Abstract
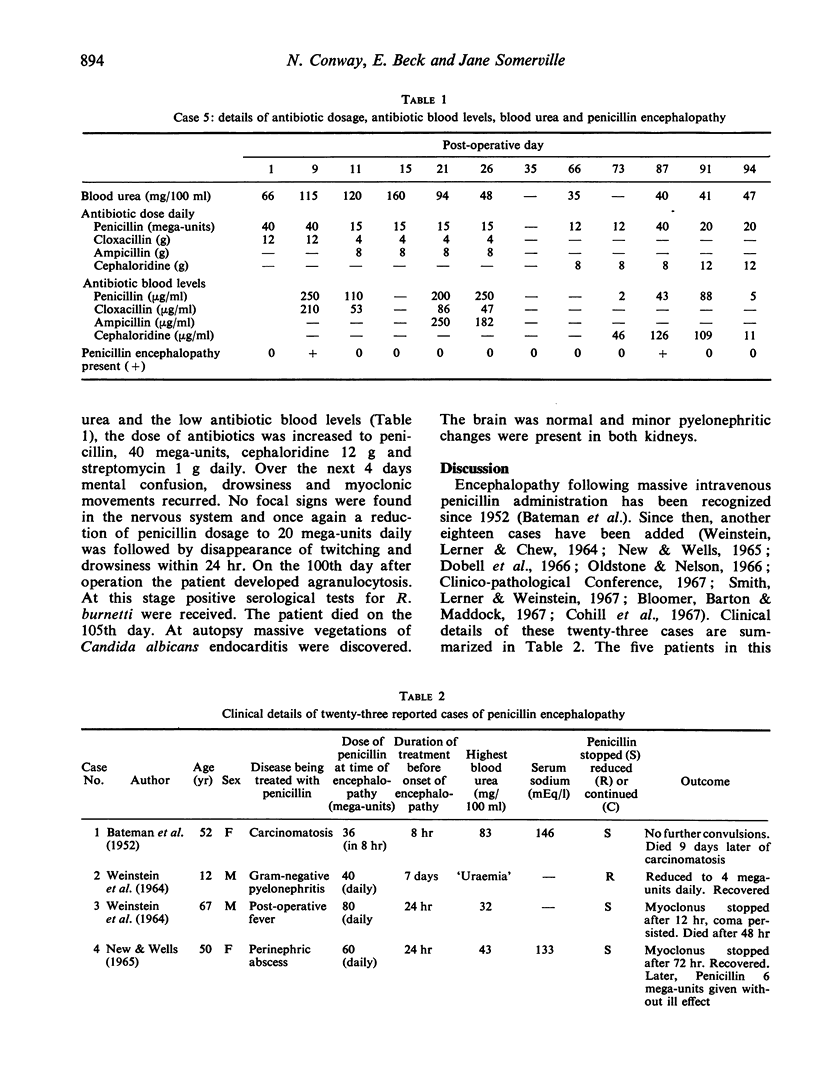
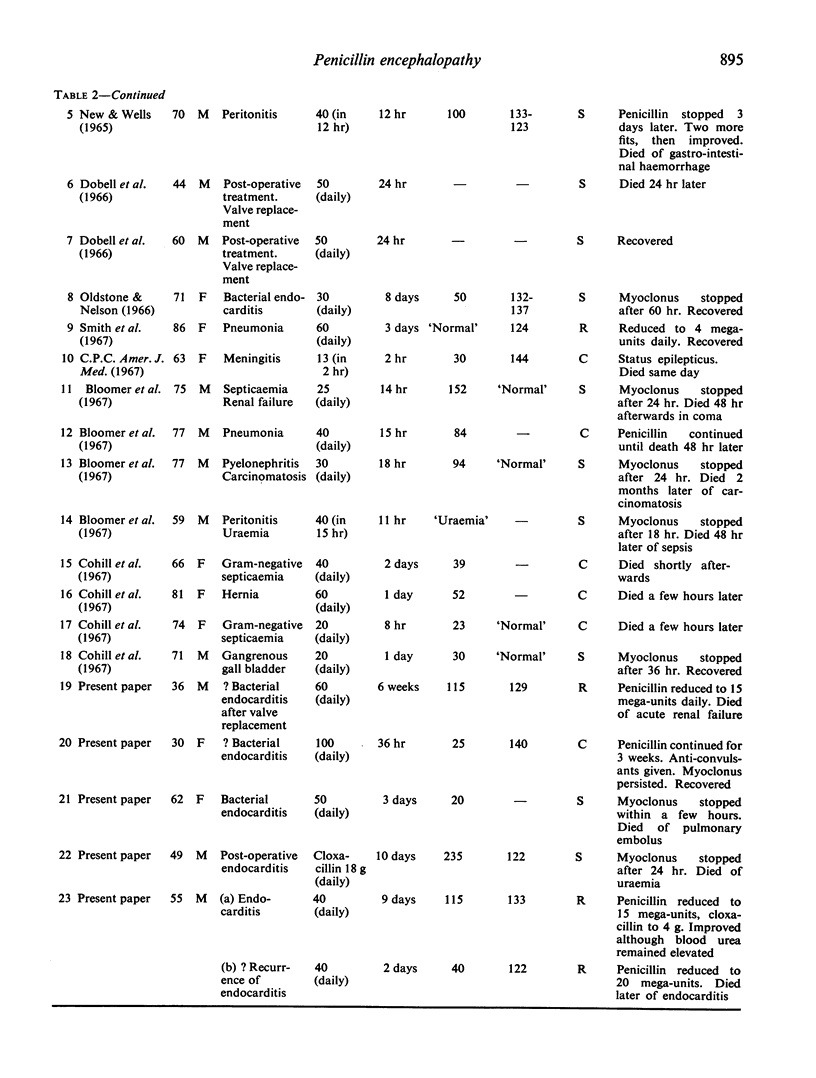
Five patients who developed characteristic myoclonic twitching, drowsiness and convulsions due to intravenous penicillin and cloxacillin are described. Three had poor renal function. Twenty-three reported cases of penicillin encephalopathy are reviewed and the aetiology of the syndrome is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATEMAN J. C., BARBERIO J. R., GRICE P., KLOPP C. T., PIERPONT H. Fatal complications of intensive antibiotic therapy in patients with neoplastic disease. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1952 Dec;90(6):763–773. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1952.00240120038004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANNON A. B., SLATKIN M. H., CHESTER B., MOSES R. Penicillin levels in the blood; significance of type of preparation, dosage, kidney function and weight. J Am Med Assoc. 1951 Apr 7;145(14):1031–1034. doi: 10.1001/jama.1951.02920320005002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohill D. F., Pezzi P. J., Greenberg S. R., Frobese A. S. Central nervous system toxicity secondary to massive doses of penicillin 'G' in the treatment of overwhelming infections. Am J Med Sci. 1967 Nov;254(5):692–694. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196711000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. F., SHOCK N. W. Age changes in glomerular filtration rate, effective renal plasma flow, and tubular excretory capacity in adult males. J Clin Invest. 1950 May;29(5):496–507. doi: 10.1172/JCI102286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOBBING J. The blood-brain barrier. Physiol Rev. 1961 Jan;41:130–188. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1961.41.1.