Abstract
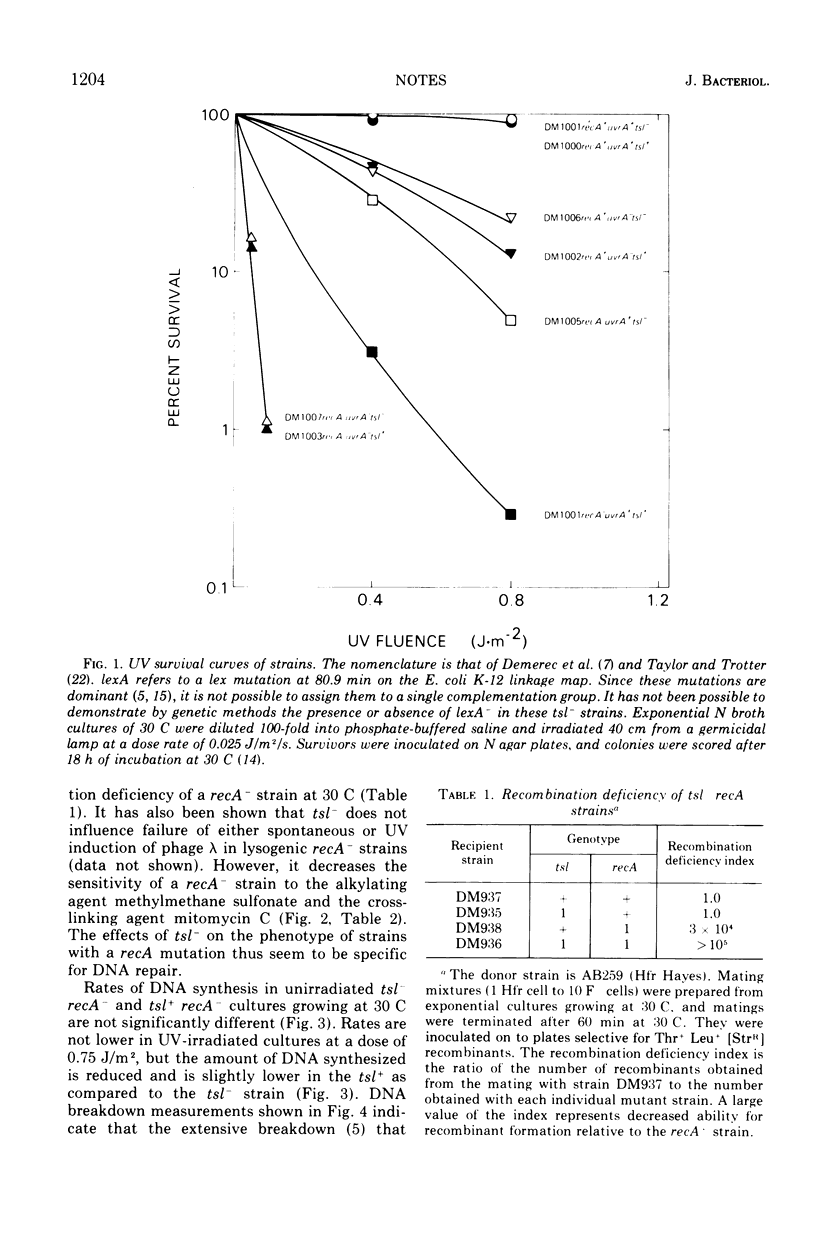
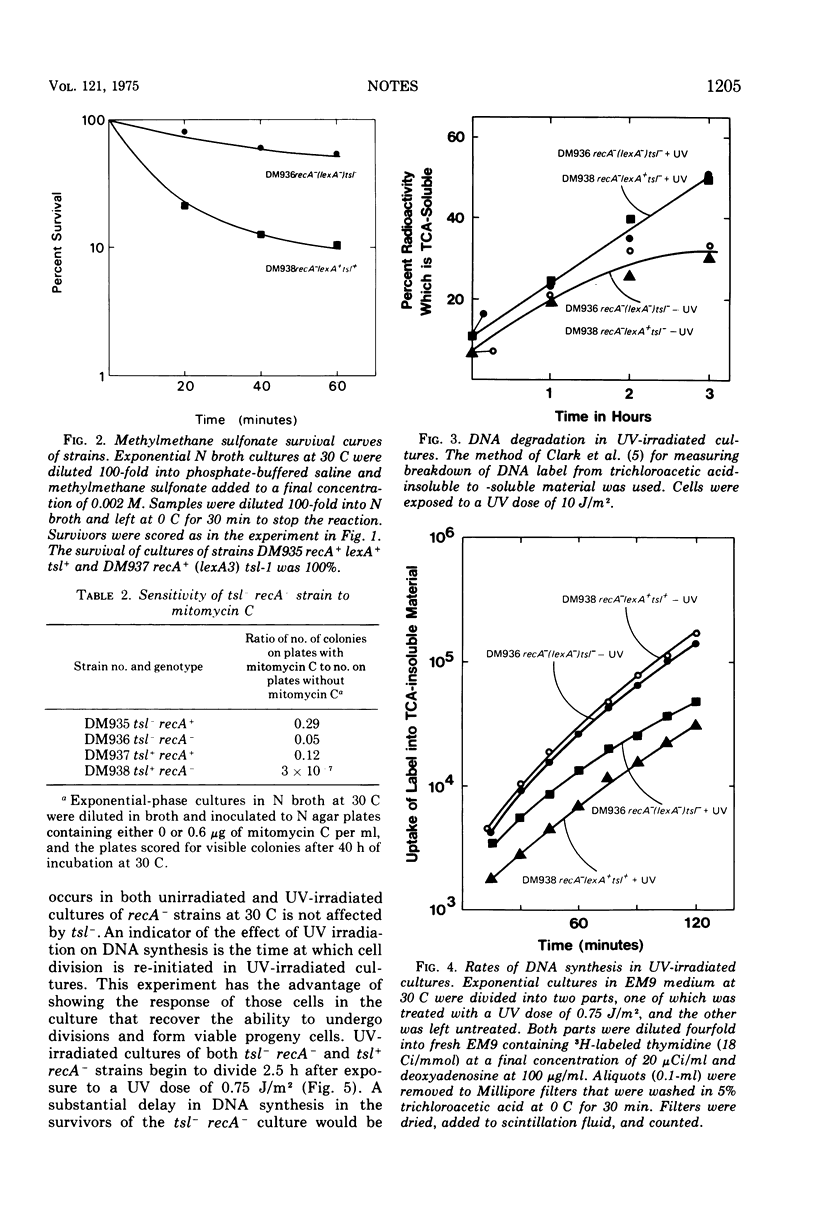
It has been shown previously that the radiation sensitivity of lexA- strains of Escherichia coli K-12 can be suppressed by thermosensitive mutations (designated tsl) that are closely linked to the lexA locus and are thought to be intragenic suppressors of lexA mutations (Mount et al., 1973). When a recA mutation is crossed into a suppressed tsl- strain, the extreme radiation sensitivity usually conferred by a recA mutation is decreased, but there is no detectable change in genetic recombination deficiency. Increased resistance to UV in the tsl-reA-strains depends upon ability to synthesize active uvrA+ product.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER H. I., HARDIGREE A. A. ANALYSIS OF A GENE CONTROLLING CELL DIVISION AND SENSITIVITY TO RADIATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.720-726.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun A., Grossman L. An endonuclease from Escherichia coli that acts preferentially on UV-irradiated DNA and is absent from the uvrA and uvrB mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1838–1842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges B. A. Genetic and physiological separation of the repair and mutagenic functions of the exrA gene in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1973 Apr;73(Suppl):123–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellazzi M., George J., Buttin G. Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. I. Further characterization of the thermosensitive mutation tif-1 whose expression mimics the effect of UV irradiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(2):139–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00269133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Chamberlin M., Boyce R. P., Howard-Flanders P. Abnormal metabolic response to ultraviolet light of a recombination deficient mutant of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):442–454. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. Recombination deficient mutants of E. coli and other bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:67–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demerec M., Adelberg E. A., Clark A. J., Hartman P. E. A proposal for a uniform nomenclature in bacterial genetics. Genetics. 1966 Jul;54(1):61–76. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donch J. J., Greenberg J. The effect of lex on UV sensitivity, filament formation and lambda induction in ion mutants of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;128(4):277–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00268515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan A. K., Smith K. C. Recovery of recombination deficient mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 from ultraviolet irradiation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:235–242. