Abstract
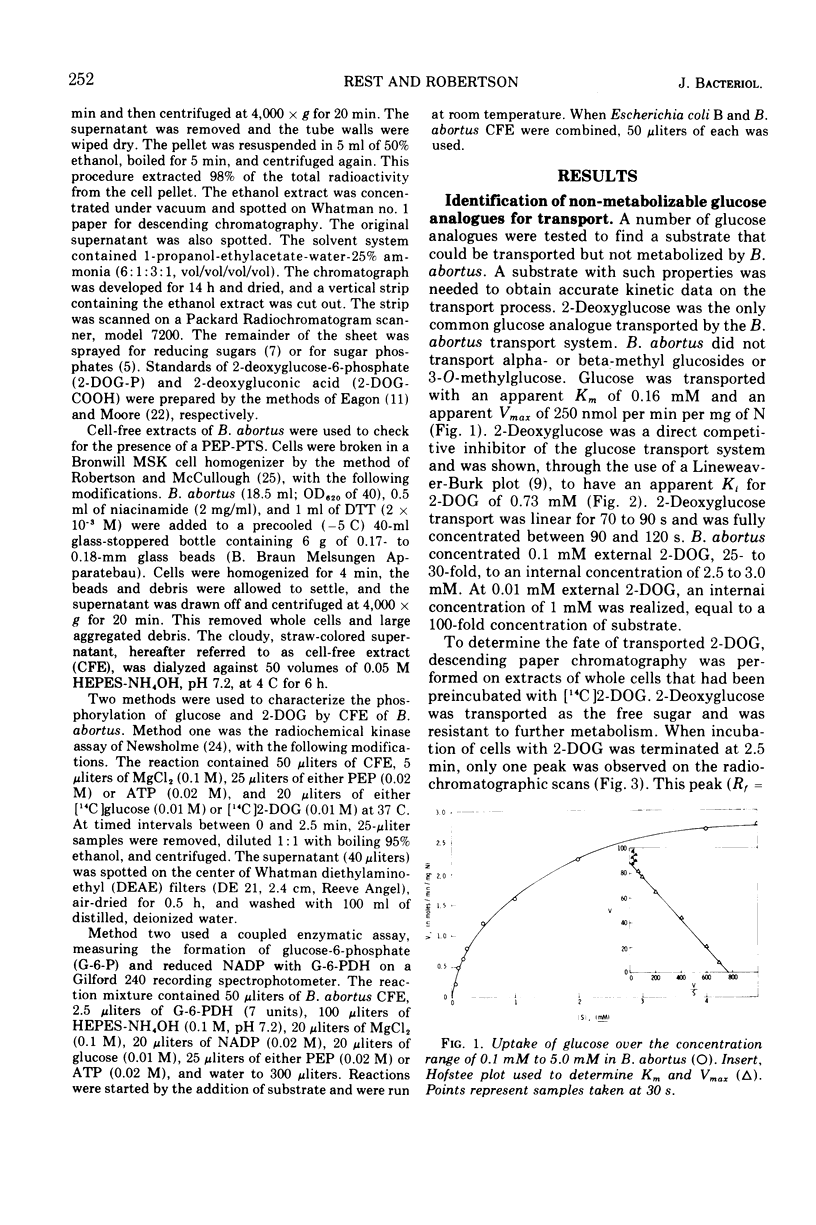
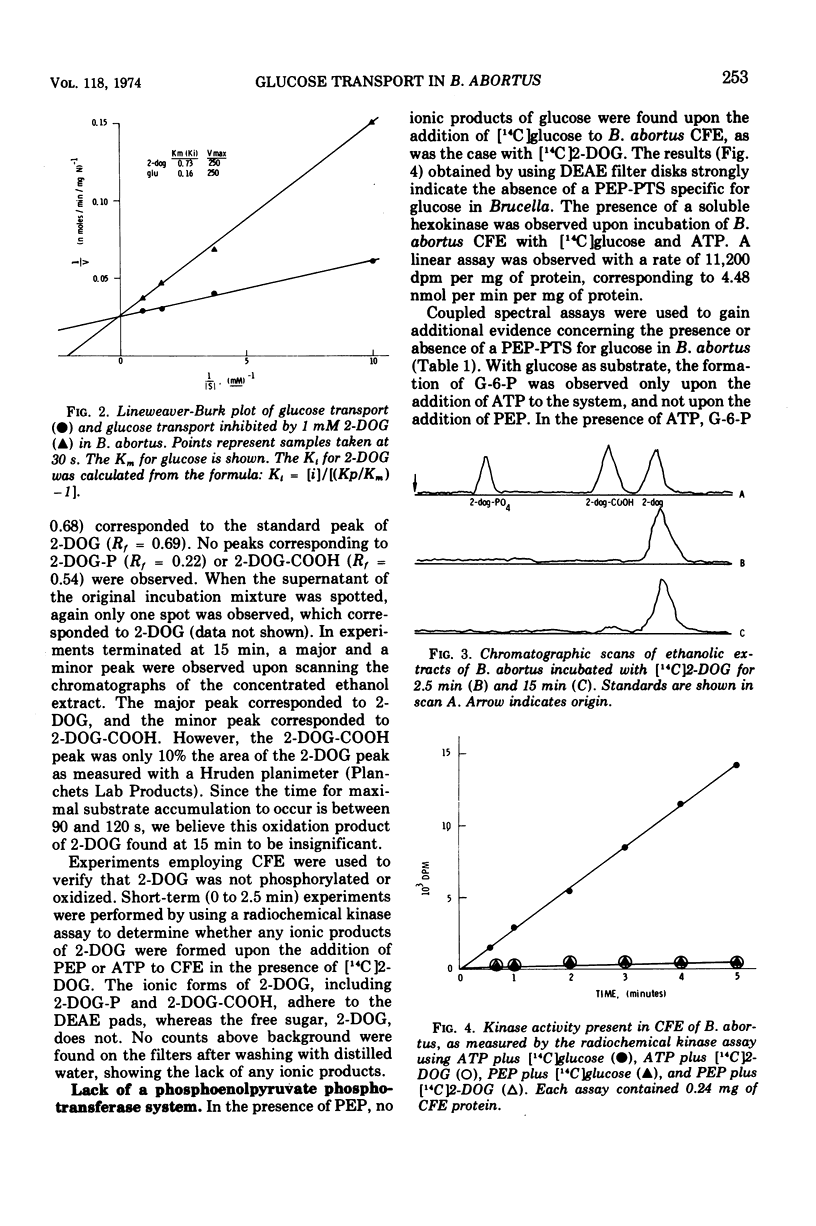
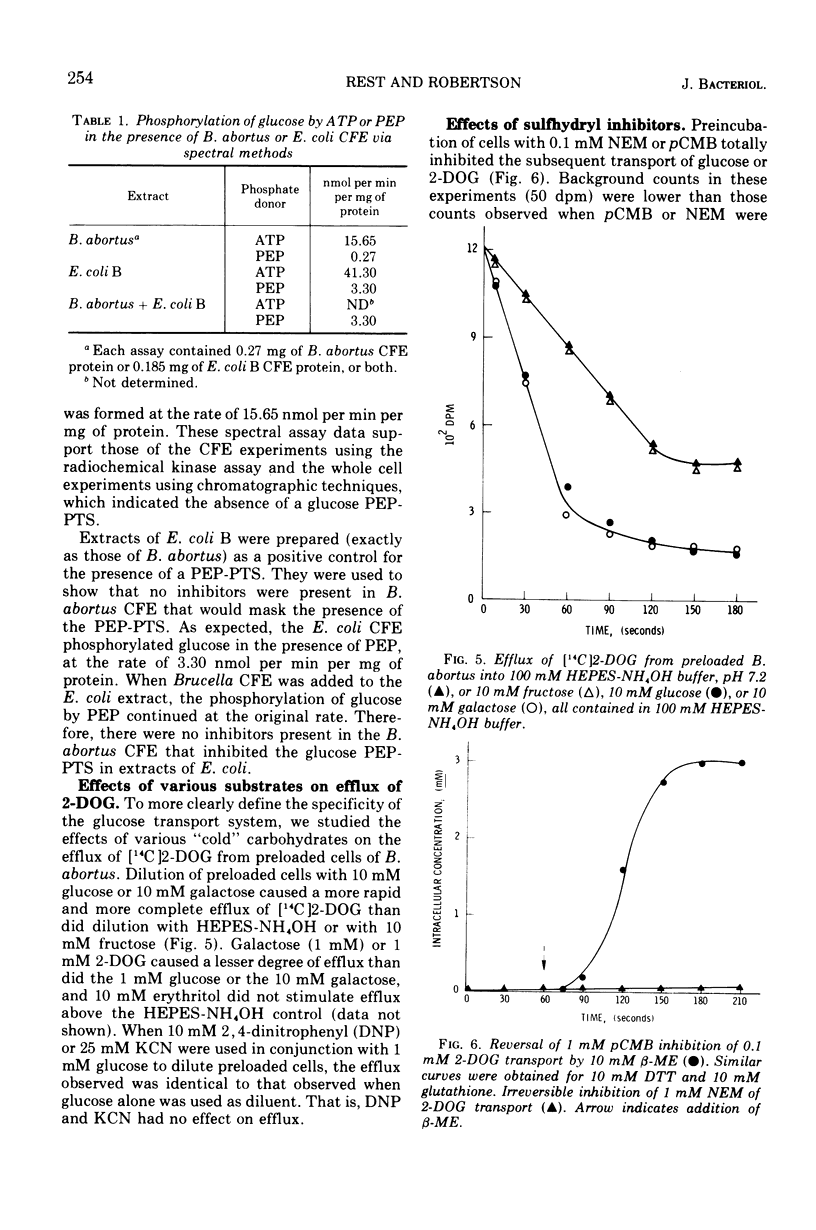
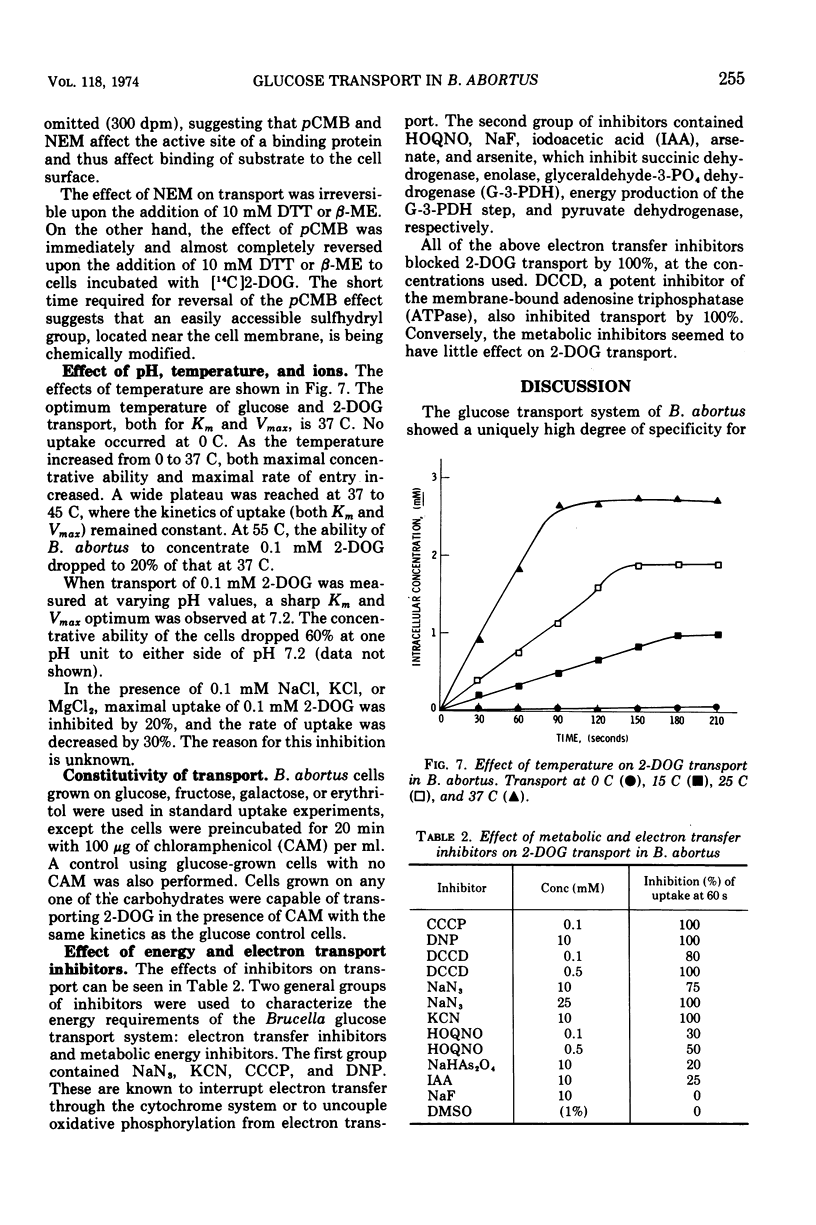
Brucella abortus British strain 19 transported glucose with an apparent Km of 0.16 mM and an apparent Vmax of 250 nmol per min per mg of N. The only common glucose analogue transported was 2-deoxyglucose (2-DOG), with an apparent Ki of 0.73 mM. Alpha- or beta-methyl glucosides and 3-O-methylglucose were not transported. Transport was linear for 70 to 90 s, depending on the concentration of substrate used. 2-Deoxyglucose was transported as the free sugar and was not further metabolized once inside the cell. There was no glucose phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase system (PEP-PTS) present, and there were no inhibitors present in Brucella cell-free extract that inhibited the Escherichia coli glucose PEP-PTS. N-Ethylmaleimide (NEM) and p-chloromercuribenzoate (pCMB) completely inhibited transport of glucose and 2-DOG. Glutathione, dithiothreitol, and β-mercaptoethanol reversed the effects of pCMB but not of NEM. A pH optimum of 7.2 and a temperature optimum of 37 to 45 C were observed for both Km and Vmax. The glucose transport system appeared to be constitutive for glucose transport in cells grown on fructose, galactose, erythritol, or glucose. The electron transfer inhibitors carbonyl cyanide, m-chlorophenylhydrazone, NaN3, 2,4-dinitrophenol, and KCN inhibited 2-DOG transport to a greater extent than did the metabolic energy inhibitors NaAsO4, iodoacetate, KF, and 2-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline-N-oxide. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, an inhibitor of membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatases, inhibited transport by 100%.