Abstract
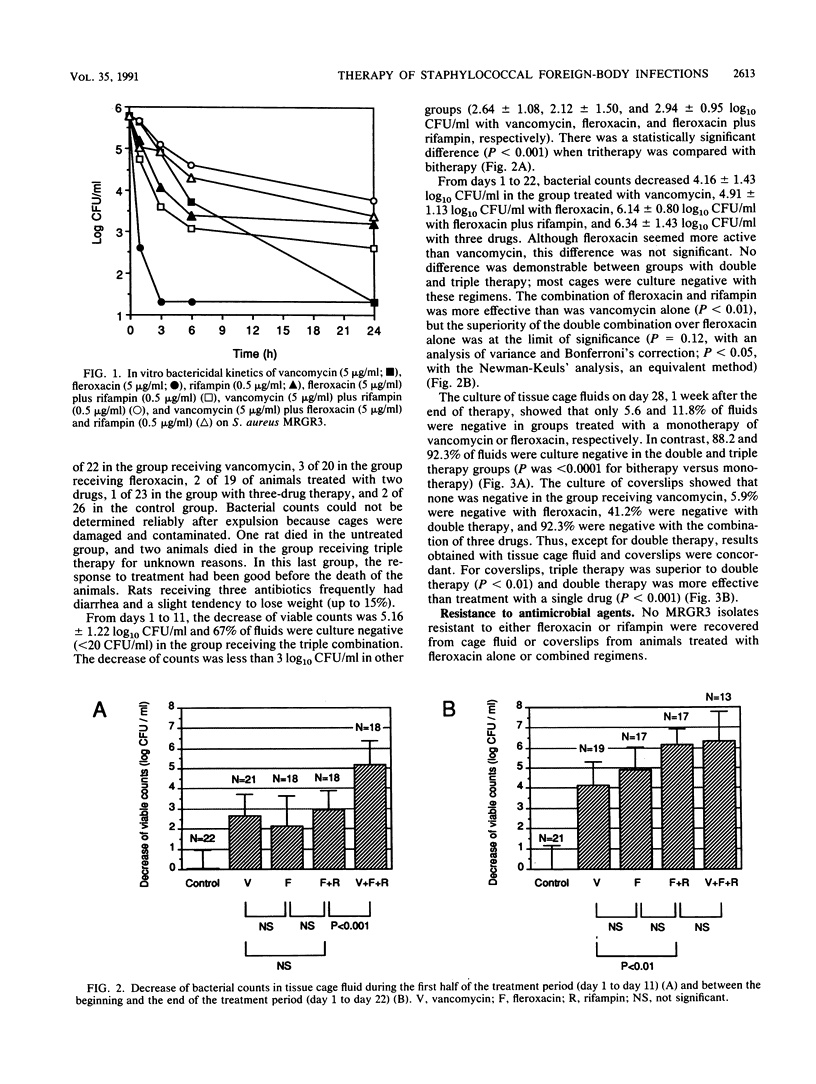
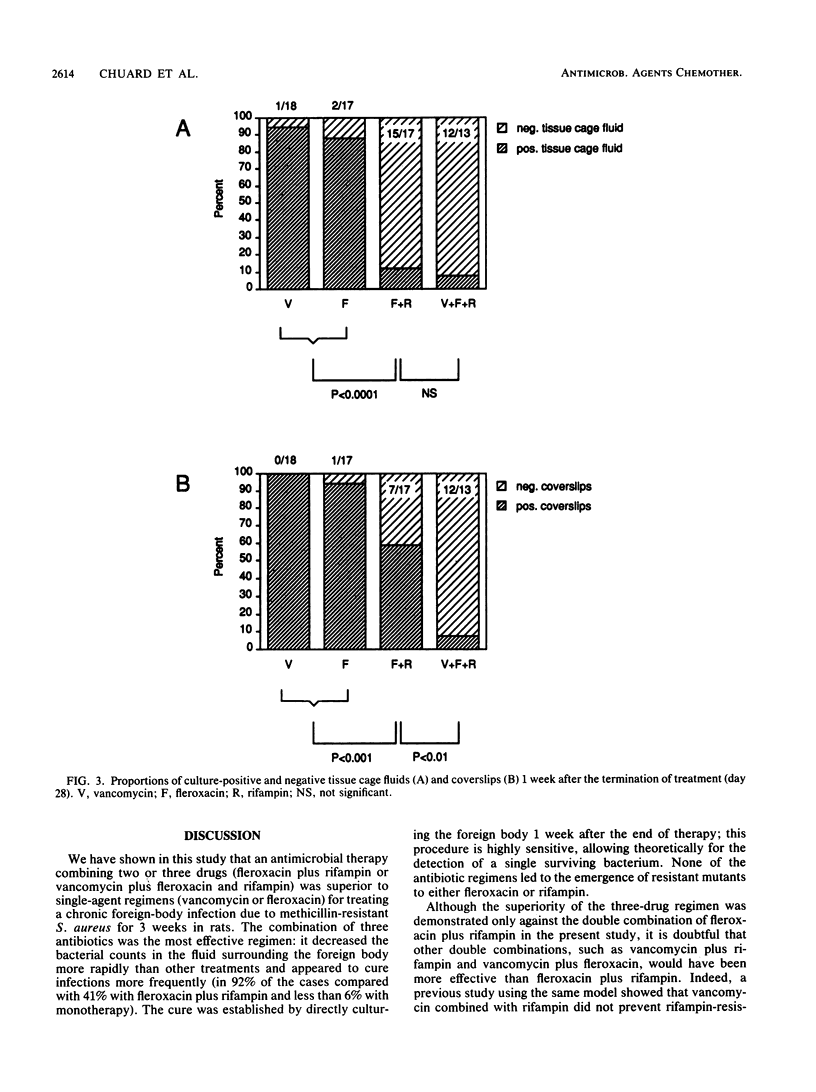
We compared the efficacy of a long-duration (3-week) therapy of vancomycin, fleroxacin, fleroxacin plus rifampin, and vancomycin plus fleroxacin and rifampin in a recently developed rat model of chronic staphylococcal foreign-body infection. Subcutaneous tissue cages containing polymethylmethacrylate coverslips were infected with 1 x 10(5) to 5 x 10(5) CFU of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Three weeks later, a quantitative culturing of the fluid that had accumulated in the cages was done (mean, 6.72 log10 CFU/ml; n = 110) and treatment was initiated after randomization. The CFUs in the cage fluid were counted on days 11 and 22 and 1 week after the termination of treatment; in addition, a final culture of coverslips (surface-bound microorganisms) was performed. The three-drug therapy was significantly superior to the other treatments on day 11 (a 5.16 log10 decrease of bacterial counts versus a 2.12 log10 to 2.94 log10 decrease for vancomycin, fleroxacin, and fleroxacin plus rifampin; P less than 0.01). On day 22, count decreases were 4.16 log10 for vancomycin, 4.91 log10 for fleroxacin (vancomycin versus fleroxacin, not significant), 6.14 log10 for two-drug therapy, and 6.34 log10 for three-drug therapy (vancomycin-fleroxacin-rifampin versus fleroxacin-rifampin, not significant; fleroxacin-rifampin versus monotherapies, P less than 0.01); the numbers of CFU in most cage fluids were under the detection limit (20 CFU/ml) in combination groups. One week after the end of treatment, 92% of fluids and coverslips (detection limit, 1 CFU) were culture negative with tritherapy, 88% of fluids and 41% of coverslips were negative with bitherapy, and less than 12% of fluids and coverslips were negative with single drugs (for coverslips, P was <0.01 for vancomycin-fleroxacin-rifampin versus fleroxacin-rifampin and P was <0.001 for fleroxacin-rifampin versus the monotherapies). No mutants resistant to rifampin or fleroxacin were detected. In conclusion, antimicrobial combinations were highly effective and superior to single drugs in treating a chronic staphylococcal foreign-body infection for 3 weeks. The three-drug therapy decreased bacterial counts more rapidly than the two-drug therapy under study and appeared to be curative in most cases.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acar J. F., Buu-Hoi A. Y. Resistance patterns of important gram-positive pathogens. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21 (Suppl 100):41–47. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_c.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg H. M., Rimland D., Carroll D. J., Terry P., Wachsmuth I. K. Rapid development of ciprofloxacin resistance in methicillin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1279–1285. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuard C., Lucet J. C., Rohner P., Herrmann M., Auckenthaler R., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus recovered from infected foreign body in vivo to killing by antimicrobials. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1369–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin R. J., Lee B. L., Sande M. A., Chambers H. F. Treatment of right-sided Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in intravenous drug users with ciprofloxacin and rifampicin. Lancet. 1989 Nov 4;2(8671):1071–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin R., Modin G., Kunz S., Rich R., Zak O., Sande M. Comparative efficacies of ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin, and vancomycin in combination with rifampin in a rat model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus chronic osteomyelitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Smith S. M., Tillem M., Cherubin C. Rifampin resistance. Development during the therapy of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Jan;145(1):146–148. doi: 10.1001/archinte.145.1.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Helsel V. L. In vitro antistaphylococcal activity of pefloxacin alone and in combination with other antistaphylococcal drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1457–1460. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmingham D., Foxall P., O'Hare M. D., Webb G., Ghosh G., Grüneberg R. N. Resistance studies with ofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Sep;22 (Suppl 100):27–34. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_c.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. P. Herd immunity and measles. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 May-Jun;5(3):463–466. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.3.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. N., Kennedy D. J., Reilly P. M., Luppen K. L., Weinandt W. J., Bollinger M. R., Aguirre F., Kodesch F., Saeed A. M. Treatment of bone, joint, and soft-tissue infections with oral ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):151–155. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F., Sande M. A. Serum bactericidal activity of rifampin in combination with other antimicrobial agents against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):611–613. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., Rouse M. S., Whitesell A. L., McConnell M. E., Wilson W. R. Treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus experimental osteomyelitis with ciprofloxacin or vancomycin alone or in combination with rifampin. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):73–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Barriere S. L., Albrecht L. M., Rybak M. J. Ciprofloxacin and rifampin, alone and in combination, for therapy of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1184–1187. