Abstract
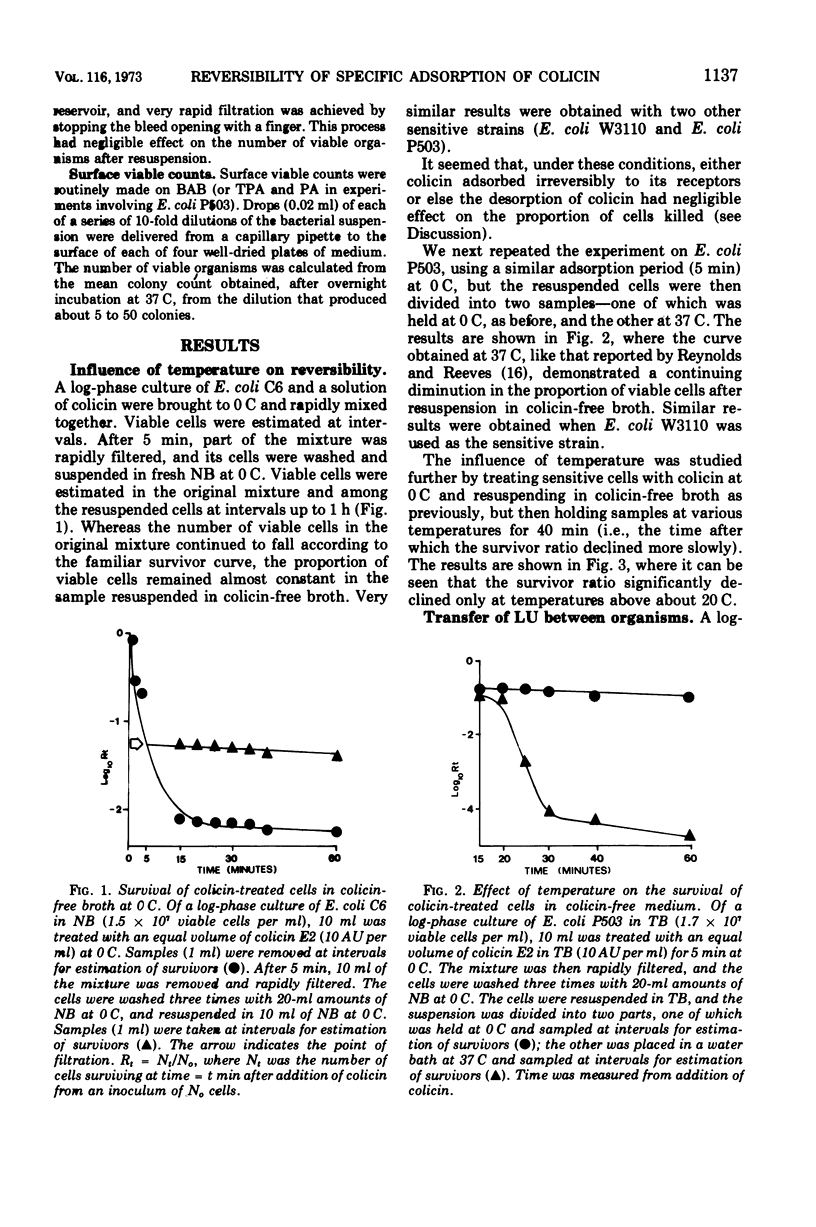
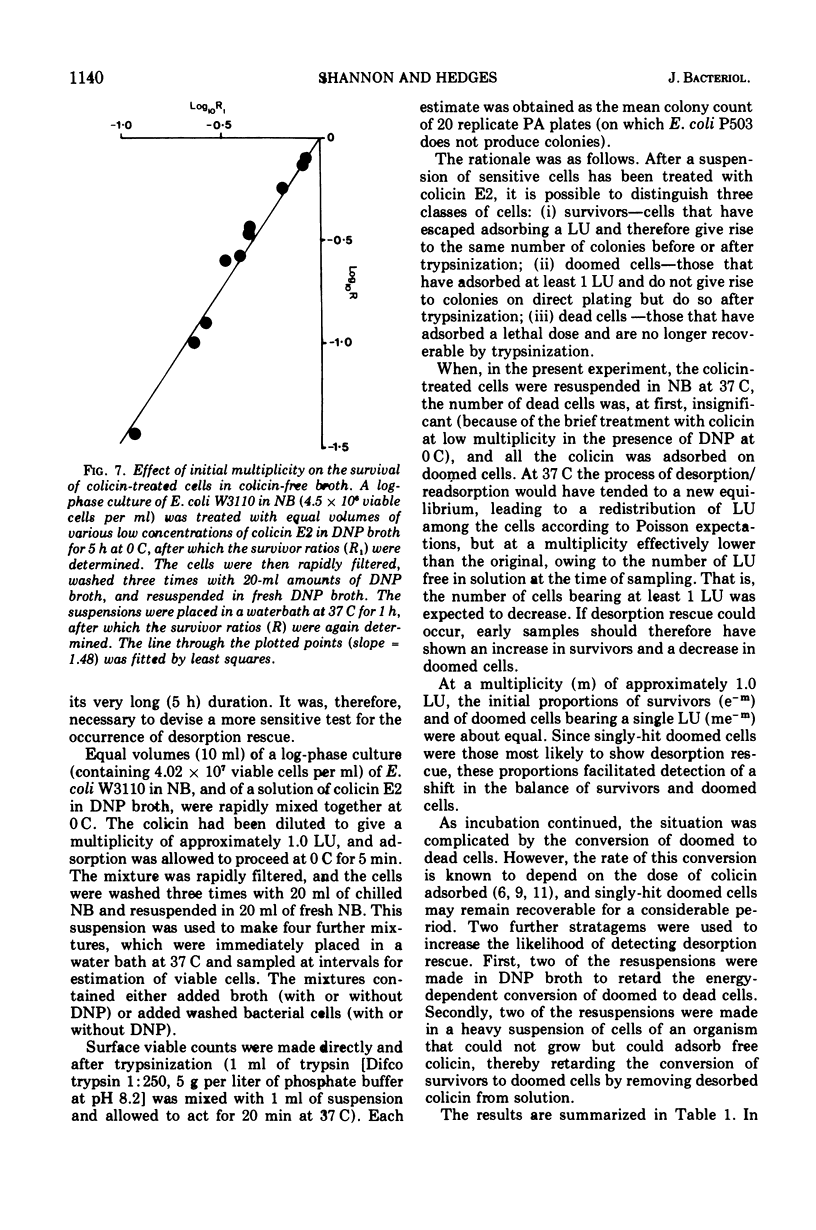
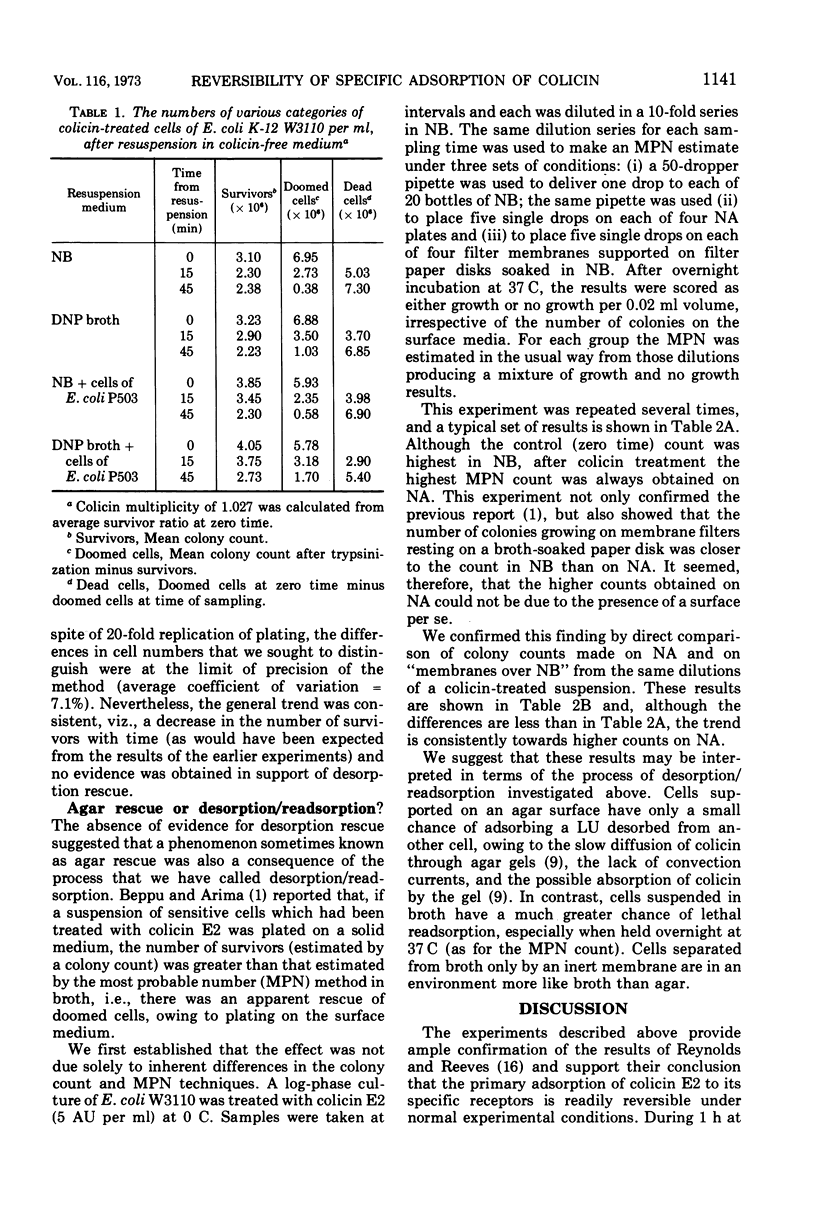
The adsorption of colicin E2-P9 to its specific receptors on cells of sensitive strains of Escherichia coli is reversible under normal experimental conditions. At temperatures above 20 C, colicin may desorb from one cell and be readsorbed by a second with potentially lethal consequences. However, desorption of colicin seems unable to rescue a cell once it has received a lethal dose. These findings have implications both for the nature and types of specific receptors, and for the assay of colicin by the survivor count (lethal unit) methods.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beppu R., Arima K. Protection of Escherichia coli from the lethal effect of colicins by high osmotic pressure. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):80–85. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.80-85.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya P., Wendt L., Whitney E., Silver S. Colicin-tolerant mutants of Escherichia coli: resistance of membranes to colicin E1. Science. 1970 May 22;168(3934):998–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3934.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Barbu E. Evaluation du nombre de récepteurs bactériens pour les colicines A, E1, E2 et K. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1970 Oct;119(4):420–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOEBEL W. F., BARRY G. T., SHEDLOVSKY T. Colicine K. I. The production of colicine K in media maintained at constant pH. J Exp Med. 1956 May 1;103(5):577–588. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.5.