Abstract
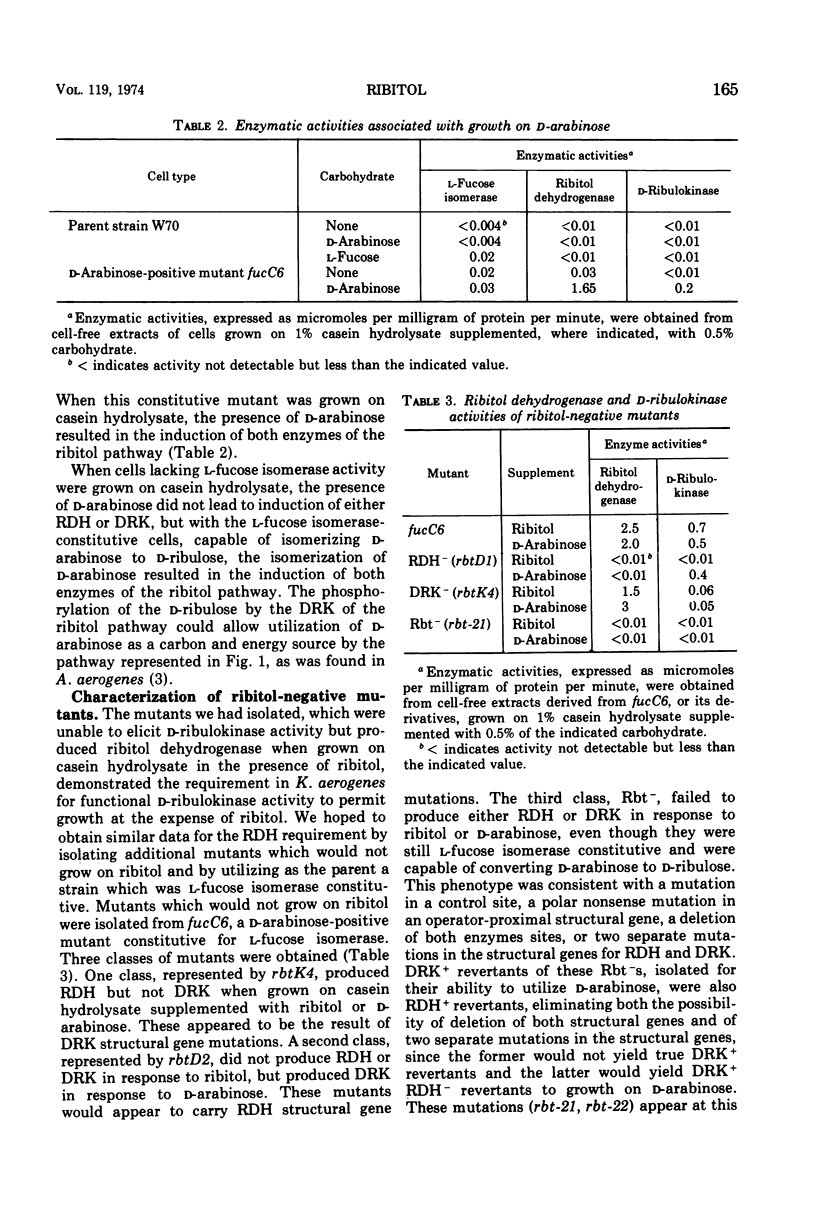
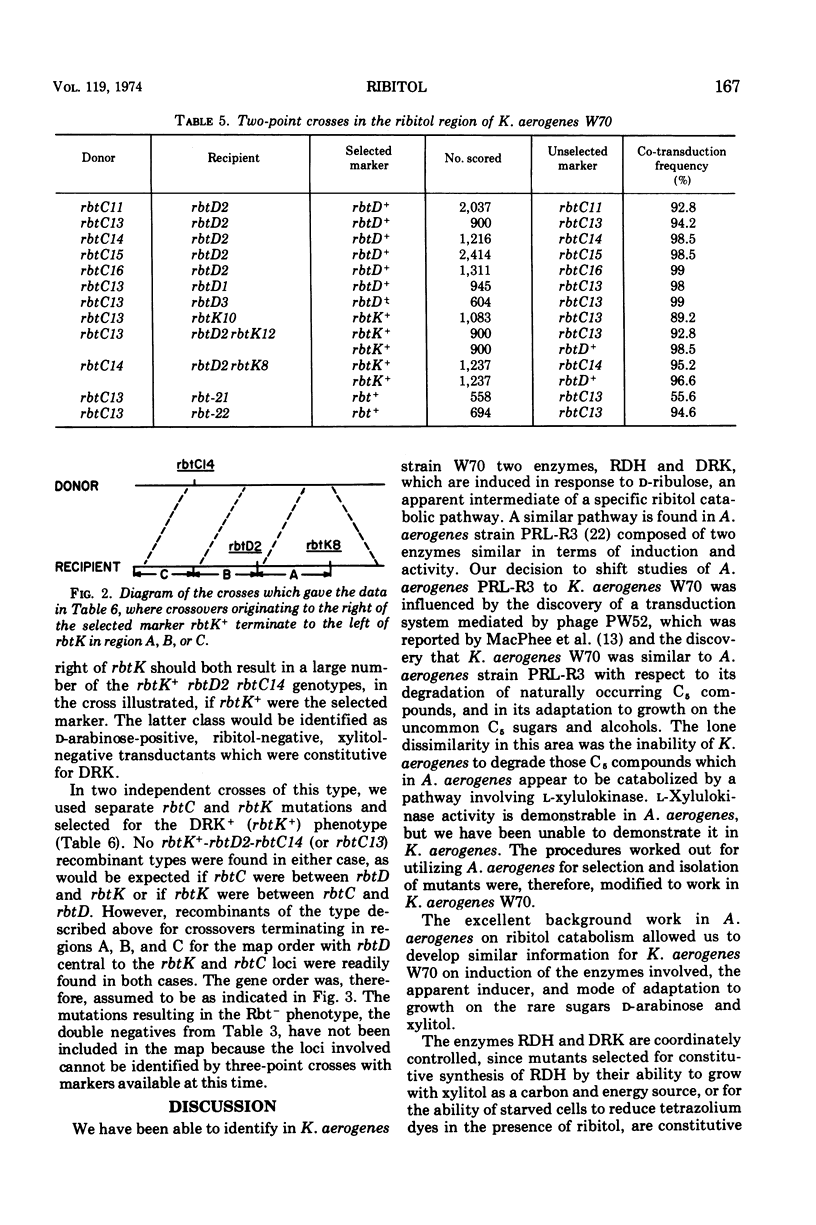
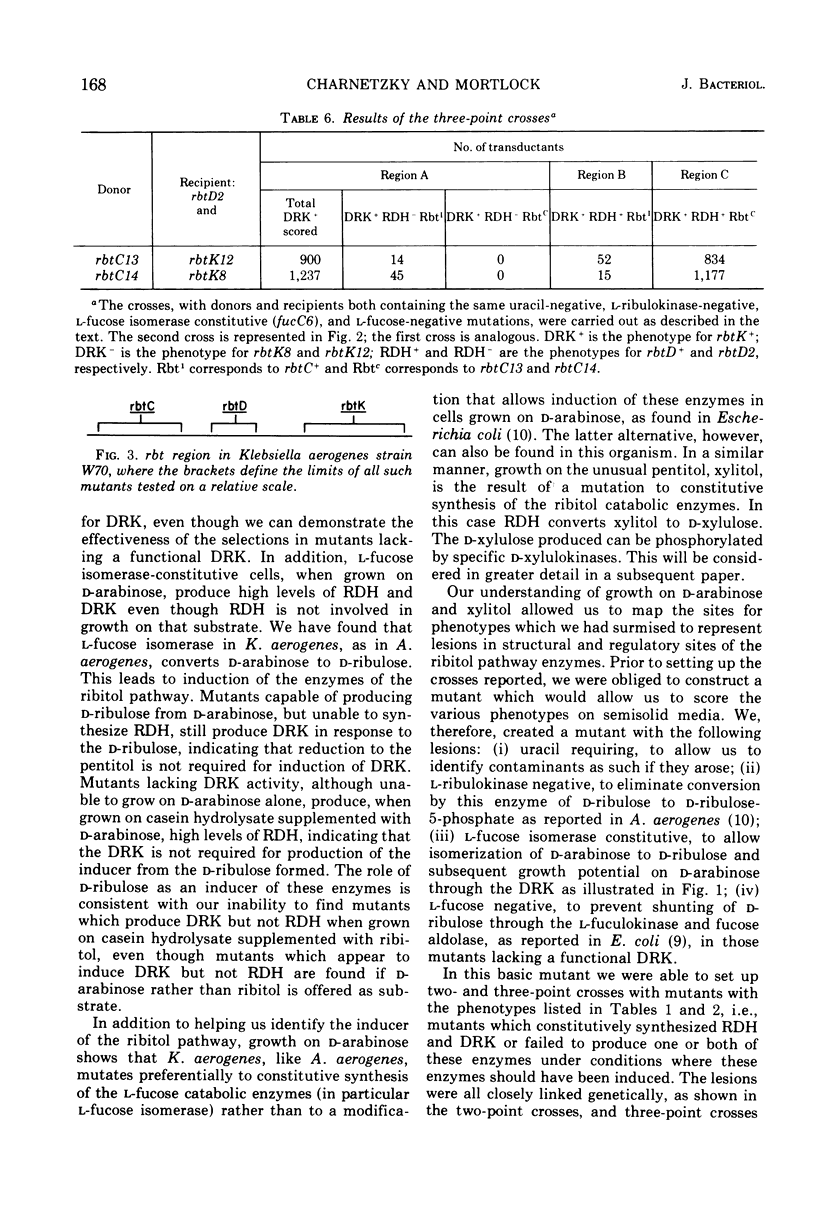
In Klebsiella aerogenes W70, there is an inducible pathway for the catabolism of ribitol consisting of at least two enzymes, ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH) and d-ribulokinase (DRK). These two enzymes are coordinately controlled and induced in response to d-ribulose, an intermediate of the pathway. Whereas wild-type K. aerogenes W70 are unable to utilize xylitol as a carbon and energy source, mutants constitutive for the ribitol pathway are able to utilize RDH to oxidize the unusual pentitol, xylitol, to d-xylulose. These mutants are able to grow on xylitol, presumably by utilization of the d-xylulose produced. Mutants constitutive for l-fucose isomerase can utilize the isomerase to convert d-arabinose to d-ribulose. In the presence of d-ribulose, RDH and DRK are induced, and such mutants are thus able to phosphorylate the d-ribulose by using the DRK of the ribitol pathway. Derivatives of an l-fucose isomerase-constitutive mutant were plated on d-arabinose, ribitol, and xylitol to select and identify mutations in the ribitol pathway. Using the transducing phage PW52, we were able to demonstrate genetic linkage of the loci involved. Three-point crosses, using constitutive mutants as donors and RDH−, DRK− double mutants as recipients and selecting for DRK+ transductants on d-arabinose, resulted in DRK+RDH+-constitutive, DRK+RDH+-inducible, and DRK+RDH−-inducible transductants but no detectable DRK+RDH− constitutive transductants, data consistent with the order rbtC-rbtD-rbtK, where rbtC is a control site and rbtD and rbtK correspond to the sites for the sites for the enzymes RDH and DRK, respectively.