Abstract
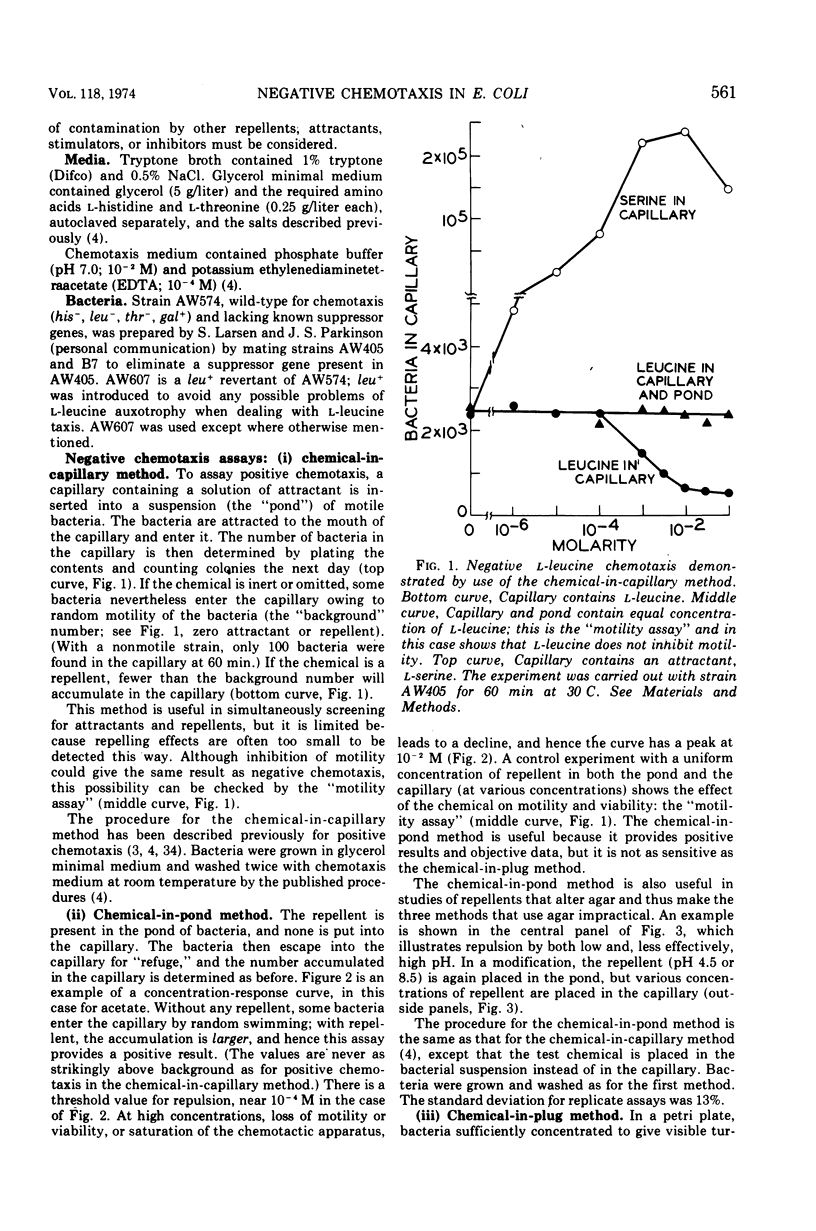
