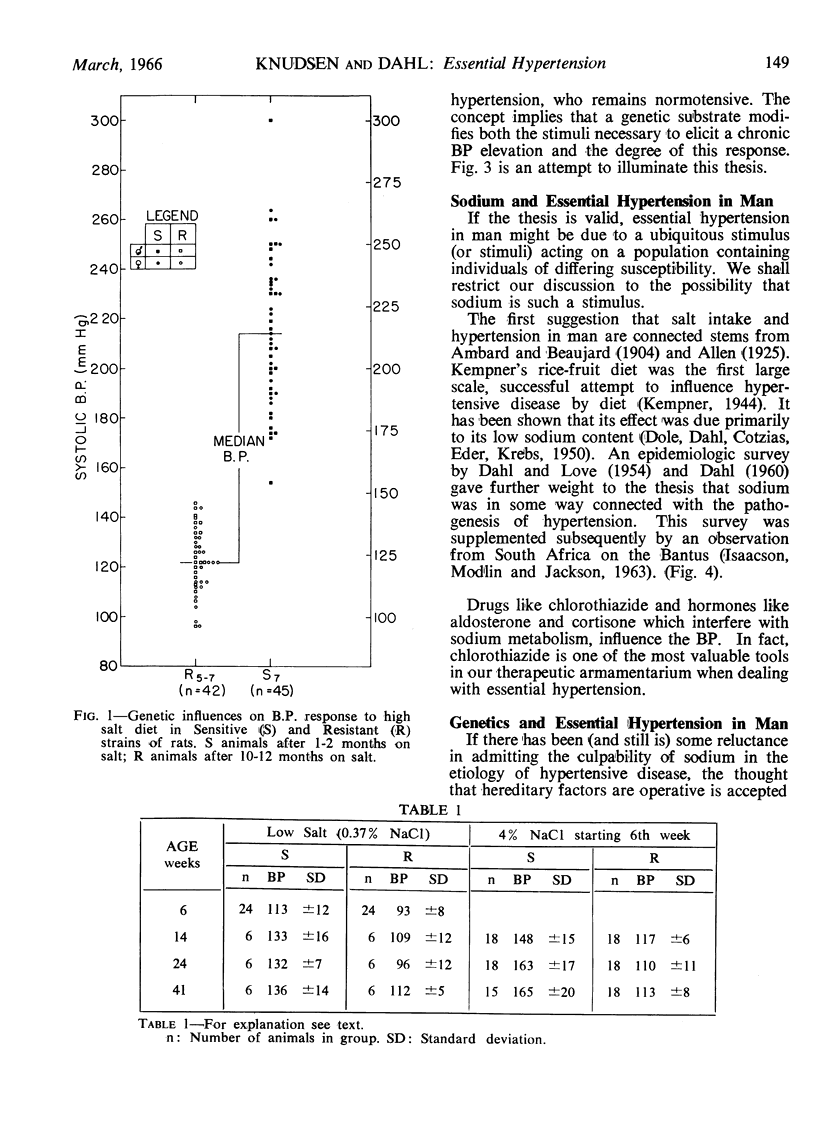
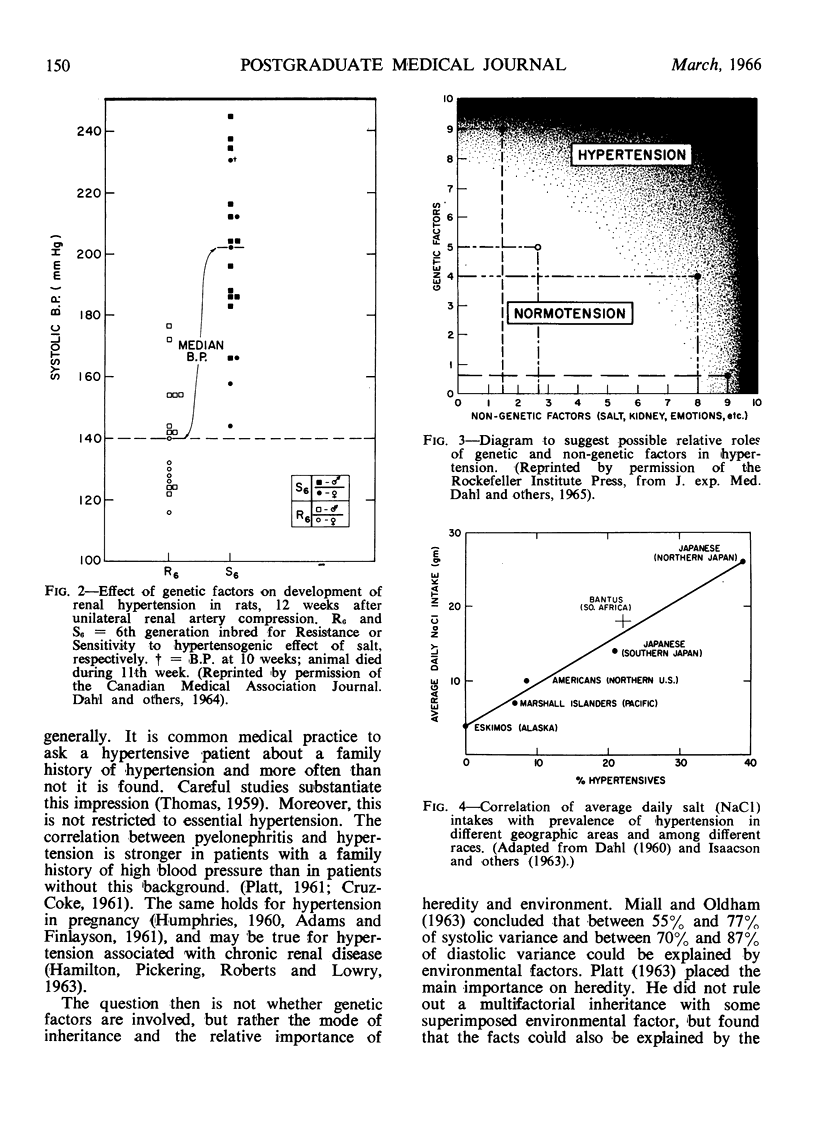
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS E. M., FINLAYSON A. Familial aspects of pre-eclampsia and hypertension in pregnancy. Lancet. 1961 Dec 23;2(7217):1375–1378. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)91197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHL L. K., HEINE M., TASSINARI L. EFFECTS OF CHRONIC EXCESS SALT INGESTION. ROLE OF GENETIC FACTORS IN BOTH DOCA-SALT AND RENAL HYPERTENSION. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:605–617. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHL L. K., HEINE M., TASSINARI L. Effects of chronia excess salt ingestion. Evidence that genetic factors play an important role in susceptibility to experimental hypertension. J Exp Med. 1962 Jun 1;115:1173–1190. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.6.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHL L. K., LOVE R. A. Evidence for relationship between sodium (chloride) intake and human essential hypertension. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1954 Oct;94(4):525–531. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1954.00250040017003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P., DAHL L. K., COTZIAS G. C., EDER H. A., KREBS M. E. Dietary treatment of hypertension; clinical and metabolic studies of patients on the rice-fruit diet. J Clin Invest. 1950 Sep;29(9):1189–1206. doi: 10.1172/JCI102357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl L. K., Heine M., Tassinari L. Effects of chronic excess salt ingestion. Further demonstration that genetic factors influence the development of hypertension: evidence from experimental hypertension due to cortisone and to adrenal regeneration. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):533–545. