Abstract
Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogen responsible for life-threatening infections in persons with impaired immune systems. Topoisomerase I is a potential target for novel antifungal agents; however, in order for this enzyme to be a therapeutically useful target, it needs to be demonstrated that the fungal and human topoisomerases differ sufficiently as to allow the fungal topoisomerase to be selectively targeted. To address this question, we isolated the topoisomerase I from C. albicans and compared its biochemical properties with those of the mammalian enzyme. Similar to other eukaryotic type I topoisomerases, the C. albicans type I topoisomerase has an apparent molecular mass of 102 kDa and covalently links to the 3' end of DNA, as shown after the reaction is interrupted by sodium dodecyl sulfate. Topoisomerase poisons such as camptothecin act by stabilizing the cleavage complex formed by the topoisomerase I and DNA. We observed that the C. albicans and mammalian type I topoisomerases differ in that the C. albicans cleavage complex is approximately 10-fold less sensitive to camptothecin than the mammalian cleavage complex is. In addition, we found that the antifungal agent eupolauridine can stabilize the cleavage complex formed by both the C. albicans and human topoisomerases and that the response of the C. albicans topoisomerase I to this drug is greater than that of the human enzyme. Thus, the topoisomerase I from C. albicans is sufficiently distinct from the human enzyme as to allow differential chemical targeting and will therefore make a good target for antifungal drug discovery.
Full text
PDF

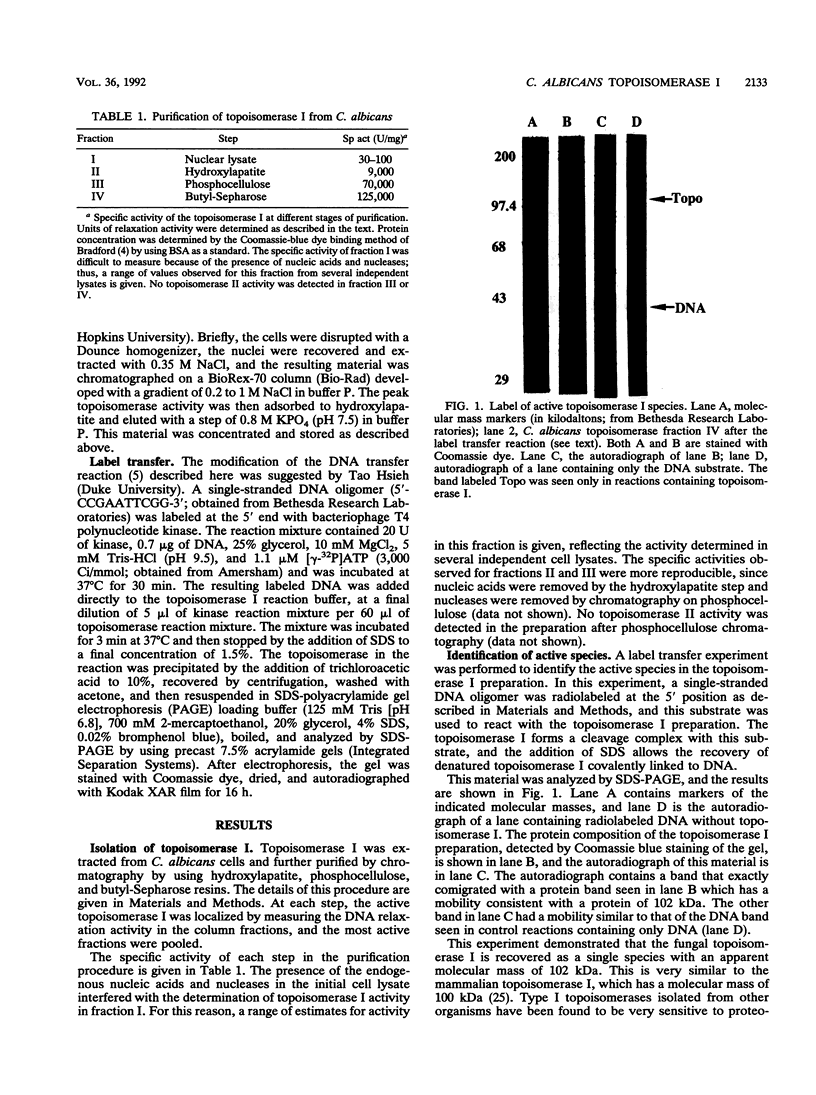

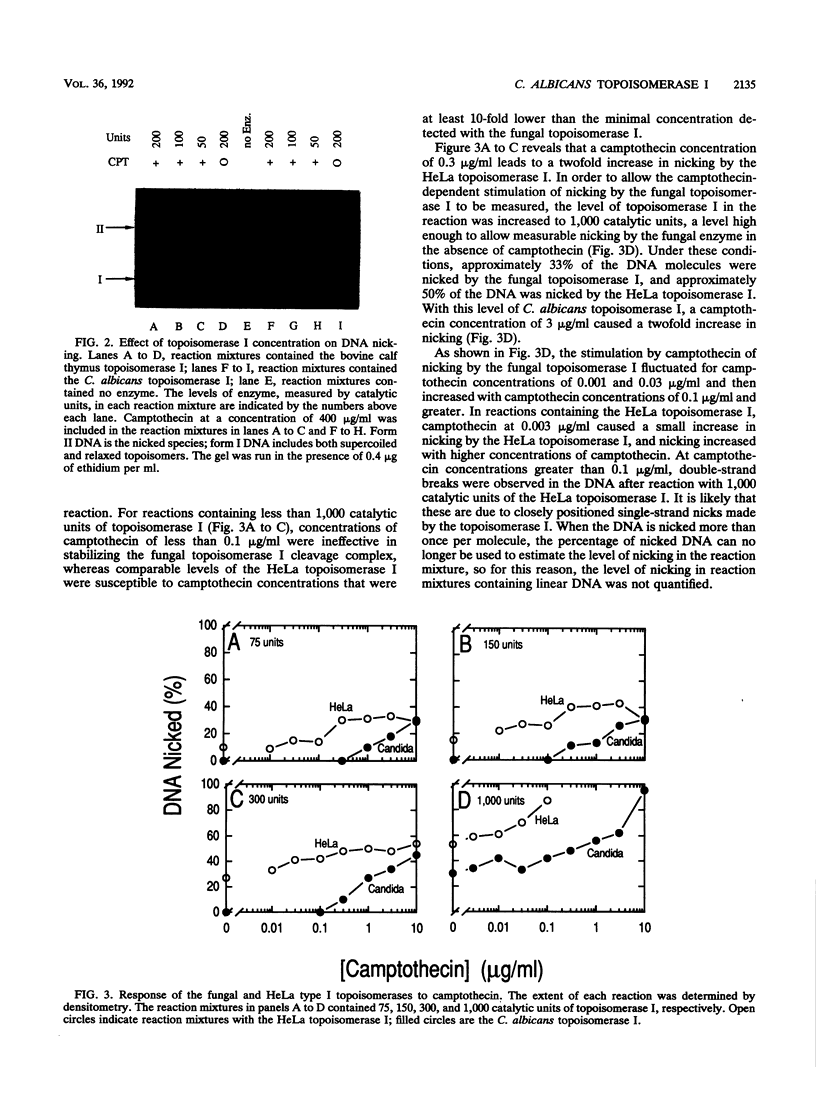
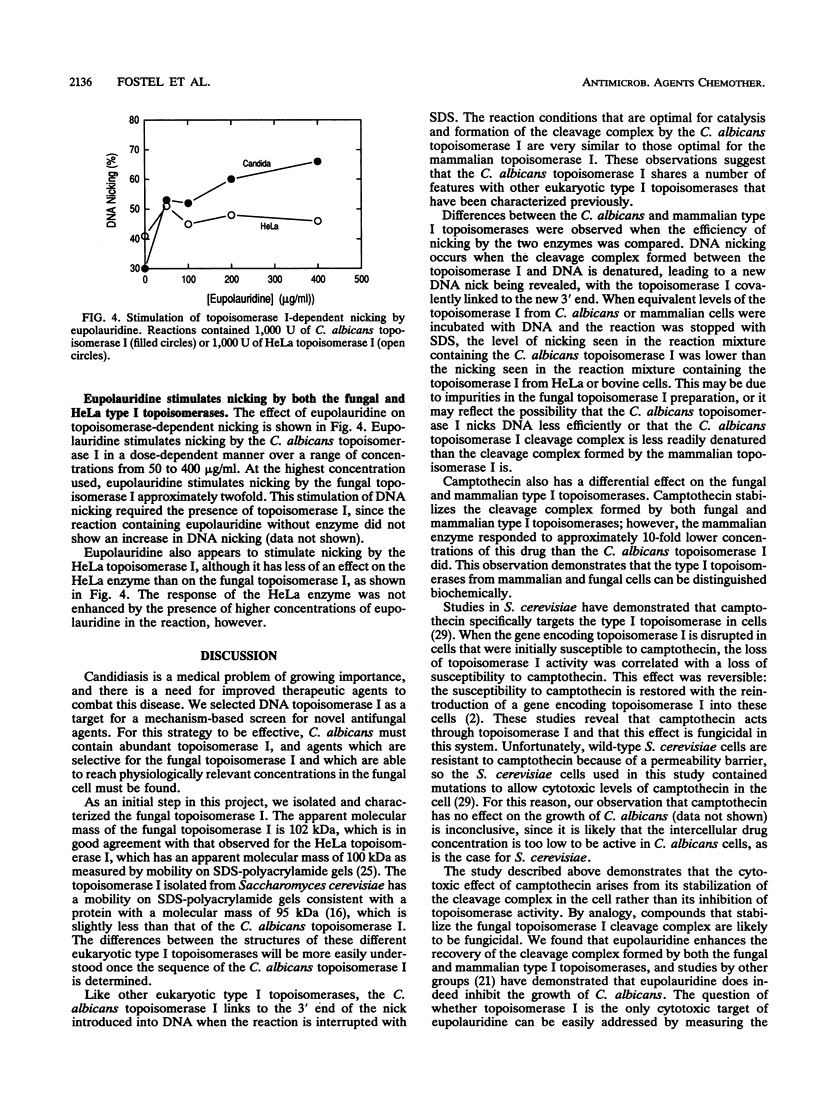


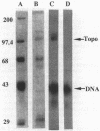
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avemann K., Knippers R., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Camptothecin, a specific inhibitor of type I DNA topoisomerase, induces DNA breakage at replication forks. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3026–3034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornsti M. A., Benedetti P., Viglianti G. A., Wang J. C. Expression of human DNA topoisomerase I in yeast cells lacking yeast DNA topoisomerase I: restoration of sensitivity of the cells to the antitumor drug camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1989 Nov 15;49(22):6318–6323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., Dulbecco R. An activity from mammalian cells that untwists superhelical DNA--a possible swivel for DNA replication (polyoma-ethidium bromide-mouse-embryo cells-dye binding assay). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by the DNA untwisting enzyme: attachment of the enzyme to 3'-terminus of the nicked DNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 25;118(3):441–446. