Abstract
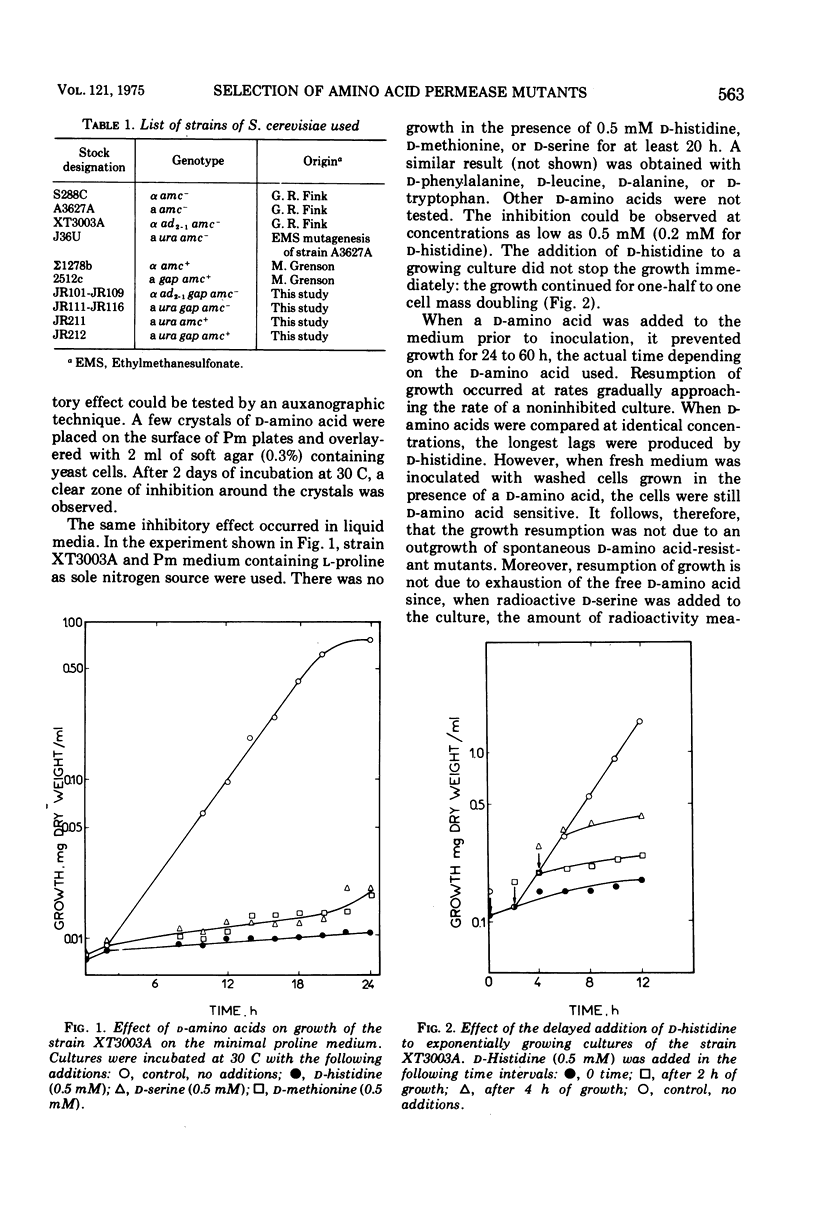
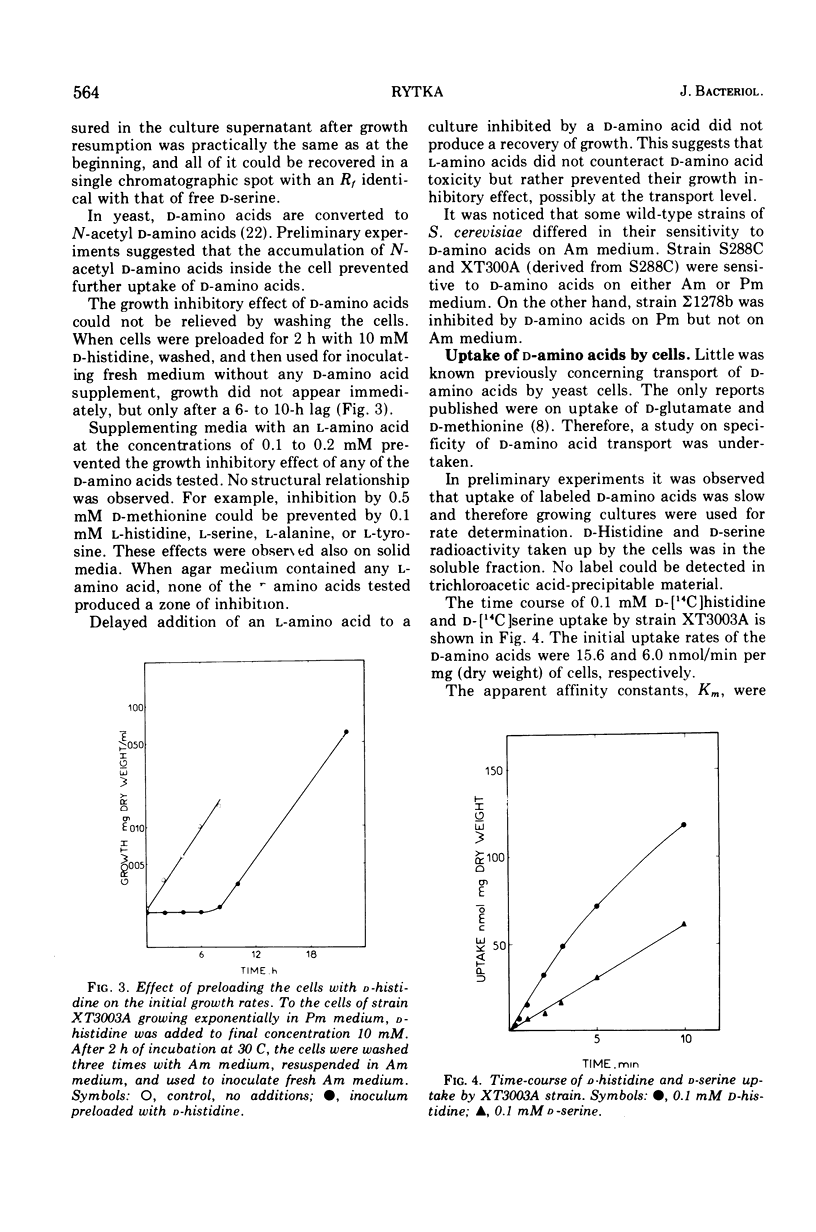
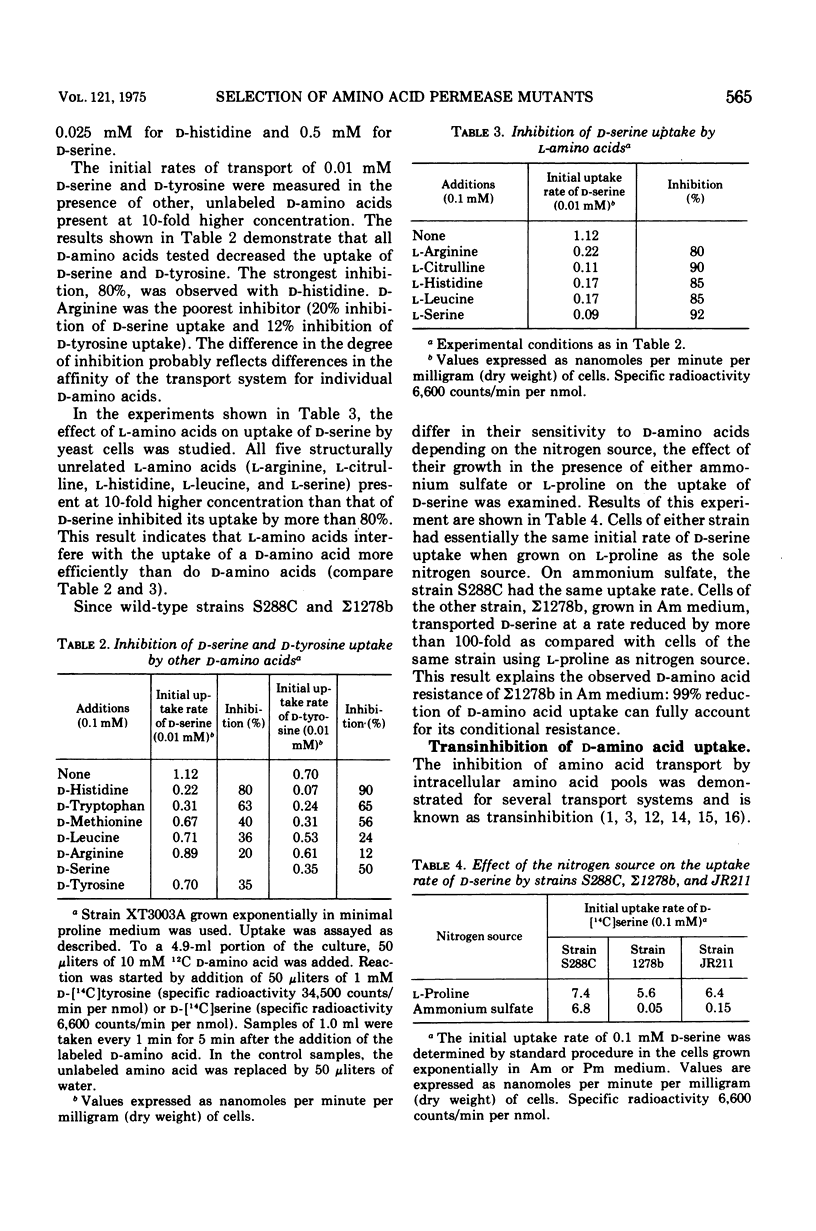
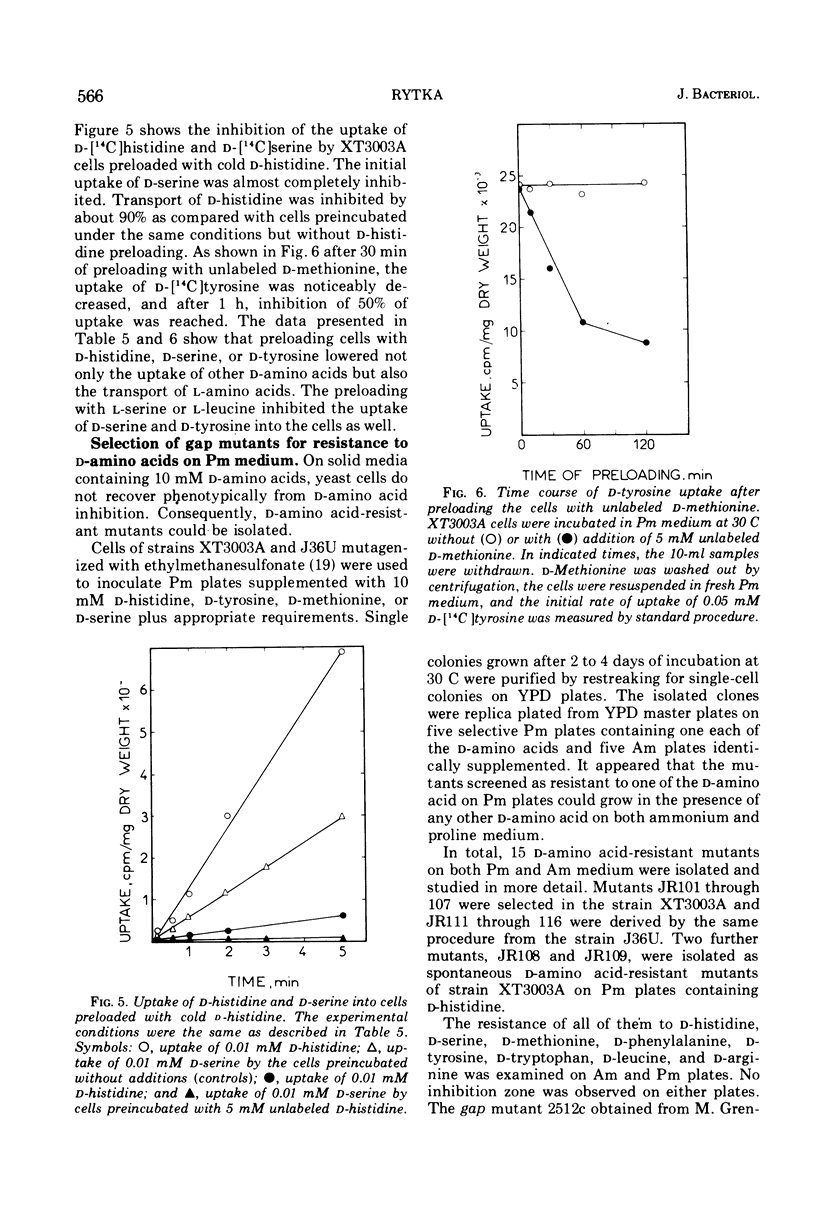
It was found that D-stereoisomers of natural amino acids inhibit the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Kinetic and genetic evidence showed that d-amino acids enter the cell by the general amino acid permease. Two classes of S. cerevisiae mutants resistant to d-amino acids were isolated. One class of mutants appeared to be defective in the general amino acid permease specified by the gene gap. In the second class, the activity of general amino acid permease was affected by ammonium ions. Mutants of the second class were isolated in a yeast strain with the general amino acid permease insensitive to the presence of ammonium ions in culture media. The mutation affecting the permease, amc, occurred in a locus unlinked to gap.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benko P. V., Wood T. C., Segel I. H. Multiplicity and regulation of amino acid transport in Penicillium chrysogenum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Feb;129(2):498–508. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H., Umbarger H. E. Biosynthesis of the branched-chain amino acids in yeast: a leucine-binding component and regulation of leucine uptake. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):277–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.277-285.