Abstract
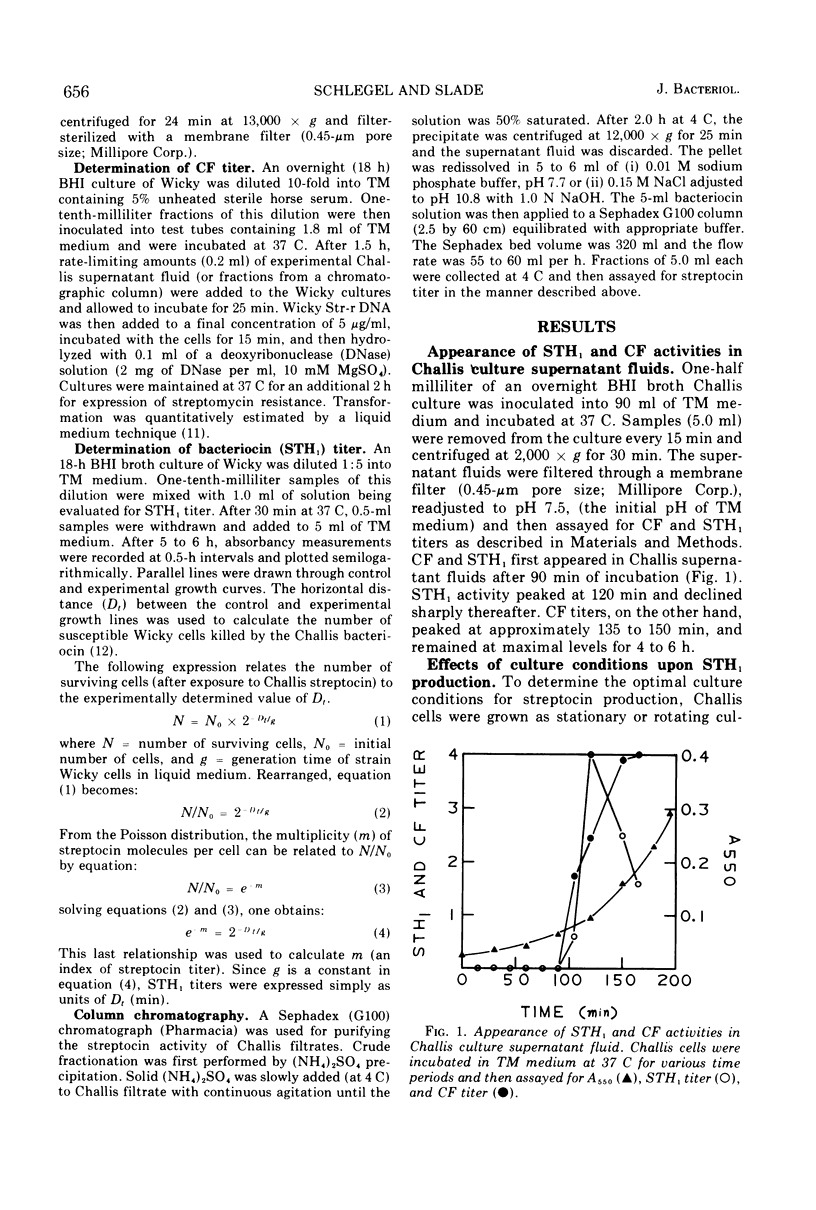
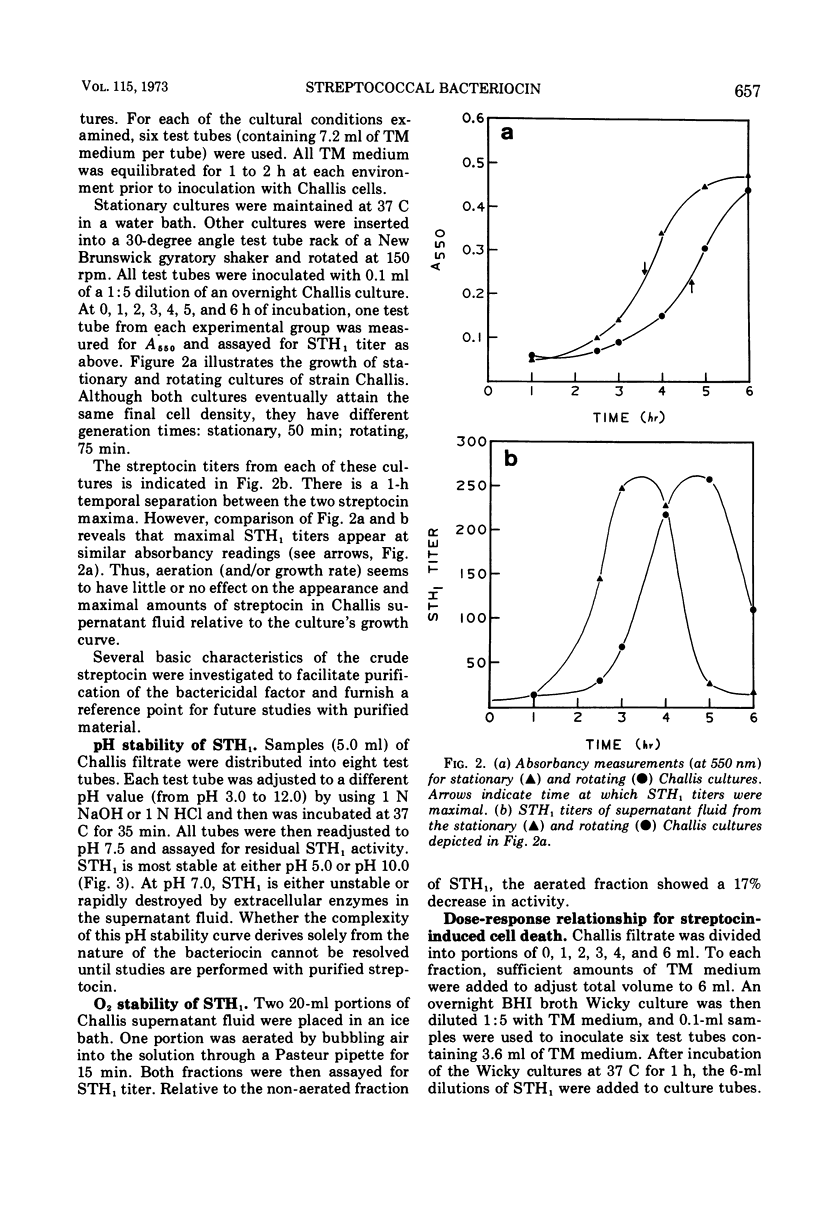
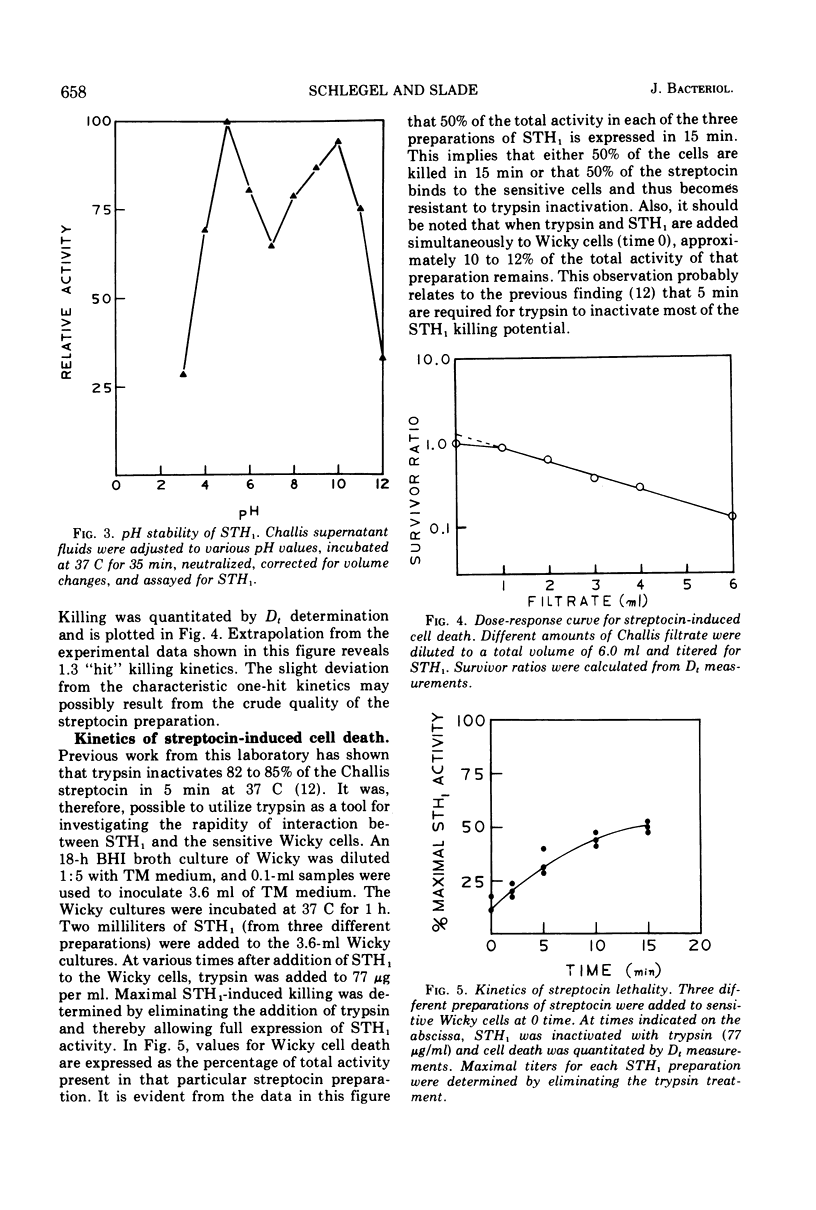
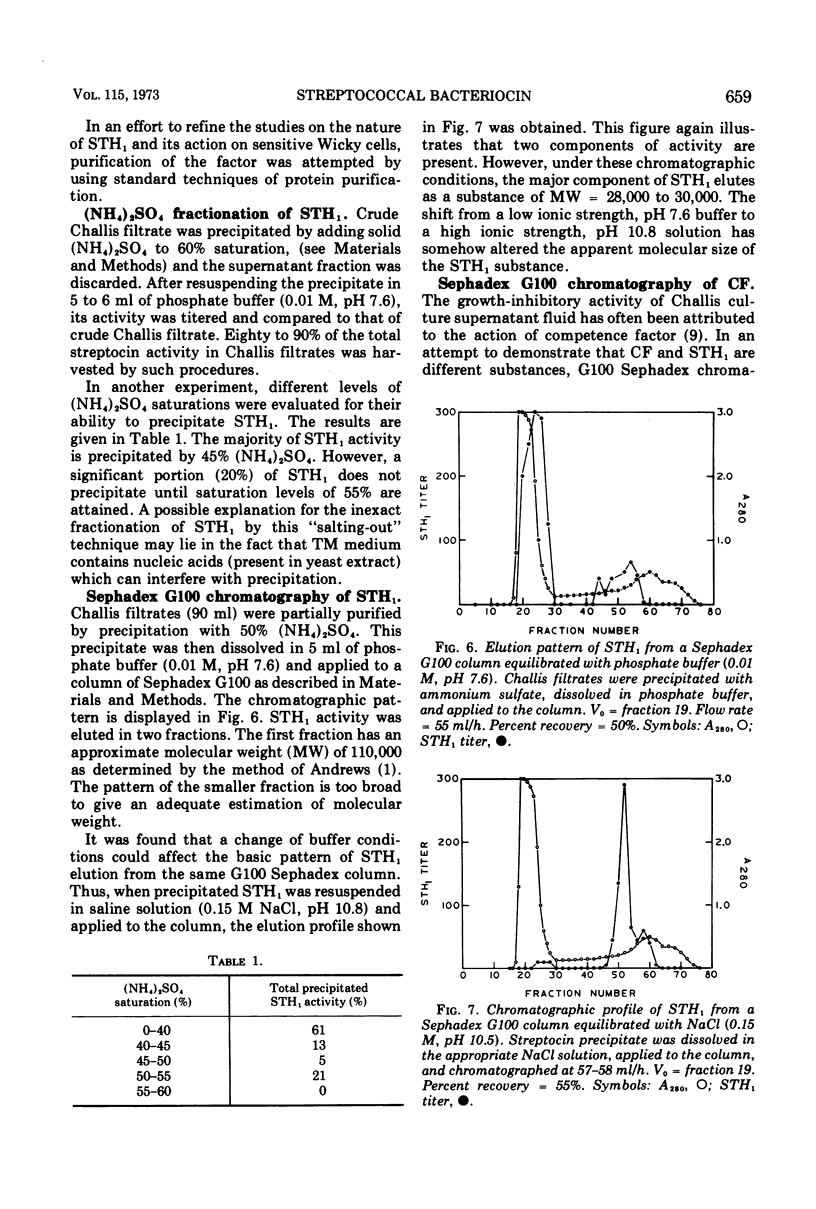
STH1, a streptocin elaborated by group H streptococcus strain Challis, is lethal for group H streptococcus strain Wicky and is produced maximally during the exponential growth phase of liquid medium cultures. Crude streptocin preparations are resistant to oxidation and display a biphasic pH stability (stability being maximal at pH 5.0 and 10.0). Survivor studies indicate that streptocin-mediated killing is a “one-hit” phenomenon and proceeds rapidly. The streptocin has been purified 50-fold with (NH4)2SO4 fractionation and Sephadex G100 chromatography and appears to exist in equilibrium between two molecular weight forms. Low ionic strength and neutral pH buffers favor the isolation of the 110,000 molecular weight form, whereas high ionic strength and alkaline pH conditions facilitate isolation of the 28,000 to 30,000 molecular weight form. These findings suggest an association-dissociation