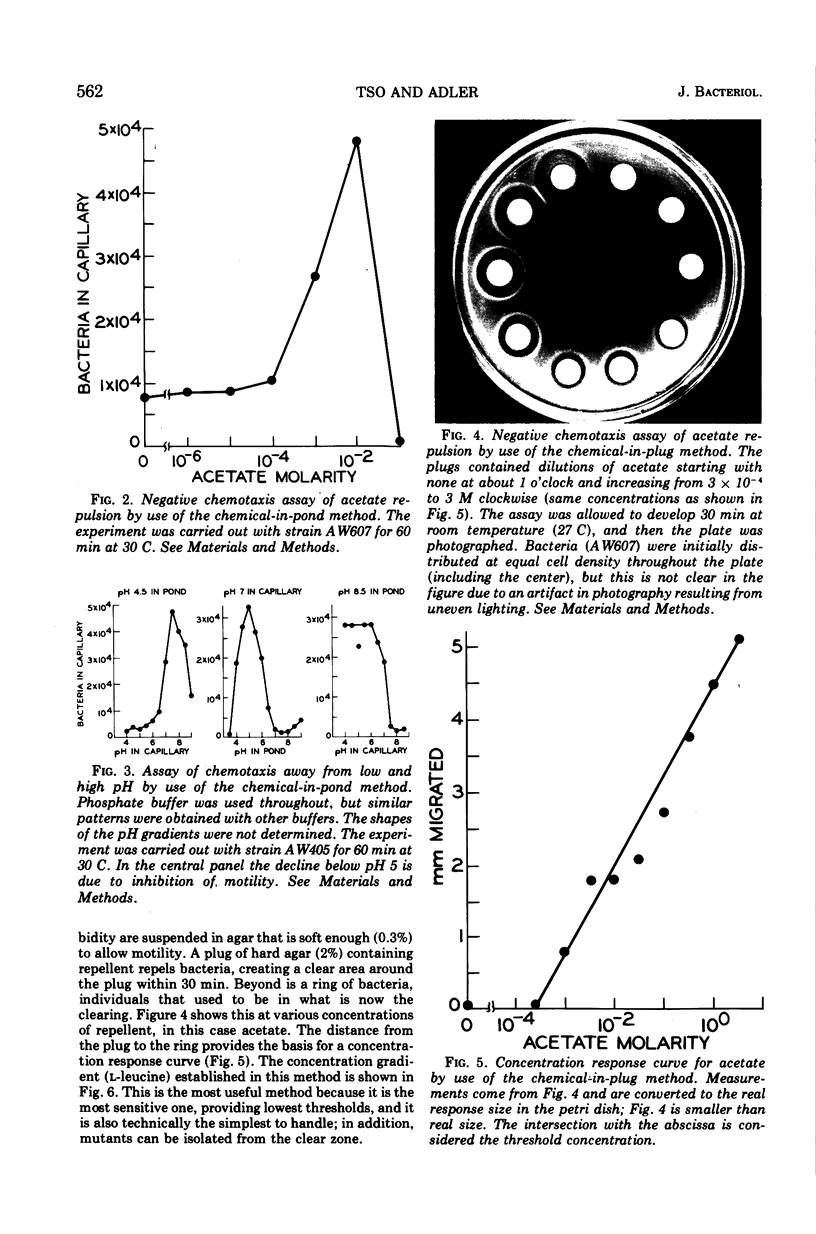
