Abstract
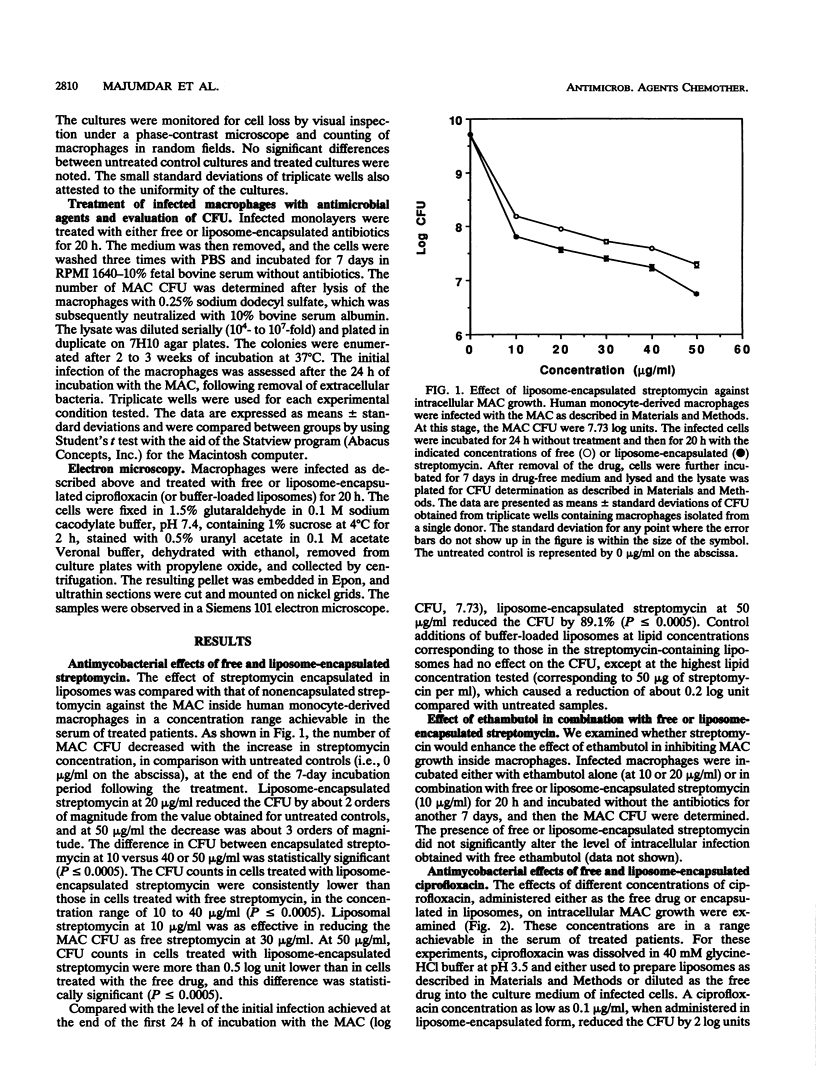
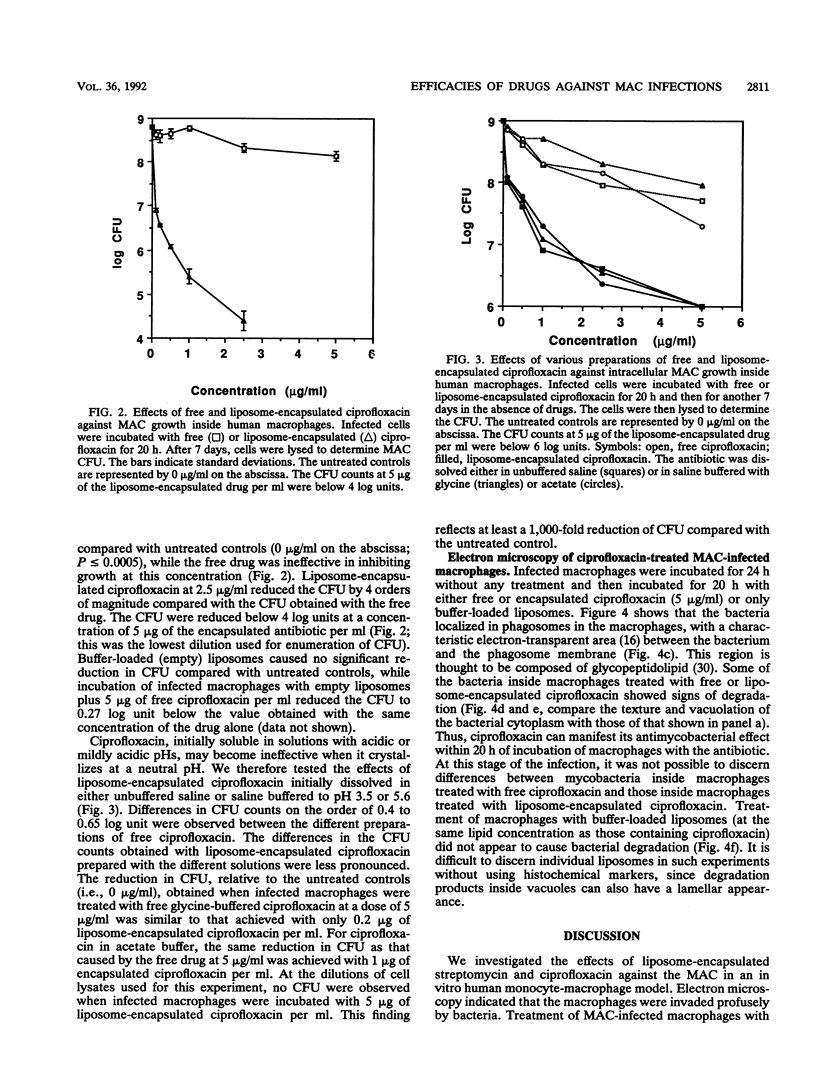
Current treatments of disseminated infection caused by the Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare complex (MAC) are generally ineffective. Liposome-mediated delivery of antibiotics to MAC-infected tissues in vivo can enhance the efficacy of the drugs (N. Düzgüneş, V. K. Perumal, L. Kesavalu, J. A. Goldstein, R. J. Debs, and P. R. J. Gangadharam, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32:1404-1411, 1988; N. Düzgüneş, D. A. Ashtekar, D. L. Flasher, N. Ghori, R. J. Debs, D. S. Friend, and P. R. J. Gangadharam, J. Infect. Dis. 164:143-151, 1991). We investigated the therapeutic efficacies of liposome-encapsulated streptomycin and ciprofloxacin against growth of the MAC inside human peripheral blood monocyte/macrophages. Treatment was initiated 24 h after infection of macrophages with the MAC and stopped after 20 h, and the cells were incubated for another 7 days. The antimycobacterial activity of streptomycin was enhanced when the drug was delivered to macrophages in liposome-encapsulated form, reducing the CFU about threefold more than the free drug did throughout the concentration range studied (10 to 50 micrograms/ml). With 50 micrograms of encapsulated streptomycin per ml, the CFU were reduced to 11% of the initial level of infection. Liposome-encapsulated ciprofloxacin was at least 50 times more effective against the intracellular bacteria than was the free drug: at a concentration of 0.1 microgram/ml, liposome-encapsulated ciprofloxacin had greater antimycobacterial activity than the free drug at 5 microgram/ml. With liposome-encapsulated ciprofloxacin at 5 micrograms/ml, the CFU were reduced by more than 1,000-fold at the end of the 7-day incubation period, compared with untreated controls. These results suggest that liposome-encapsulated ciprofloxacin or other fluoroquinolones may be effective against MAC infections in vivo.