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Strand breakage by the DNA untwisting enzyme results in covalent attachment of the enzyme to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3800–3804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. L., Yang L., Rowe T. C., Halligan B. D., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Nonintercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage-reunion reaction of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13560–13566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew R. E., Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Interaction between DNA and Escherichia coli protein omega. Formation of a complex between single-stranded DNA and omega protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):511–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K., Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerase II mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: topoisomerase II is required for segregation of daughter molecules at the termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann G., Pflugfelder G., Steiner E. K., Javaherian K., Howard G. C., Wang J. C., Elgin S. C. Drosophila DNA topoisomerase I is associated with transcriptionally active regions of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6958–6962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Laipis P., Wang J. C. The purification and characterization of DNA topoisomerases I and II of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10422–10429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Caranfa M. J., Holden K. G., Jakas D. R., Gallagher G., Mattern M. R., Mong S. M., Bartus J. O., Johnson R. K., Kingsbury W. D. Modification of the hydroxy lactone ring of camptothecin: inhibition of mammalian topoisomerase I and biological activity. J Med Chem. 1989 Mar;32(3):715–720. doi: 10.1021/jm00123a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Goto T., Wang J. C., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II is required at the time of mitosis in yeast. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Hertzberg R., Hecht S., Liu L. F. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14873–14878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hufford C. D., Liu S., Clark A. M., Oguntimein B. O. Anticandidal activity of eupolauridine and onychine, alkaloids from Cleistopholis patens. J Nat Prod. 1987 Sep-Oct;50(5):961–964. doi: 10.1021/np50053a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaxel C., Kohn K. W., Wani M. C., Wall M. E., Pommier Y. Structure-activity study of the actions of camptothecin derivatives on mammalian topoisomerase I: evidence for a specific receptor site and a relation to antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1465–1469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Davis J. L., Calendar R. Novel topologically knotted DNA from bacteriophage P4 capsids: studies with DNA topoisomerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3979–3989. