Abstract
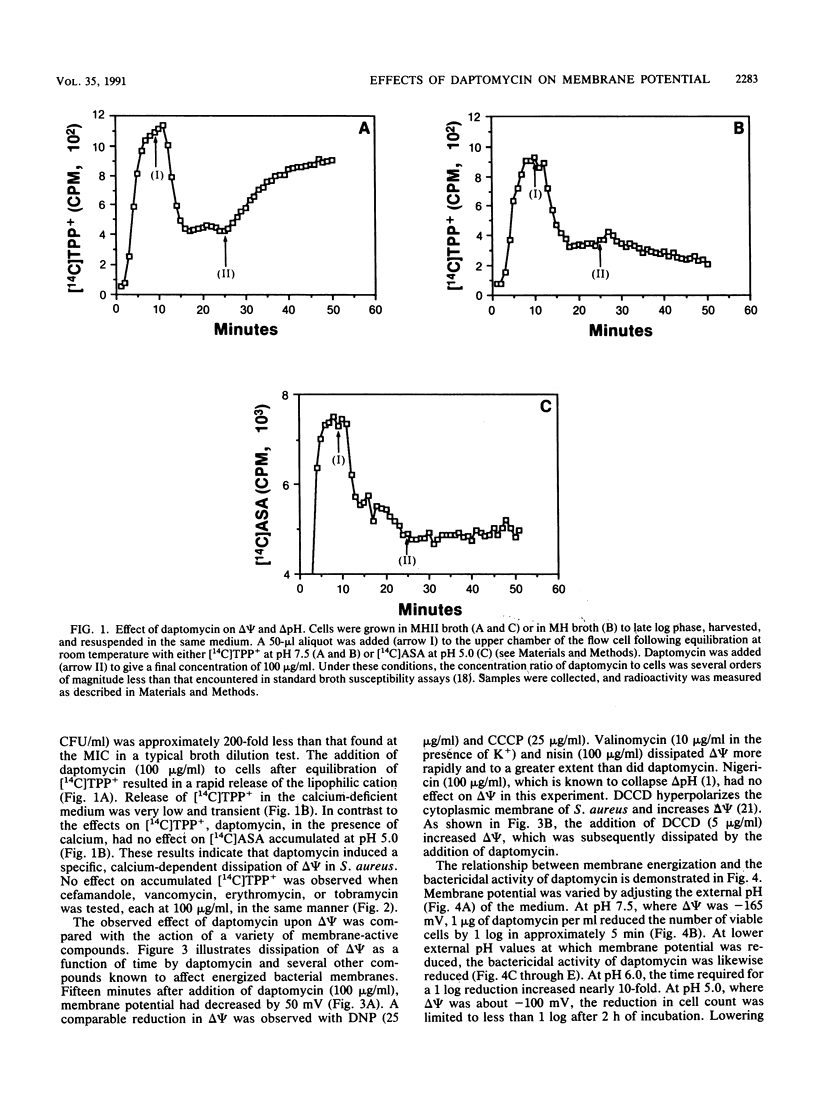
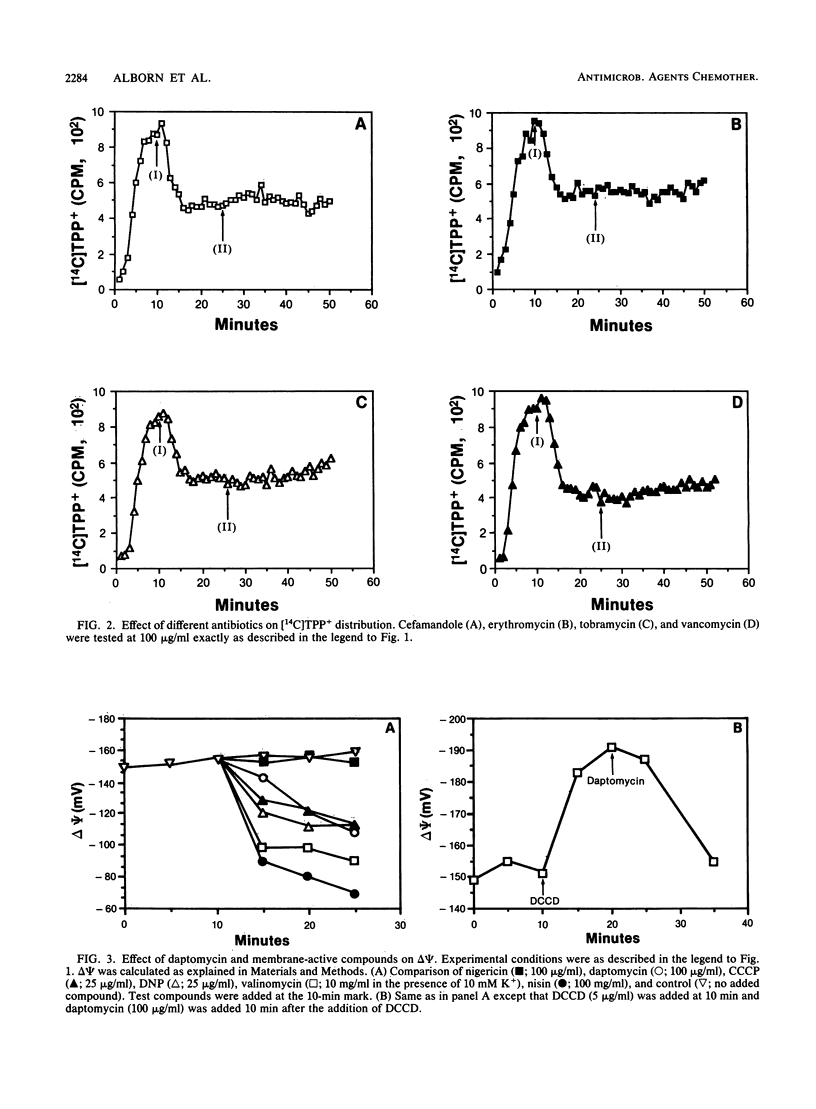
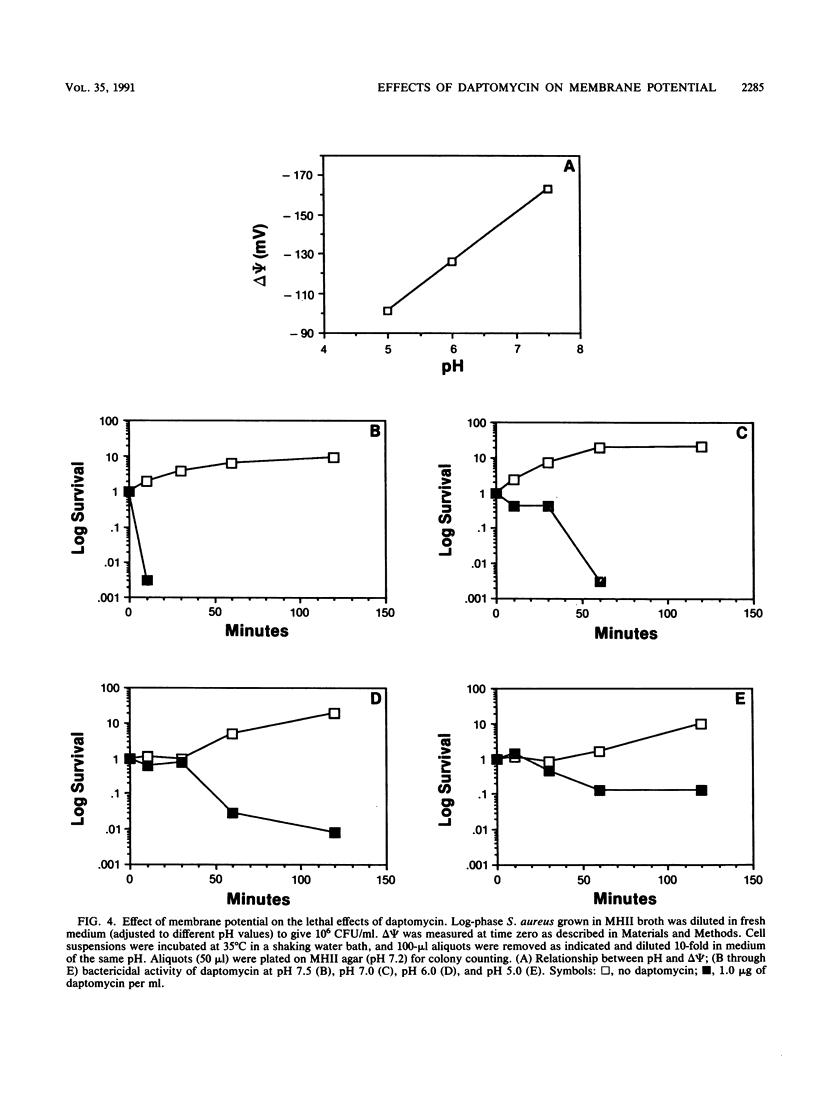
Daptomycin (LY146032) caused a calcium-dependent dissipation of the membrane potential (delta psi) in Staphylococcus aureus without noticeably affecting the chemical gradient (delta pH) across the membrane. The effect of daptomycin on membrane energization may account for many of the inhibitory effects on macromolecular biosyntheses and membrane function reported for this antibiotic. Our evidence indicates that the bactericidal activity of daptomycin is dependent on an available delta psi.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed S., Booth I. R. The use of valinomycin, nigericin and trichlorocarbanilide in control of the protonmotive force in Escherichia coli cells. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 15;212(1):105–112. doi: 10.1042/bj2120105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen N. E., Hobbs J. N., Alborn W. E., Jr Inhibition of peptidoglycan biosynthesis in gram-positive bacteria by LY146032. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1093–1099. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew J. H., Wale M. C., Wale L. J., Greenwood D. The effect of cultural conditions on the activity of LY146032 against staphylococci and streptococci. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Aug;20(2):213–221. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canepari P., Boaretti M., Lleó M. M., Satta G. Lipoteichoic acid as a new target for activity of antibiotics: mode of action of daptomycin (LY146032). