Abstract
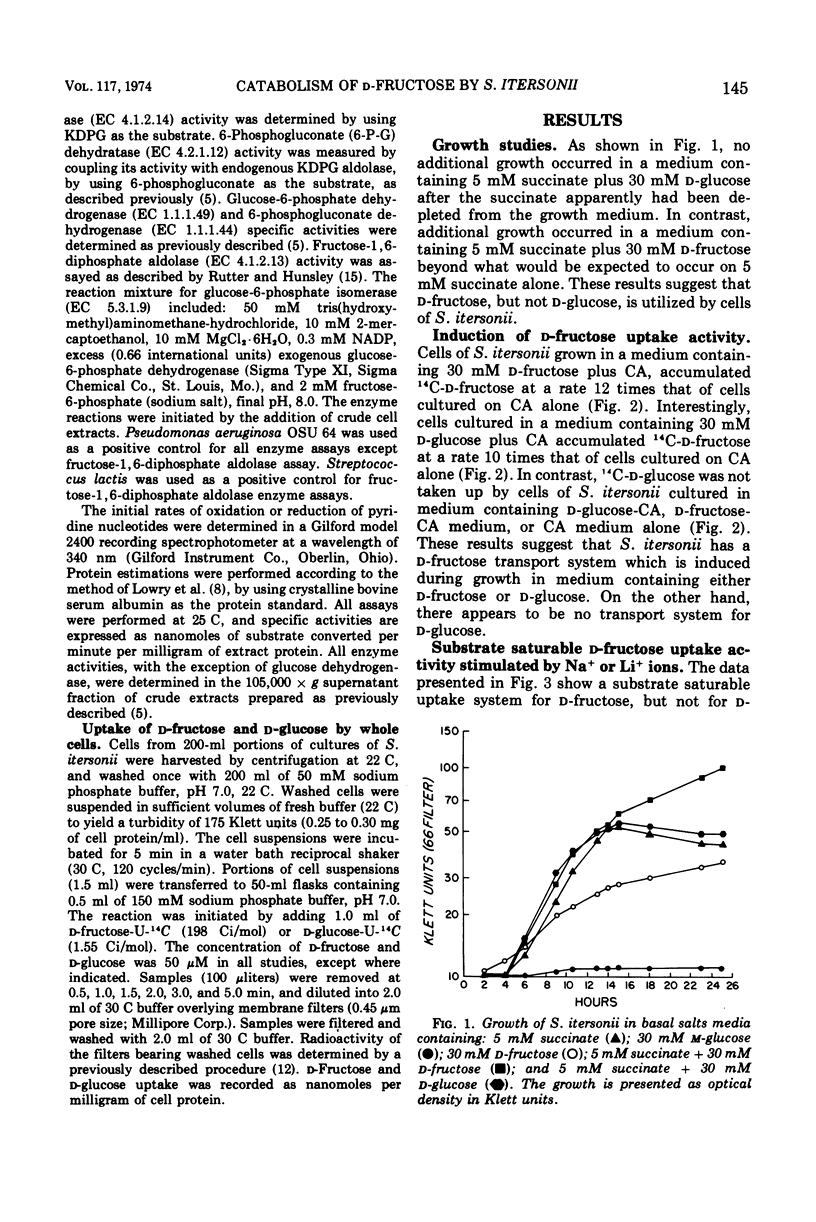
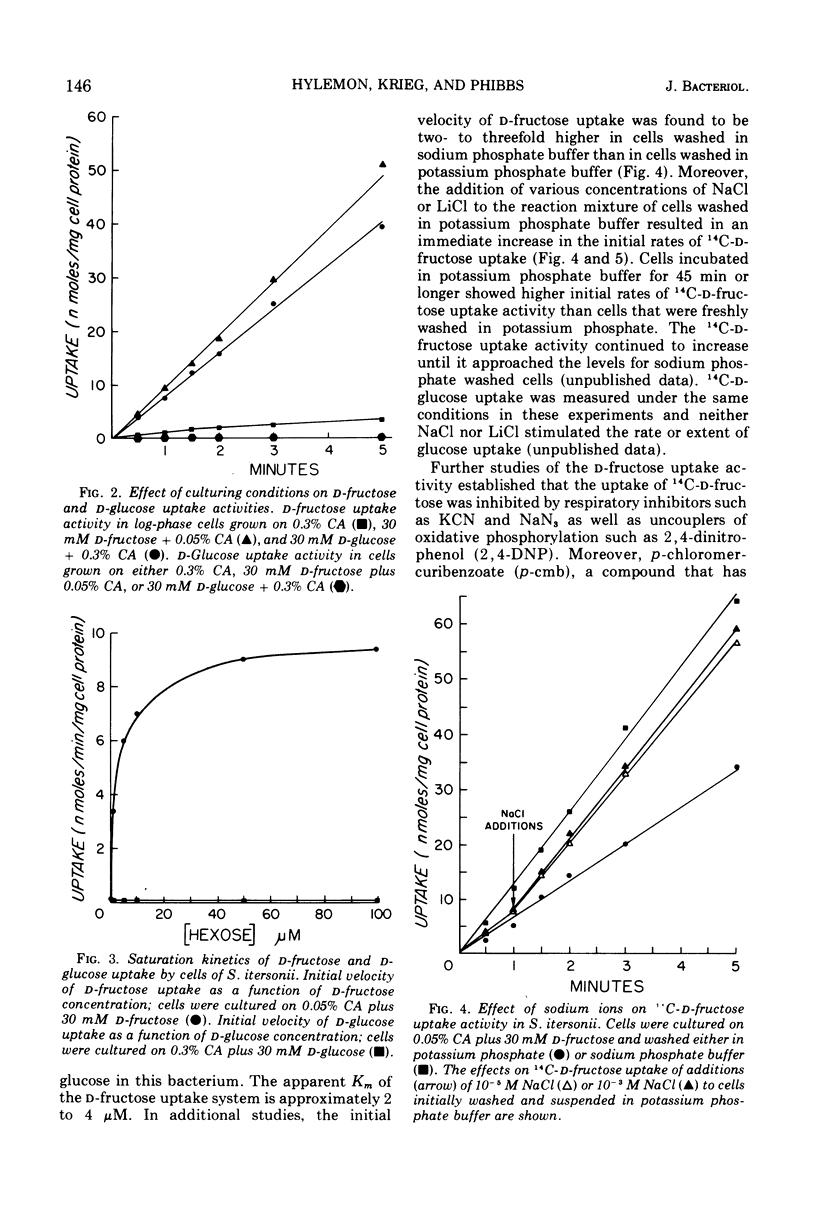
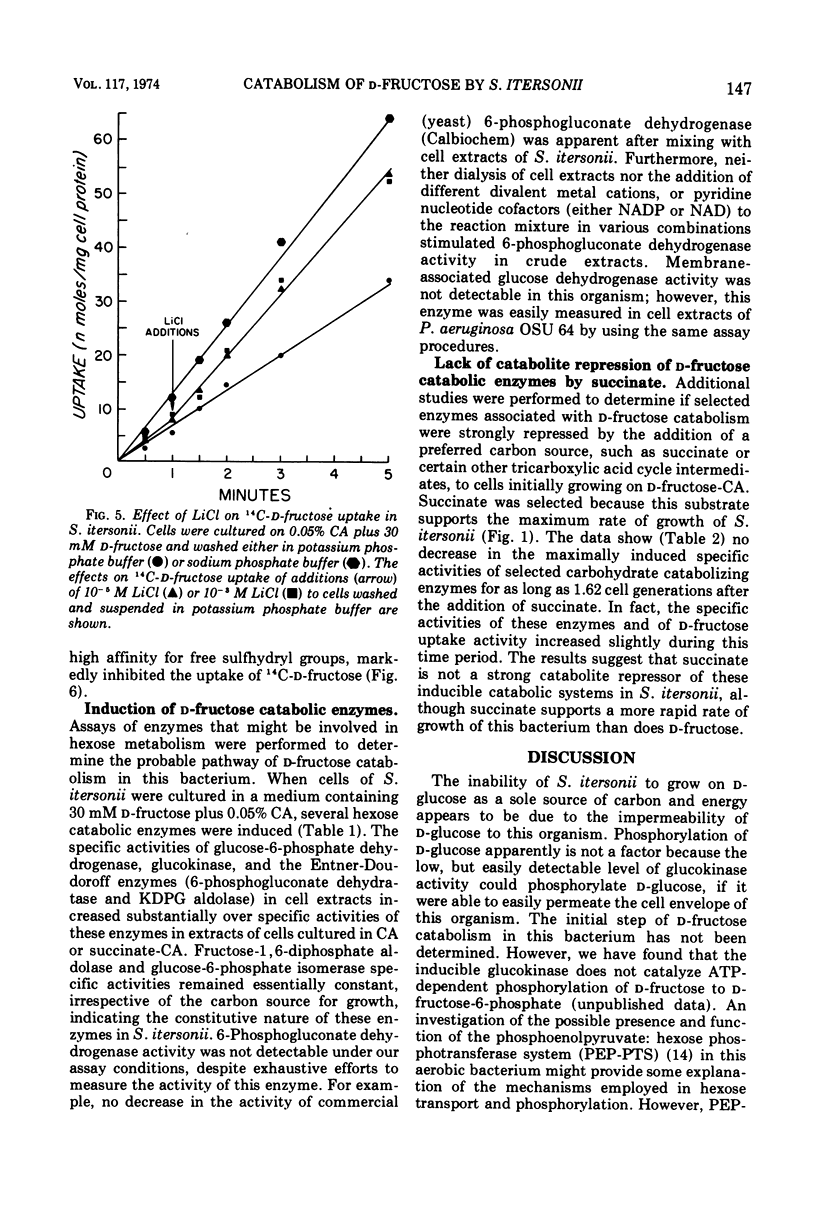
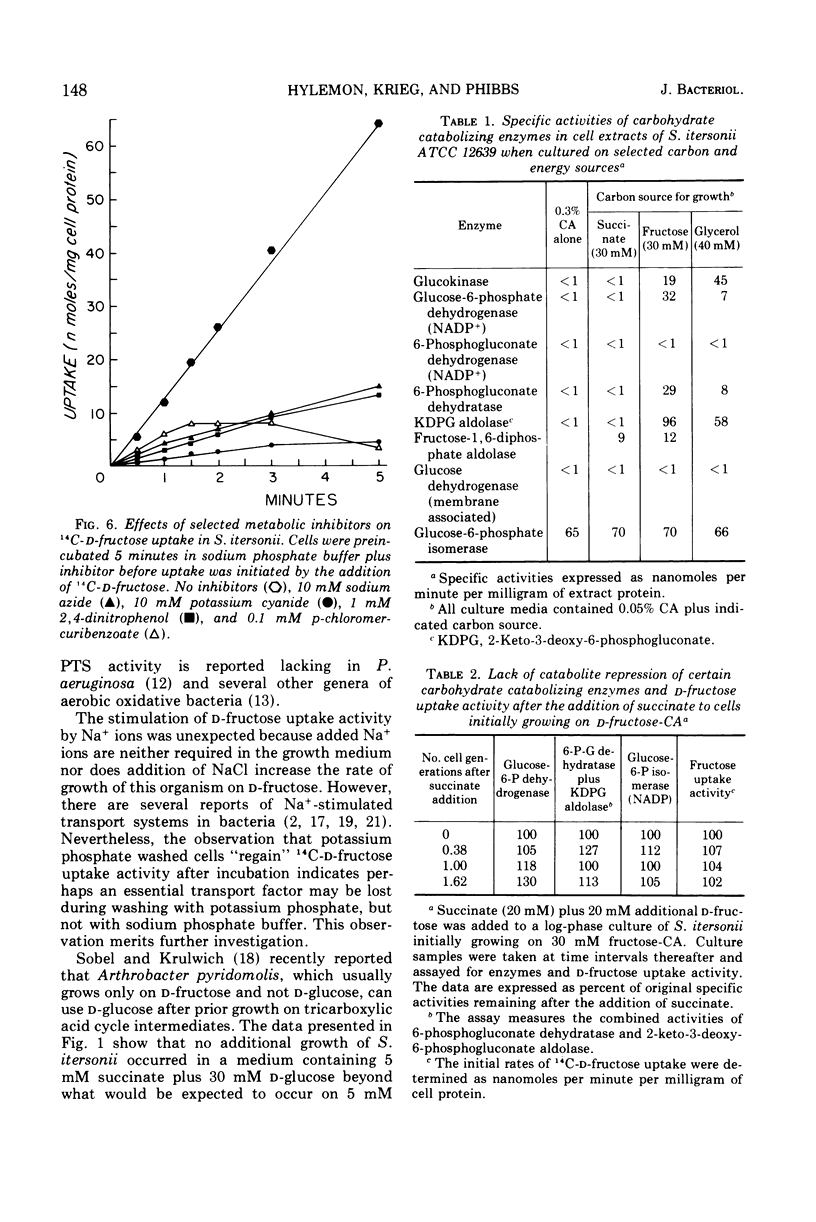
Spirillum itersonii ATCC 12639 utilized d-fructose but neither d-glucose nor d-gluconate as a sole source of carbon and energy. The substrate saturation kinetics for d-fructose and d-glucose uptake by whole cells indicated the presence of a carrier-mediated transport system for d-fructose but not for d-glucose. The d-fructose uptake activity was induced (10- to 12-fold increase) during growth on d-fructose-Casamino Acids (CA) or d-glucose-CA medium, but not CA alone. d-Fructose uptake activity was stimulated by Na+ or Li+, but was inhibited by KCN, NaN3, 2,4-dinitrophenol, and p-chloromercuribenzoate. High specific activities of glucokinase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase, and 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase were detected in extracts of cells cultured on d-fructose-CA medium. These enzymatic activities were undetectable in extracts of