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Miller K. G. Eukaryotic DNA topoisomerases: two forms of type I DNA topoisomerases from HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3487–3491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Rowe T. C., Yang L., Tewey K. M., Chen G. L. Cleavage of DNA by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15365–15370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. R., McCoubrey W. K., Jr, McConaughy B. L., Young L. S., Been M. D., Brewer B. J., Champoux J. J. Multiple forms of rat liver type I topoisomerase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:137–144. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitiss J., Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerase-targeting antitumor drugs can be studied in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7501–7505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N., Zechiedrich E. L., Gale K. C. Catalytic function of DNA topoisomerase II. Bioessays. 1991 Jun;13(6):269–273. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. E. DNA topoisomerases as targets for cancer therapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 15;34(24):4191–4195. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Rowe T., Glisson B., Yalowich J., Liu L. Role of topoisomerase II in mediating epipodophyllotoxin-induced DNA cleavage. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5857–5860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. Double strand DNA cleavage by type II DNA topoisomerase from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8421–8428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. F., Herrera R. E., Nordheim A. Rapid induction of c-fos transcription reveals quantitative linkage of RNA polymerase II and DNA topoisomerase I enzyme activities. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90724-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Peebles C. L., Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid: purification of Escherichia coli nalA gene product and its relationship to DNA gyrase and a novel nicking-closing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewey K. M., Rowe T. C., Yang L., Halligan B. D., Liu L. F. Adriamycin-induced DNA damage mediated by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Science. 1984 Oct 26;226(4673):466–468. doi: 10.1126/science.6093249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Yanagida M. Isolation of type I and II DNA topoisomerase mutants from fission yeast: single and double mutants show different phenotypes in cell growth and chromatin organization. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1737–1744. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]