Full text
PDF


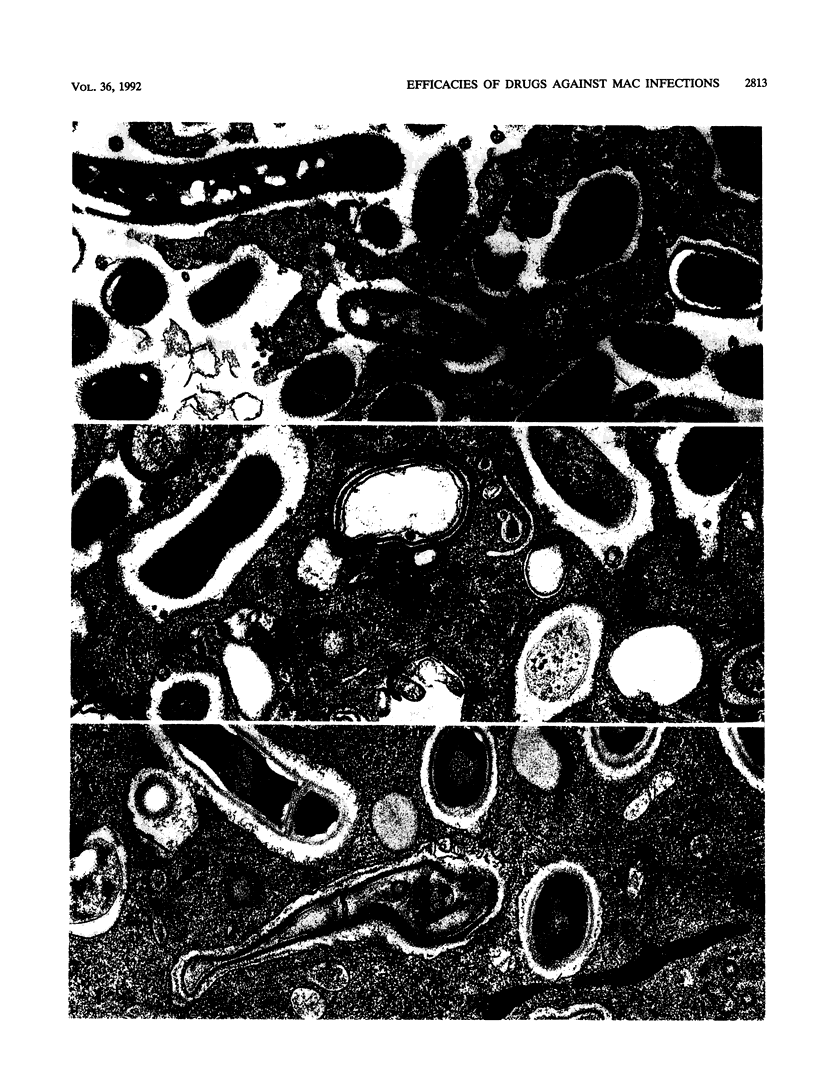


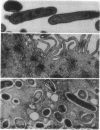
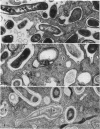
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agins B. D., Berman D. S., Spicehandler D., el-Sadr W., Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J. Effect of combined therapy with ansamycin, clofazimine, ethambutol, and isoniazid for Mycobacterium avium infection in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):784–787. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Gold J. W., Dryjanski J., Whimbey E., Polsky B., Hawkins C., Brown A. E., Bernard E., Kiehn T. E. Treatment of infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):738–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashtekar D., Düzgünes N., Gangadharam P. R. Activity of free and liposome encapsulated streptomycin against Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) inside peritoneal macrophages. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Oct;28(4):615–617. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.4.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., Lokerse A. F., Roerdink F. H., Regts D., Michel M. F. Free versus liposome-entrapped ampicillin in treatment of infection due to Listeria monocytogenes in normal and athymic (nude) mice. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):917–924. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Yau-Young A. O., Lin J. P., Cogger J., Young L. S. Treatment of disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection of beige mice with liposome-encapsulated aminoglycosides. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1262–1268. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cynamon M. H., Swenson C. E., Palmer G. S., Ginsberg R. S. Liposome-encapsulated-amikacin therapy of Mycobacterium avium complex infection in beige mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1179–1183. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dautzenberg B., Truffot C., Legris S., Meyohas M. C., Berlie H. C., Mercat A., Chevret S., Grosset J. Activity of clarithromycin against Mycobacterium avium infection in patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. A controlled clinical trial. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Sep;144(3 Pt 1):564–569. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.3_Pt_1.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra J., van Galen W. J., Hulstaert C. E., Kalicharan D., Roerdink F. H., Scherphof G. L. Interaction of liposomes with Kupffer cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jan;150(1):161–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90711-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düzgüneş N., Ashtekar D. R., Flasher D. L., Ghori N., Debs R. J., Friend D. S., Gangadharam P. R. Treatment of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex infection in beige mice with free and liposome-encapsulated streptomycin: role of liposome type and duration of treatment. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):143–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düzgüneş N., Perumal V. K., Kesavalu L., Goldstein J. A., Debs R. J., Gangadharam P. R. Enhanced effect of liposome-encapsulated amikacin on Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare complex infection in beige mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1404–1411. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenlon C. H., Cynamon M. H. Comparative in vitro activities of ciprofloxacin and other 4-quinolones against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium intracellulare. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):386–388. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehel C., Ryter A., Rastogi N., David H. The electron-transparent zone in phagocytized Mycobacterium avium and other mycobacteria: formation, persistence and role in bacterial survival. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Nov-Dec;137B(3):239–257. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangadharam P. R., Ashtekar D. A., Ghori N., Goldstein J. A., Debs R. J., Düzgünes N. Chemotherapeutic potential of free and liposome encapsulated streptomycin against experimental Mycobacterium avium complex infections in beige mice. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Sep;28(3):425–435. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay J. D., DeYoung D. R., Roberts G. D. In vitro activities of norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. avium complex, M. chelonei, M. fortuitum, and M. kansasii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):94–96. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins K. Potential toxicity of ciprofloxacin. Ophthalmology. 1991 Feb;98(2):120–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga Y., Konoshita T. Post-column derivatization of guanidino compounds in high-performance liquid chromatography using ninhydrin. J Chromatogr. 1981 Nov 13;226(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffner S. E., Svenson S. B., Källenius G. Synergistic effects of antimycobacterial drug combinations on Mycobacterium avium complex determined radiometrically in liquid medium. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;6(5):530–535. doi: 10.1007/BF02014241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr Mycobacterium avium complex infection in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 9;324(19):1332–1338. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105093241906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemens S. P., Cynamon M. H., Swenson C. E., Ginsberg R. S. Liposome-encapsulated-gentamicin therapy of Mycobacterium avium complex infection in beige mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):967–970. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Bodey G. P., Frankel L. S., Mehta K. Treatment of hepatosplenic candidiasis with liposomal-amphotericin B. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Feb;5(2):310–317. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.2.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozenne G., Morel A., Menard J. F., Thauvin C., Samain J. P., Lemeland J. F. Susceptibility of Mycobacterium avium complex to various two-drug combinations of antituberculosis agents. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):878–881. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi N., Frehel C., Ryter A., Ohayon H., Lesourd M., David H. L. Multiple drug resistance in Mycobacterium avium: is the wall architecture responsible for exclusion of antimicrobial agents? Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):666–677. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rulong S., Aguas A. P., da Silva P. P., Silva M. T. Intramacrophagic Mycobacterium avium bacilli are coated by a multiple lamellar structure: freeze fracture analysis of infected mouse liver. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3895–3902. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3895-3902.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tomioka H. Therapeutic efficacy of liposome-entrapped rifampin against Mycobacterium avium complex infection induced in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):429–433. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Olson F., Heath T., Vail W., Mayhew E., Papahadjopoulos D. Preparation of unilamellar liposomes of intermediate size (0.1-0.2 mumol) by a combination of reverse phase evaporation and extrusion through polycarbonate membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 2;601(3):559–571. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadakuma T., Ikewaki N., Yasuda T., Tsutsumi M., Saito S., Saito K. Treatment of experimental salmonellosis in mice with streptomycin entrapped in liposomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):28–32. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneja D. P., Kaur D. Study on hepatotoxicity and other side-effects of antituberculosis drugs. J Indian Med Assoc. 1990 Oct;88(10):278–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajko D. M., Nassos P. S., Hadley W. K. Therapeutic implications of inhibition versus killing of Mycobacterium avium complex by antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jan;31(1):117–120. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Inderlied C. B., Berlin O. G., Gottlieb M. S. Mycobacterial infections in AIDS patients, with an emphasis on the Mycobacterium avium complex. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1024–1033. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]