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON R. L., WOOD W. A. Purification and properties of L-xylulokinase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1029–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson T. M., Oliver E. J., Mortlock R. P. Regulation of pentitol metabolism by aerobacter aerogenes. II. Induction of the ribitol pathway. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):932–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.932-936.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Studies on D-ribulose and its enzymatic conversion to D-arabinose. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):71–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camyre K. P., Mortlock R. P. Growth of Aerobacter aerogenes on D-arabinose and L-xylose. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):1157–1158. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.1157-1158.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z., BORENFREUND E. A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J Biol Chem. 1951 Oct;192(2):583–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIN E. C., LERNER S. A., JORGENSEN S. E. A method for isolating constitutive mutants for carbohydrate-catabolizing enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:422–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90423-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. Metabolism of D-arabinose: a new pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):90–96. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.90-96.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. The metabolism of D-arabinose: alternate kinases for the phosphorylation of D-ribulose in Escherichia coli and Aerobacter aerogenes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jun;150(2):774–781. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R., Cohen S. S. D-phosphoarabinoisomerase and D-ribulokinase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4304–4315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTLOCK R. P., WOOD W. A. METABOLISM OF PENTOSES AND PENTITOLS BY AEROBACTER AEROGENES. I. DEMONSTRATION OF PENTOSE ISOMERASE, PENTULOKINASE, AND PENTITOL DEHYDROGENASE ENZYME FAMILIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.838-844.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee D. G., Sutherland I. W., Wilkinson J. F. Transduction in Klebsiella. Nature. 1969 Feb 1;221(5179):475–476. doi: 10.1038/221475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortlock R. P., Fossitt D. D., Wood W. A. A basis for utlization of unnatural pentoses and pentitols by Aerobacter aerogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):572–579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver E. J., Bisson T. M., LeBlanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. D-Ribulose production by a mutant of Aerobacter aerogens. Anal Biochem. 1969 Feb;27(2):300–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver E. J., Mortlock R. P. Growth of Aerobacter aerogenes on D-arabinose: origin of the enzyme activities. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):287–292. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.287-292.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver E. J., Mortlock R. P. Metabolism of D-arabinose by Aerobacter aerogenes: purification of the isomerase. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):293–299. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.293-299.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD W. A., McDONOUGH M. J., JACOBS L. B. Rihitol and D-arabitol utilization by Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1961 Aug;236:2190–2195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. L., Mortlock R. P. Regulation of D-xylose and D-arabitol catabolism by Aerobacter aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1404–1411. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1404-1411.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


