistant to ciprofloxacin, while 23% had intermediate susceptibility to ciprofloxacin. Fleroxacin is an effective antimicrobial agent against most staphylococci.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin N. X., Brittain D. C., Neu H. C. In vitro activity of Ro 23-6240, a new fluorinated 4-quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):675–680. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. C., Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Ayers L. W., Gavan T. L., Gerlach E. H., Thornsberry C. RO 23-6240 (AM-833), a new fluoroquinolone: in vitro antimicrobial activity and tentative disk diffusion interpretive criteria. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 May;7(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Wolfshohl J. F. Identification of Staphylococcus species with the API STAPH-IDENT system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):509–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.509-516.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manek N., Andrews J. M., Wise R. In vitro activity of Ro 23-6240, a new difluoroquinolone derivative, compared with that of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):330–332. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlod D. J., Saravolatz L. D., Somerville M. M. In-vitro susceptibility of staphylococci to fleroxacin in comparison with six other quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Oct;22 (Suppl 500):35–41. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_d.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidekamm E., Portmann R., Suter K., Partos C., Dell D., Lücker P. W. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of fleroxacin, a trifluorinated quinolone, in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1909–1914. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