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anraku Y. Transport of sugars and amino acids in bacteria. I. Purification and specificity of the galactose- and leucine-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3116–3122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano A., Cohen N. S., Baker R. F., Brodie A. F. Orientation of the cell membrane in ghosts and electron transport particles of Mycobacterium phlei. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3386–3397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asghar S. S., Levin E., Harold F. M. Accumulation of neutral amino acids by Streptococcus faecalis. Energy coupling by a proton-motive force. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5225–5233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANDURSKI R. S., AXELROD B. The chromatographic identification of some biologically important phosphate esters. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):405–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. I. The site of energy coupling between D-lactic dehydrogenase and beta-galactoside transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5518–5522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagon R. G. 2-Deoxyglucose transportation via passive diffusion and its oxidation, not phosphorylation, to 2-deoxygluconic acid by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Biochem. 1971 May;49(5):606–613. doi: 10.1139/o71-087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Papineau D. Cation transport and electrogenesis by Streptococcus faecalis. I. The membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1972;8(1):27–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01868093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Altendorf K., Harold F. M. Role of an electrical potential in the coupling of metabolic energy to active transport by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Independent regulation of hexose catabolizing enzymes and glucose transport activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1041–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90813-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. The role of the phosphoenolpyruvate-phosphotransferase system in the transport of sugars by isolated membrane preparations of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3711–3724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. L., Boyer P. D. Energization of active transport by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7257–7265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F. J., Reeves J. P., Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. 8. Valinomycin-induced rubidium transport. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3551–3565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley M., Dawes E. A. The regulation of transport of glucose and methyl alpha-glucoside in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):141–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1320141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukkada A. J., Long G. L., Romano A. H. The uptake of 2-deoxy-D-glucose by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its regulation. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):155–162. doi: 10.1042/bj1320155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Robinson J., Taylor K. A radiochemical enzymatic activity assay for glycerol kinase and hexokinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Mar 15;132(2):338–346. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. Purification and properties of a sulfate-binding protein from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5886–5892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Eagon R. G. Transport and phosphorylation of glucose, fructose, and mannitol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jun;138(2):470–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Amino-acid-binding protein released from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5732–5734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. C., McCullough W. G. The glucose catabolism of the genus Brucella. I. Evaluation of pathways. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. C., McCullough W. G. The glucose catabolism of the genus Brucella. II. Cell-free studies with B. abortus (S-19). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. Restoration of active transport in an Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1124–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1124-1129.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. P., Wiley W. R. Regulation of sugar transport in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):487–492. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.487-492.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsay S. S., Brown K. K., Gaudy E. T. Transport of glycerol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.82-88.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabu K. Amino acid transport in Mycobacterium smegmatis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):6–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.6-13.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


