Abstract
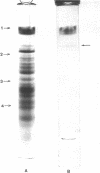
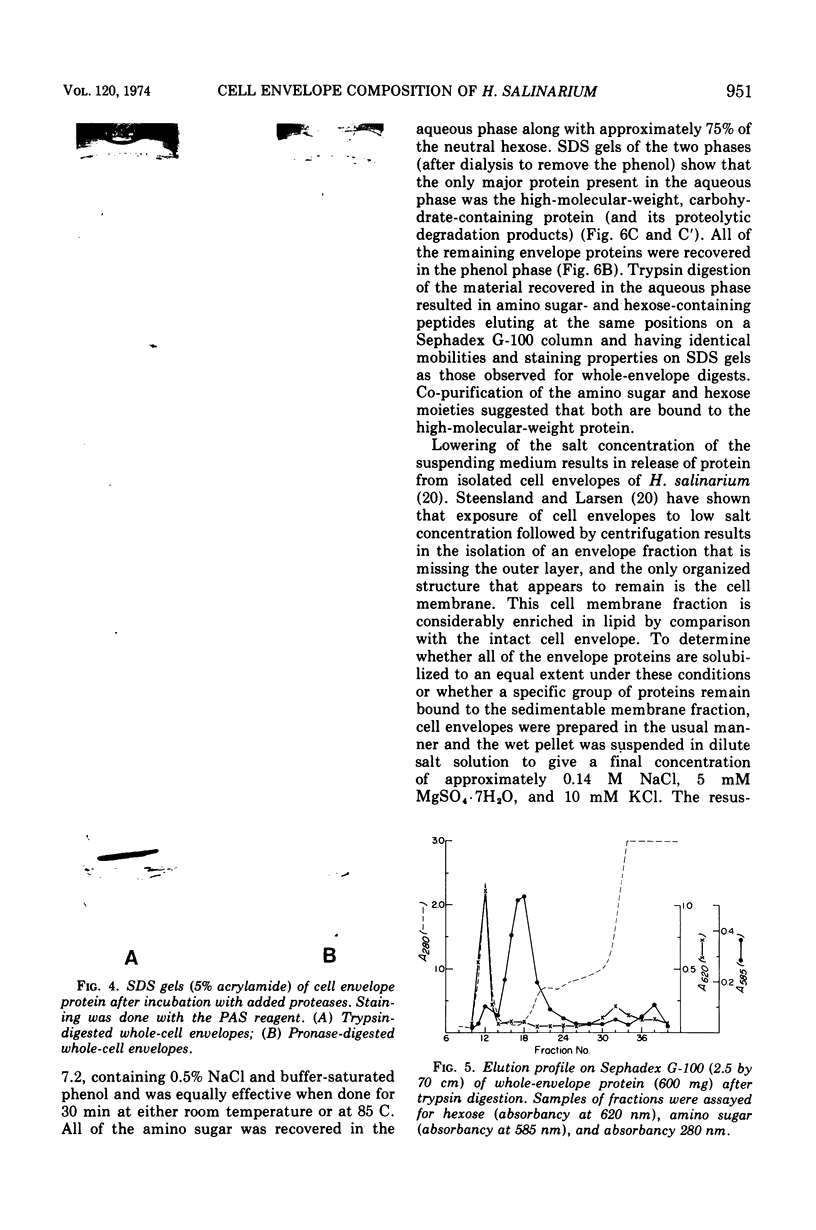
The isolated cell envelope of Halobacterium salinarium strain 1 contained 15 to 20 proteins that were resolved by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. All but one of these proteins had molecular weights of 130,000 or less and together accounted for 50 to 60% of the total envelope protein. The remaining 40 to 50% of the envelope protein was accounted for by a single protein with an apparent molecular weight of approximately 194,000 that stained for carbohydrate with periodate-Schiff reagent. The proteolytic enzymes trypsin and Pronase were used to show that the carbohydrate is covalently bound to the protein. Separation of amino sugar- and hexose-containing tryptic peptides by gel filtration indicated that all of the nonlipid carbohydrate of the cell envelope is covalently bound to protein. The results of partial purification by phenol extraction indicated that both the amino sugar and hexose are bound to the 194,000-molecular-weight protein. Exposure of isolated cell envelopes to low salt concentration resulted in solubilization of a majority of the envelope proteins. A relatively small number of proteins, including the high-molecular-weight, carbohydrate-containing protein, remained bound to the sedimentable cell membrane fraction.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun V., Bosch V. Sequence of the murein-lipoprotein and the attachment site of the lipid. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jun 23;28(1):51–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. Y., Doy C. H., Mercer E. H. Ultrastructure of the obligate halophilic bacterium Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):196–201. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.196-201.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER D. J., BAYLEY S. T., BORING J., KATES M., GIBBONS N. E. MORPHOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CELL ENVELOPES OF THE EXTREME HALOPHILE, HALOBACTERIUM CUTIRUBRUM. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Jun;10:483–497. doi: 10.1139/m64-058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M., Palameta B., Perry M. P., Adams G. A. A new glycolipid sulfate ester in Halobacterium cutirubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 14;137(1):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. L., Wicken A. J., Brown A. D. The outer layer of the cell envelope of Halobacterium halobium. Can J Biochem. 1969 Jan;47(1):71–74. doi: 10.1139/o69-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norberg P., von Hofsten B. Proteolytic enzymes from extremely halophilic bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Feb;55(2):251–256. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda S., Weinbaum G. An envelope-specific glycoprotein from Escherichia coli B. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2819–2825. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S. M. Filter-paper partition chromatography of sugars: 1. General description and application to the qualitative analysis of sugars in apple juice, egg white and foetal blood of sheep. with a note by R. G. Westall. Biochem J. 1948;42(2):238–250. doi: 10.1042/bj0420238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Comparison of the envelope protein compositions of several gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1404–1405. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1404-1405.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Examination of the protein composition of the cell envelope of Escherichia coli by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):882–889. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.882-889.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. II. Heterogeneity of major outer membrane polypeptides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Aug;157(2):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90674-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steensland H., Larsen H. A study of the cell envelope of the halobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):325–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Rowen R. A morphological study of Halobacterium halobium and its lysis in media of low salt concentration. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):365–393. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wober W., Alaupović P. Studies on the protein moiety of endotoxin from gram-negative bacteria. Characterization of the protein moiety isolated by phenol treatment of endotoxin from Serratia marcescens 08 and Escherichia coli 0 141:K85(B). Eur J Biochem. 1971 Apr;19(3):340–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M. C., Heath E. C. Isolation and characterization of lipopolysaccharide protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2572–2576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]