Abstract
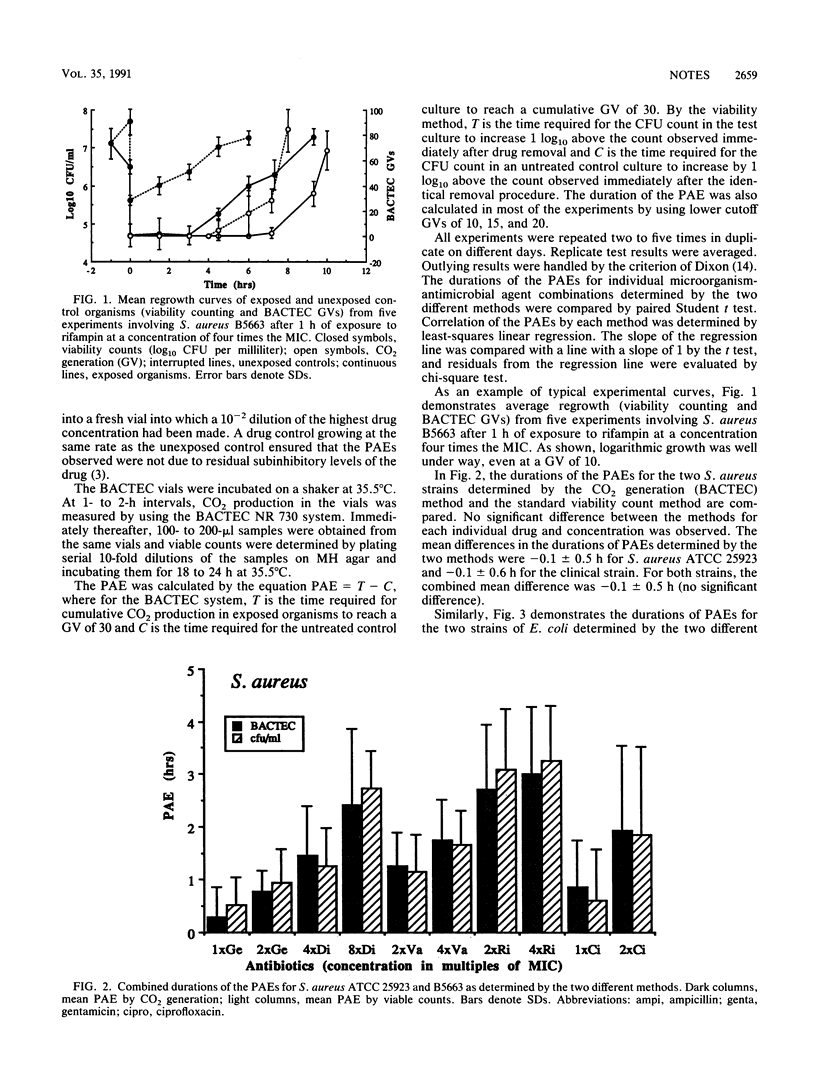
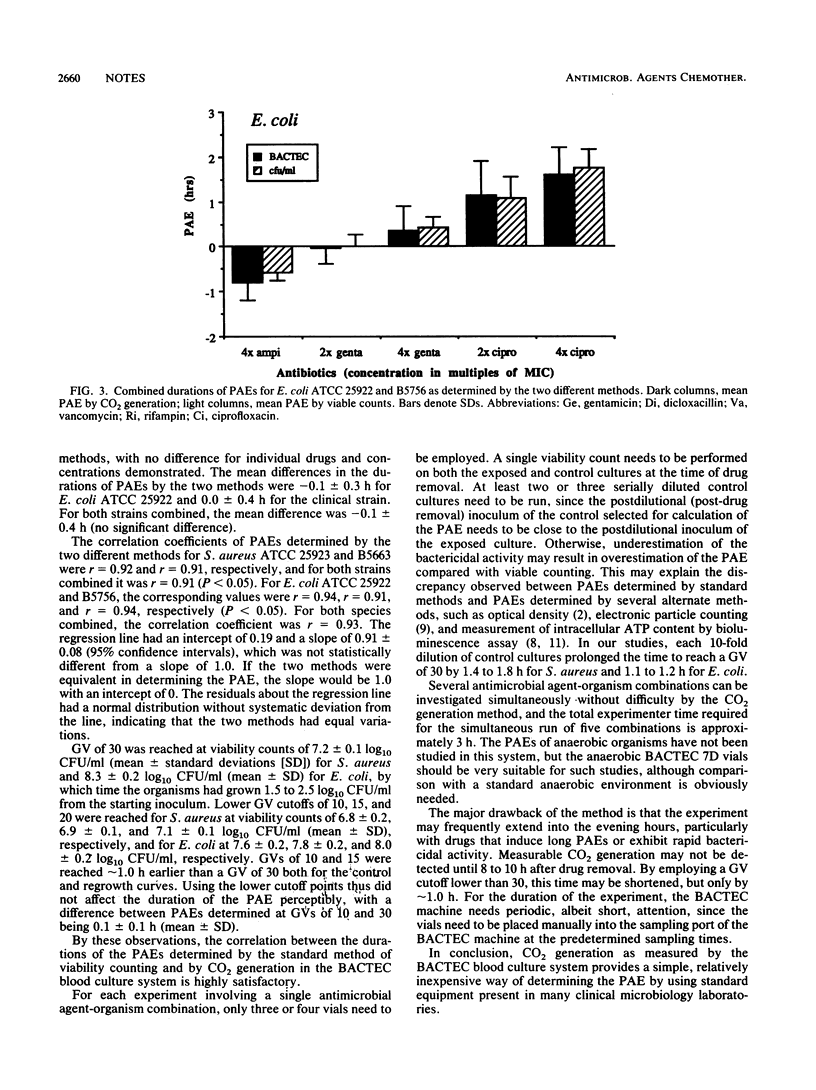
The duration of the postantibiotic effect (PAE) determined by bacterial CO2 production measured by using the BACTEC NR 730 blood culture system was compared with PAEs determined by standard viability counting. PAEs for Staphylococcus aureus after exposure to dicloxacillin, vancomycin, rifampin, gentamicin, and ciprofloxacin and for Escherichia coli after exposure to ampicillin, gentamicin, and ciprofloxacin were quantitated by the two methods, and an excellent correlation (r = 0.93) was demonstrated. The difference in the PAE durations determined by the two methods was 0.1 +/- 0.4 (mean +/- standard deviation) h. Thus, the BACTEC CO2 generation method provides a simple, alternate way of determining the PAE in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baquero F., Culebras E., Patrón C., Pérez-Díaz J. C., Medrano J. C., Vicente M. F. Postantibiotic effect of imipenem on gram-positive and gram-negative micro-organisms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Dec;18 (Suppl E):47–59. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_e.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould I. M., Jason A. C., Milne K. Use of the Malthus Microbial Growth Analyser to study the post antibiotic effect of antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Oct;24(4):523–531. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanberger H., Nilsson L. E., Kihlström E., Maller R. Postantibiotic effect of beta-lactam antibiotics on Escherichia coli evaluated by bioluminescence assay of bacterial ATP. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):102–106. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson B., Nilsson L., Maller R., Sörén L. Postantibiotic effect of aminoglycosides on gram-negative bacteria evaluated by a new method. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jul;22(1):23–33. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattie H. Kinetics of antimicrobial action. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler H. L., Curby W. A., Forgacs P., Rosenberg F. Comparison of electronic and viability counting methods for determination of postantibiotic effect of oxacillin on Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Dec;33(12):2155–2156. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.12.2155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenholt I., Isaksson B., Nilsson L., Cars O. Postantibiotic and bactericidal effect of imipenem against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;8(2):136–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01963897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescott D. L., Nix D. E., Holden P., Schentag J. J. Comparison of two methods for determining in vitro postantibiotic effects of three antibiotics on Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):450–453. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah P. M., Hubener K. G., Stille W. In-vitro-Untersuchungen zur intermittierenden Therapie mit Penicillin G und Ampicillin. Med Welt. 1978 May 26;29(21):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm A. W. Netilmicin in the treatment of gram-negative bacteremia: single daily versus multiple daily dosage. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):931–937. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstanley T. G., Hastings J. G. Penicillin-aminoglycoside synergy and post-antibiotic effect for enterococci. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Feb;23(2):189–199. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