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL C. E., HALL O. SALT HYPERTENSION: FACILITATED INDUCTION IN TWO RAT STRAINS. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1964;22:529–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACSON L. C., MODLIN M., JACKSON W. P. Sodium intake and hypertension. Lancet. 1963 Apr 27;1(7287):946–946. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91717-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDINGHAM J. M. Hypertension and disturbances of tissue water, sodium and potassium distribution associated with steroid administration in adrenalectomised rats. Clin Sci. 1954 Nov;13(4):543–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENEELY G. R., DAHL L. K. Electrolytes in hypertension: the effects of sodium chloride. The evidence from animal and human studies. Med Clin North Am. 1961 Mar;45:271–283. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)33891-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLATT R. Heredity in hypertension. Lancet. 1963 Apr 27;1(7287):899–904. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91686-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIAN L. Interrelationship of electrolytes, juxtaglomerular cells and hypertension. Physiol Rev. 1960 Apr;40:280–312. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIAN L., JANECEK J., TOMBOULIAN A., FERREIRA D. Sodium and potassium in the walls of arterioles in experimental renal hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1961 Oct;40:1922–1925. doi: 10.1172/JCI104417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf G., Dahl L. K., Miller N. E. Voluntary sodium chloride intake of two strains of rats with opposite genetic susceptibility to experimental hypertension. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Nov;120(2):301–305. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


