Abstract
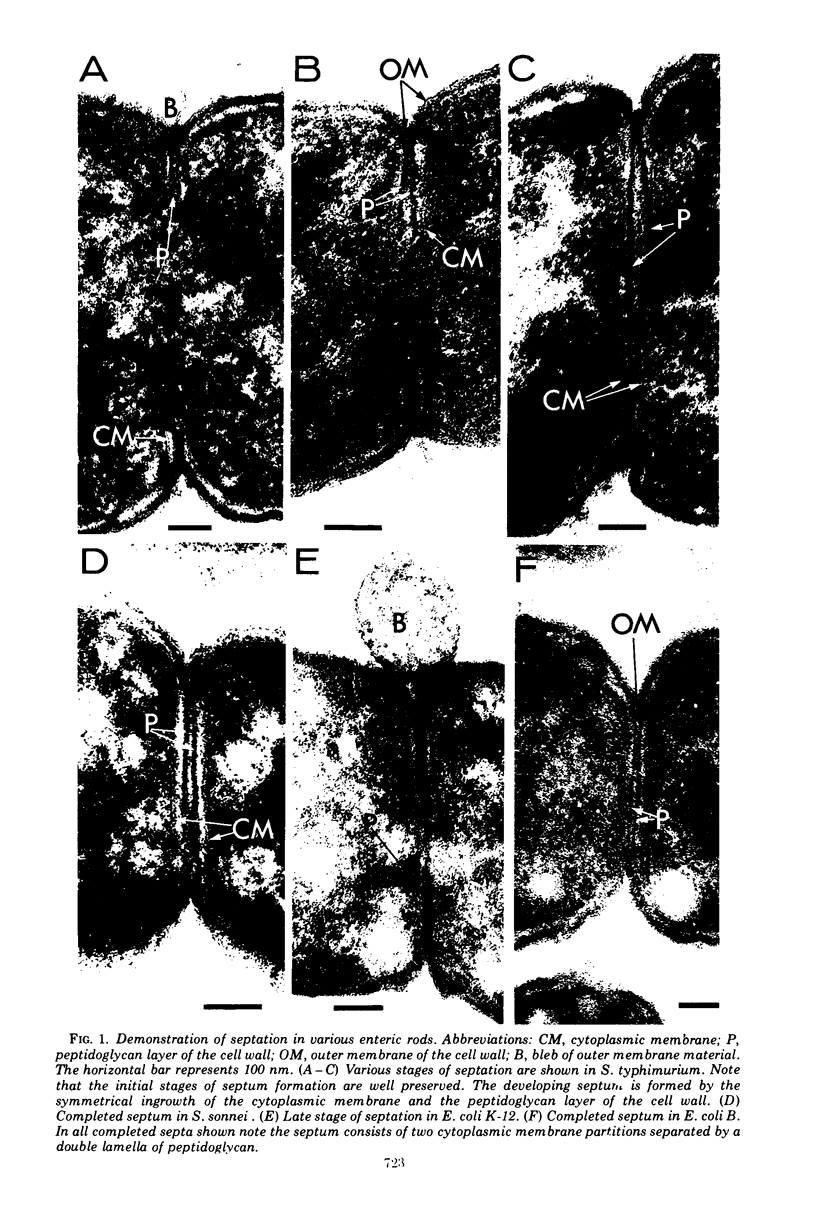
Through use of an initial fixative employing a combination of crotonaldehyde and glutaraldehyde, septa were preserved in thin sections of dividing cells of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella sonnei, and Escherichia coli when grown at 30 C in a dilute basal medium. The same procedures, however, revealed only a constrictive division process in Proteus vulgaris and Erwinia sp. This adds to the evidence that septation, although difficult to demonstrate, is the process of cell division in the enteric gram-negative rods and the pseudomonads and that constriction is a fixation artifact in these organisms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burdett I. D., Murray R. G. Electron microscope study of septum formation in Escherichia coli strains B and B-r during synchronous growth. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1039–1056. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1039-1056.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett I. D., Murray R. G. Septum formation in Escherichia coli: characterization of septal structure and the effects of antibiotics on cell division. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):303–324. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.303-324.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti S. F., Gettner M. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF CELLULAR DIVISION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83(3):544–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.544-550.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Roth I. L., Eagon R. G. Ultrastructure of the cell wall and the mechanism of cellular division of a gram-variable coccus. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Mar;17(3):421–424. doi: 10.1139/m71-069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grula E. A., Smith G. L. Cell division in a species of Erwinia. IX. Electron microscopy of normally dividing cells. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):1054–1058. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.1054-1058.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstetter C. E. DNA synthesis during the division cycle of rapidly growing Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):507–518. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90424-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohiyama M., Cousin D., Ryter A., Jacob F. Mutants thermosensibles d'Escherichia coli K 12. I. Isolement et caractérisation rapide. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Apr;110(4):465–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORITA R. Y., STAVE P. W. ELECTRON MICROGRAPH OF AN ULTRATHIN SECTION OF BEGGIATOA. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:940–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.940-942.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier S., Murray R. G. The fine structure of Thioploca ingrica and a comparison with Beggiatoa. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Aug;11(4):645–655. doi: 10.1139/m65-087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATA T. The molecular synchrony and sequential replication of DNA in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Apr;49:551–559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.4.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Boman H. G., Bloom G. D. Cell division in a chain-forming envA mutant of Escherichia coli K12. Fine structure of division sites and effects of EDTA, lysozyme and ampicillin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(5):651–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodolakis A., Thomas P., Starka J. Morphological mutants of Escherichia coli. Isolation and ultrastructure of a chain-forming envC mutant. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):409–416. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M., Schaechter M. Control of cell division in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Jun;38(2):199–221. doi: 10.1128/br.38.2.199-221.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steed P., Murray R. G. The cell wall and cell division of gram-negative bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Apr;12(2):263–270. doi: 10.1139/m66-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebe W. J., Chapman G. B. Fine structure of selected marine pseudomonads and achromobacters. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1862–1873. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1862-1873.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]