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1220–1226. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E. S., Mandel L. J., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Quantitative association between electrical potential across the cytoplasmic membrane and early gentamicin uptake and killing in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):863–867. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.863-867.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Thauvin C., Gerson B., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro activity and mechanism of action of A21978C1, a novel cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):357–362. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Willey S., Reiszner E., Spitzer P. G., Caputo G., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro and in vivo activity of LY 146032, a new cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):532–535. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey J. H., Lea E. J. The role of acyl chain character and other determinants on the bilayer activity of A21978C an acidic lipopeptide antibiotic. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 24;859(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90217-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey J. H., Maget-Dana R., Ptak M. The lipopeptide antibiotic A21978C has a specific interaction with DMPC only in the presence of calcium ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 2;985(1):60–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey J. H., Ptak M. Fluorescence indicates a calcium-dependent interaction between the lipopeptide antibiotic LY146032 and phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4639–4645. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mates S. M., Eisenberg E. S., Mandel L. J., Patel L., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Membrane potential and gentamicin uptake in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6693–6697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. G., Dilger J. P. Transport of protons across membranes by weak acids. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jul;60(3):825–863. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.3.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The use of flow dialysis for determinations of deltapH and active transport. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:680–688. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhr E., Sahl H. G. Mode of action of the peptide antibiotic nisin and influence on the membrane potential of whole cells and on cytoplasmic and artificial membrane vesicles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):841–845. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taber H. W., Mueller J. P., Miller P. F., Arrow A. S. Bacterial uptake of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):439–457. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.439-457.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