cells grown in CA or succinate-CA medium. No decrease in the maximally induced specific activities of these enzymes occurred after the addition of succinate to cells during exponential growth on d-fructose-CA. Fructose 1,6-diphosphate aldolase and glucose-6-phosphate isomerase specific activities were approximately the same irrespective of cultural conditions. These results indicated that d-glucose was not utilized by cells of S. itersonii because this bacterium was impermeable to this hexose.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Frank L., Hopkins I. Sodium-stimulated transport of glutamate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):329–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.329-336.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK G., EBERHARDT U., SCHLEGEL H. G. VERWERTUNG VON FRUCTOSE DURCH HYDROGENOMONAS H 16. (I.) Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Apr 2;48:95–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK G. VERWERTUNG VON FRUCTOSE DURCH HYDROGENOMONAS H 16. II. CRYPTISCHES VERHALTEN GEGENUEBER GLUCOSE. Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Jul 15;49:96–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Independent regulation of hexose catabolizing enzymes and glucose transport activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1041–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90813-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König C., Sammler I., Wilde E., Schlegel H. G. Konstitutive Glucose-6-phosphat-Dehydrogenase bei Glucose verwertenden Mutanten von einem kryptischen Wildstamm. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;67(1):51–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElroy L. J., Wells J. S., Jr, Krieg N. R. Mode of extension of cell surface during growth of Spirillum volutans. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):499–501. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.499-501.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng F. M., Dawes E. A. Chemostat studies on the regulation of glucose metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by citrate. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):129–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1320129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Eagon R. G. Transport and phosphorylation of glucose, fructose, and mannitol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jun;138(2):470–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Roseman S. A sodium-dependent sugar co-transport system in bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):132–138. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80168-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Functions of Na+ and K+ in the active transport of -aminoisobutyric acid in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):4066–4074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVII. Ion-dependent retention of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid and its relation to Na+ dependent transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1016–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