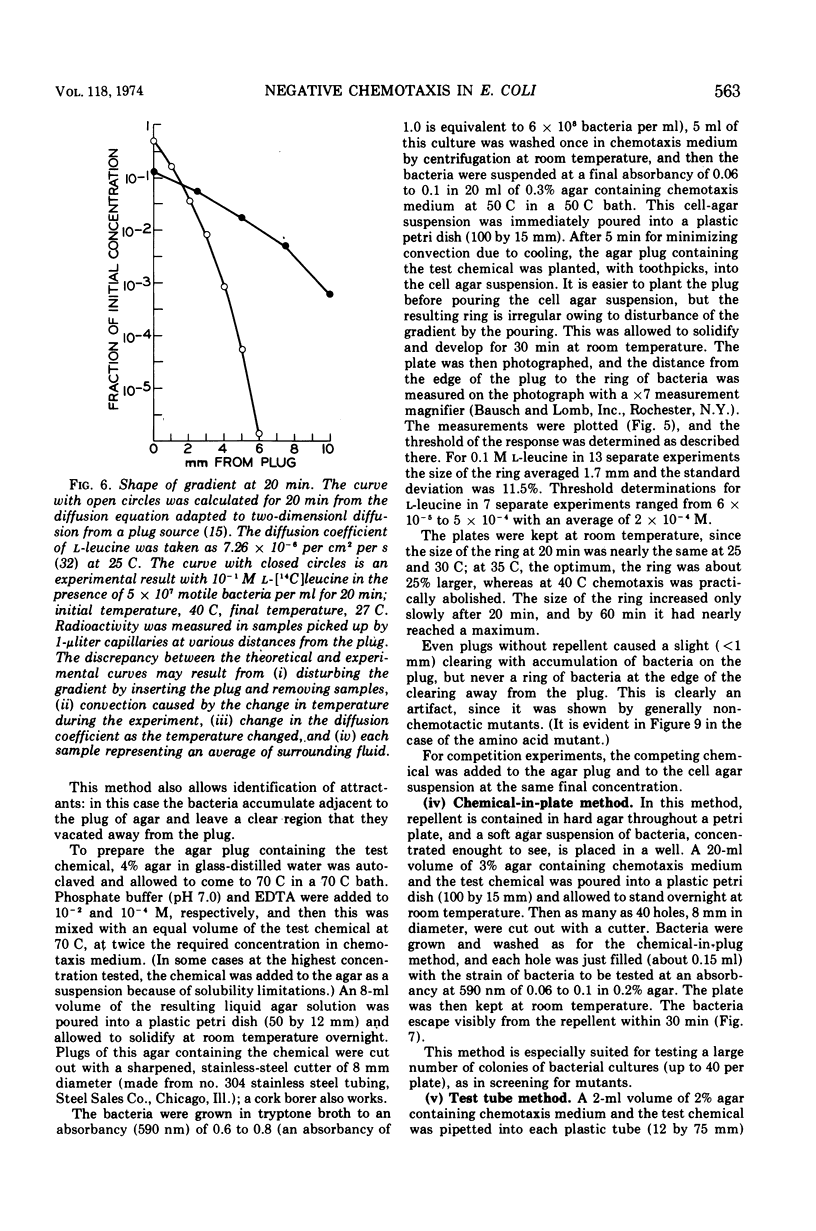
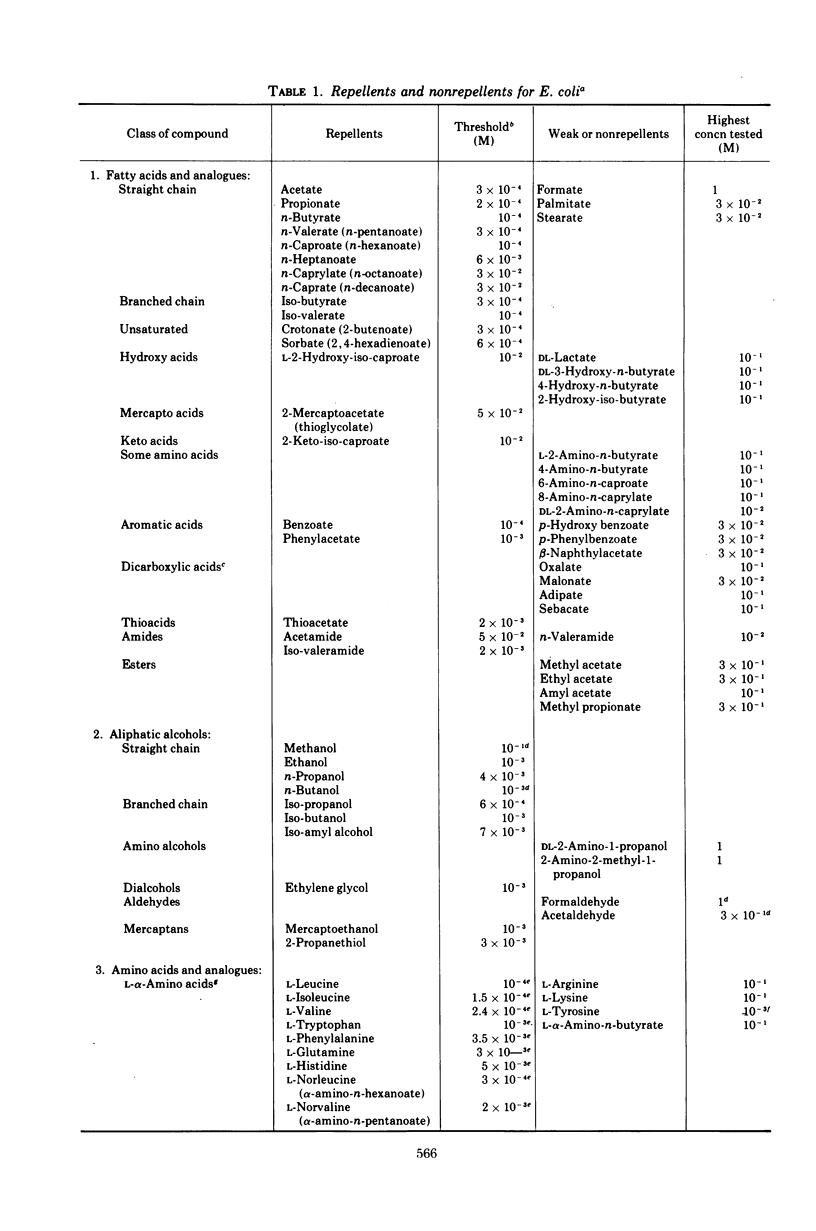