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobell A. R., Wyant J. D., Seamans K. B., Gloor P. Penicillin epilepsy. Studies on the blood-brain barrier during cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1966 Oct;52(4):469–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN R. B., SHEFF M. F., MAHER J. F., SCHREINER G. E. The blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier in uremia. Ann Intern Med. 1962 Feb;56:233–240. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-56-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman R. A. Active transport and the blood-brain barrier to penicillin and related orgnic acids. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1964;89:51–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New P. S., Wells C. E. Cerebral toxicity associated with massive intravenous penicillin therapy. Neurology. 1965 Nov;15(11):1053–1058. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.11.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Nelson E. Central nervous system manifestations of penicillin toxicity in man. Neurology. 1966 Jul;16(7):693–700. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.7.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H., Lerner P. I., Weinstein L. Neurotoxicity and "massive" intravenous therapy with penicillin. A study of possible predisposing factors. Arch Intern Med. 1967 Jul;120(1):47–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINSTEIN L., LERNER P. I., CHEW W. H. CLINICAL AND BACTERIOLOGIC STUDIES OF THE EFFECT OF "MASSIVE" DOSES OF PENICILLIN G ON INFECTIONS CAUSED BY GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI. N Engl J Med. 1964 Sep 10;271:525–533. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196409102711101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