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges A. J. An examination of single-hit and multi-hit hypotheses in relation to the possible kinetics of colicin adsorption. J Theor Biol. 1966 Aug;11(3):383–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland E. M., Holland I. B. Induction of DNA breakdown and inhibition of cell division by colicin E2. Nature of some early steps in the process and properties of the E-2-specific nuclease system. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):223–239. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYR-HARTING A. THE ADSORPTION OF COLICINE. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:255–266. doi: 10.1002/path.1700870206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda A., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. I. Studies with radioactive colicins. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):685–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.685-694.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui E., Mizuno D. Stabilization of colicin E2 by bovine serum albumin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1136–1137. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1136-1137.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF COLICINES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVES P. THE ADSORPTION AND KINETICS OF KILLING BY COLICIN CA42-E2. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1965 Apr;43:191–200. doi: 10.1038/icb.1965.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVES P. THE BACTERIOCINS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:24–45. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.24-45.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS B. L., REEVES P. R. Some observations on the mode of action of colicin F. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Apr 23;11:140–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds B. L., Reeves P. R. Kinetics of adsorption of colicin CA42-E2 and reversal of its bactericidal activity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):301–309. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.301-309.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabet S. F., Schnaitman C. A. Localization and solubilization of colicin receptors. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):422–430. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.422-430.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon R., Hedges A. J. Kinetics of lethal adsorption of colicin E-2 by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1353–1359. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1353-1359.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smarda J., Lanek B. Possibility of use of colicin-refractory mutants in the study of localization of colicin receptors. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1971;16(6):481–484. doi: 10.1007/BF02872724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smarda J. Some problems of the immediate action of colicines on susceptible bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltzien H. U., Jesaitis M. A. The nature of the cilicin K receptor of Escherichia coli Cullen. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):534–553. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


