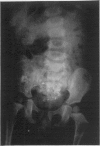
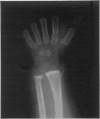
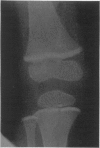
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMMANITI L., LONGOBARDI G. [Chronic lead poisoning caused by lead nipple protectors in a 5-month-old infant]. Arch Ital Pediatr Pueric. 1962 Nov;22:241–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAETJER A. M., JOARDAR S. N., McQUARY W. A. Effect of environmental temperature and humidity on lead poisoning in animals. Arch Environ Health. 1960 Dec;1:463–477. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1960.10662721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSON P. F., CHISOLM J. J., Jr A reliable qualitative urine coproporphyrin test for lead intoxication in young children. J Pediatr. 1960 Jun;56:759–767. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(60)80312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSON P. F. Influence of climatic factors on blood lead levels in children with pica. Guys Hosp Rep. 1962;111:306–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIEHUSEN F. C., PULASKI E. J. Lead poisoning after ingestion of a foreign body retained in the stomach. N Engl J Med. 1956 Jun 21;254(25):1179–1181. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195606212542507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY J. E., BAUMGARTNER R. J. Subsequent mental development of children with lead encephalopathy, as related to type of treatment. J Pediatr. 1958 Sep;53(3):311–315. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(58)80217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS R. K. Lead poisoning; review of the literature and report on 45 cases. Pediatrics. 1959 Mar;23(3):585–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS R. K., MALOOF C. Edathamil calcium-disodium (versenate) in treatment of lead poisoning in children. AMA Am J Dis Child. 1954 May;87(5):559–569. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1954.02050090547004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barltrop D., Killala N. J. Faecal excretion of lead by children. Lancet. 1967 Nov 11;2(7524):1017–1019. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90289-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barltrop D. The prevalence of pica. Am J Dis Child. 1966 Aug;112(2):116–123. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1966.02090110060004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVAGNA G., BEARD R. R. Potassium loss from lead-poisoned erythrocytes. Failure to demonstrate correlation with age of cells. Med Lav. 1962 Dec;53:779–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHISOLM J. J., Jr, HARRISON H. E. The exposure of children to lead. Pediatrics. 1956 Dec;18(6):943–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHISOLM J. J., Jr, HARRISON H. E. The treatment of acute lead encephalopathy in children. Pediatrics. 1957 Jan;19(1):2–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford M. D., Morris J. N. Lead in drinking water. Lancet. 1967 Nov 18;2(7525):1087–1088. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90364-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOREMAN H. Use of chelating agents in treatment of metal poisoning (with special emphasis on lead). Fed Proc. 1961 Sep;20(3):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD J., ROWLEY W., ELAM H., PERLSTEIN M. Lead encephalopathy in children. Intravenous use of urea in its management. N Engl J Med. 1961 May 18;264:1027–1030. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196105182642004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTELIUS M. F., MILLICAN F. K., LAYMAN E. M., COHEN G. J., DUBLIN C. C. Nutritional studies of children with pica. I Controlled study evaluating nutritional status. Pediatrics. 1962 Jun;29:1012–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDERSON D. A. A follow-up of cases of plumbism in children. Australas Ann Med. 1954 Aug;3(3):219–224. doi: 10.1111/imj.1954.3.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEHOE R. A. The Harben Lectures, 1960: The metabolism of lead in man in health and disease. 3. Present hygienic problems relating to the absorption of lead. J R Inst Public Health. 1961 Aug;24:177–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANZKOWSKY P. Investigation into the aetiology and treatment of pica. Arch Dis Child. 1959 Apr;34(174):140–148. doi: 10.1136/adc.34.174.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANHOOD J., ROMAN C., BERTIN V., LATORRE M., DOBERTI A. [Study of lead poisoning in children of the town of San Enrique de las Condes]. Rev Chil Pediatr. 1960 Jun;31:286–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELLINS R. B., JENKINS C. D. Epidemiological and psychological study of lead poisoning in children. J Am Med Assoc. 1955 May 7;158(1):15–20. doi: 10.1001/jama.1955.02960010017004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONCRIEFF A. A., KOUMIDES O. P., CLAYTON B. E., PATRICK A. D., RENWICK A. G., ROBERTS G. E. LEAD POISONING IN CHILDREN. Arch Dis Child. 1964 Feb;39:1–13. doi: 10.1136/adc.39.203.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OHLSSON W. T. Penicillamine as lead-chelating substance in man. Br Med J. 1962 May 26;1(5290):1454–1456. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5290.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIMENTA de MELLO R. Effect of light on urinary coproporphyrin excretion in lead-poisoned rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Apr;76(4):823–825. doi: 10.3181/00379727-76-18642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAVERS E., RENDLE-SHORT J., HARVEY C. C. The Rotherham lead-poisoning outbreak. Lancet. 1956 Jul 21;271(6934):113–116. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90863-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITAKER J. A., AUSTIN W., NELSON J. D. Edathamil calcium disodium(Versenate) diagnostic test for lead poisoning. Pediatrics. 1962 Mar;29:384–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITAKER J. A., VIETTI T. J. Fluorescence of the erythrocytes in lead poisoning in children: an aid to rapid diagnosis. Pediatrics. 1959 Nov;24:734–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]