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD-FLANDERS P., SIMSON E., THERIOT L. A LOCUS THAT CONTROLS FILAMENT FORMATION AND SENSITIVITY TO RADIATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI K-12. Genetics. 1964 Feb;49:237–246. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Boyce R. P., Theriot L. Three loci in Escherichia coli K-12 that control the excision of pyrimidine dimers and certain other mutagen products from DNA. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1119–1136. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P. DNA repair. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:175–200. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mound D. W., Walker A. C., Kosel C. Suppression of lex mutations affecting deoxyribonucleic acid repair in Escherichia coli K-12 by closely linked thermosensitive mutations. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):950–956. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.950-956.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W., Kosel C. Properties of strains of Escherichia coli K12 carrying mutant lex-1 and uvrA6 alleles. Mol Gen Genet. 1973;120(4):291–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00268143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W., Low K. B., Edmiston S. J. Dominant mutations (lex) in Escherichia coli K-12 which affect radiation sensitivity and frequency of ultraviolet lght-induced mutations. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):886–893. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.886-893.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Howard-Flanders P. Discontinuities in the DNA synthesized in an excision-defective strain of Escherichia coli following ultraviolet irradiation. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Reno D. L., Howard-Flanders P. Exchanges between DNA strands in ultraviolet-irradiated Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):25–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick S. G., Bridges B. A. Survival, mutation and capacity to repair single-strand DNA breaks after gamma irradiation in different Exr - strains of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(2):93–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00269129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. C., Meun D. H. Repair of radiation-induced damage in Escherichia coli. I. Effect of rec mutations on post-replication repair of damage due to ultraviolet radiation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Linkage map of Escherichia coli strain K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):504–524. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.504-524.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