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabeel M., Grenson M. Regulation of histidine uptake by specific feedback inhibition of two histidine permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):197–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gits J. J., Grenson M. Multiplicity of the amino acid permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. 3. Evidence for a specific methionine-transporting system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 3;135(3):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenson M., Crabeel M., Wiame J. M., Béchet J. Inhibition of protein synthesis and simulation of permease turnover in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 26;30(4):414–419. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90760-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenson M., Hennaut C. Mutation affecting activity of several distinct amino acid transport systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):477–482. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.477-482.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenson M., Hou C., Crabeel M. Multiplicity of the amino acid permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. IV. Evidence for a general amino acid permease. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):770–777. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.770-777.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenson M., Mousset M., Wiame J. M., Bechet J. Multiplicity of the amino acid permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Evidence for a specific arginine-transporting system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):325–338. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90387-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenson M. Multiplicity of the amino acid permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Evidence for a specific lysine-transporting system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSON H. O., COHEN G. N. Incorporation des amino-acides endogènes et exogènes dans les protéines de la levure. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Jul;95(1):73–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne D C, Mortimer R K. Chromosome Mapping in Saccharomyces: Centromere-Linked Genes. Genetics. 1960 Aug;45(8):1085–1110. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.8.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. R., Segel I. H. Control of the general amino acid permease of Penicillium chrysogenum by transinhibition and turnover. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):387–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroute F., Piérard A., Grenson M., Wiame J. M. The biosynthesis of carbamoyl phosphate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jul;40(1):127–142. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pall M. L. Amino acid transport in Neurospora crassa. IV. Properties and regulation of a methionine transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):201–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pall M. L., Kelly K. A. Specificity of transinhibition of amino acid transport in neurospora. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Mar 5;42(5):940–947. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. H., Anthony C., Drabble W. T. Activity and regulation of an acidic amino acid permease of Aspergillus nidulans. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):75P–75P. doi: 10.1042/bj1240075pa. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SORSOLI W. A., SPENCE K. D., PARKS L. W. AMINO ACID ACCUMULATION IN ETHIONINE-RESISTANT SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:20–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.20-24.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwencke J., Magaña-Schwencke N. Derepression of a proline transport system in Saccharomyces chevalieri by nitrogen starvation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 11;173(2):302–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surdin Y., Sly W., Sire J., Bordes A. M., Robichon-Szulmajster H. Propriétés et contrôle génétique du système d'accumulation des acides aminés chez Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 18;107(3):546–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenk M. H., Schmitt J. H. Reinigung und Eigenschaften von Acetyl-CoA: D-Aminosäure-alpha-N-Acetyltransferase aus Hefe. Biochem Z. 1965 Jun 3;342(1):54–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