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Barriere S. L., Albrecht L. M., Rybak M. J. Efficacy of fleroxacin in experimental methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):519–521. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limb D. I., Dabbs D. J., Spencer R. C. In-vitro selection of bacteria resistant to the 4-quinolone agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Jan;19(1):65–71. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucet J. C., Herrmann M., Rohner P., Auckenthaler R., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Treatment of experimental foreign body infection caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2312–2317. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr Gram-positive bacteria: spread and antimicrobial resistance in university and community hospitals in the USA. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21 (Suppl 100):49–55. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_c.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Quick J. N., Jensen B., Homann S., Johnson S., Tenquist J., Shanholtzer C., Petzel R. A., Sinn L., Gerding D. N. Emergence of ciprofloxacin resistance in nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Resistance during ciprofloxacin plus rifampin therapy for methicillin-resistant S aureus colonization. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Oct;150(10):2151–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piercy E. A., Barbaro D., Luby J. P., Mackowiak P. A. Ciprofloxacin for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):128–130. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebas P., Martinez Ruiz R., Roman F., Mendaza P., Rodriguez Diaz J. C., Daza R., de Letona J. M. Early resistance to rifampin and ciprofloxacin in the treatment of right-sided Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):204–205. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.204-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yourassowsky E., Van der Linden M. P., Crokaert F., Glupczynski Y. Effect of antibiotics carry-over on bacterial counting by 'spiral plating'. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21(1):138–140. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.1.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak O., Tosch W., Sande M. A. Correlation of antibacterial activities of antibiotics in vitro and in animal models of infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):273–282. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Waldvogel F. A., Vaudaux P., Nydegger U. E. Pathogenesis of foreign body infection: description and characteristics of an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):487–497. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