relationship between macromolecules of 28,000 to 30,000 molecular weight. Purified STH1 has no “competence factor” (CF) activity. In addition, CF has no STH1 activity and displays no inhibitory effect on exponential-phase Wicky cultures as determined by absorbancy measurements. It appears, therefore, that initiation of the competent state for transformation in strain Wicky is not necessarily accompanied by gross alterations in cell growth.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D., DAVIE J. M. PROBABLE IDENTITY OF A GROUP D HEMOLYSIN WITH A BACTERIOCINE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:708–712. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.708-712.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley D. C., Hadden C. T., Nester E. W. Macromolecular synthesis in Bacillus subtilis during development of the competent state. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):668–679. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.668-679.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Gibbons R. J. Bacteriocins from human and rodent streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 Mar;14(3):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer J., Brandis H. Charakterisierung eines Streptococcus agalactiae-Bacteriocins. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1972 Mar;219(3):290–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuttner A. G. Production of bacteriocines by group A streptococci with special reference to the nephritogenic types. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):279–291. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy C., Nester E. W. Macromolecular synthesis in newly transformed cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):131–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.131-140.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overturf G. D., Mortimer E. A., Jr Studies of the relationship between the production of bacteriocines by group A streptococci and acute glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):694–701. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula R., Spencer L. R. Some features of competent streptococci. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Apr;18(4):487–491. doi: 10.1139/m72-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogul M., Carr S. R. Variable ammonia production among smooth and rough strains of Pseudomonas pseudomallei: resemblance to bacteriocin production. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):372–380. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.372-380.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Slade H. D. Bacteriocin production by transformable group H streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):824–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.824-829.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Slade H. D. Determination of the rate of transformation from growth curves of transformed streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):199–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.199-202.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