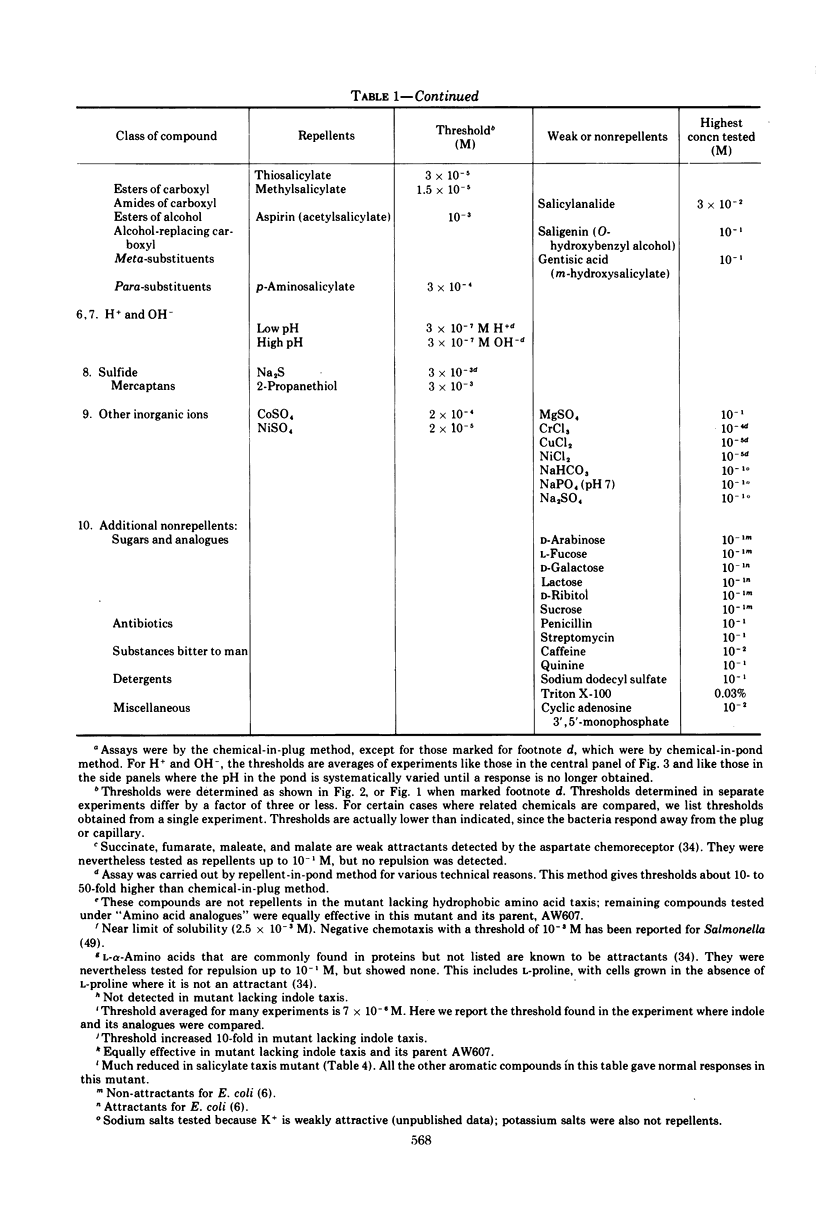
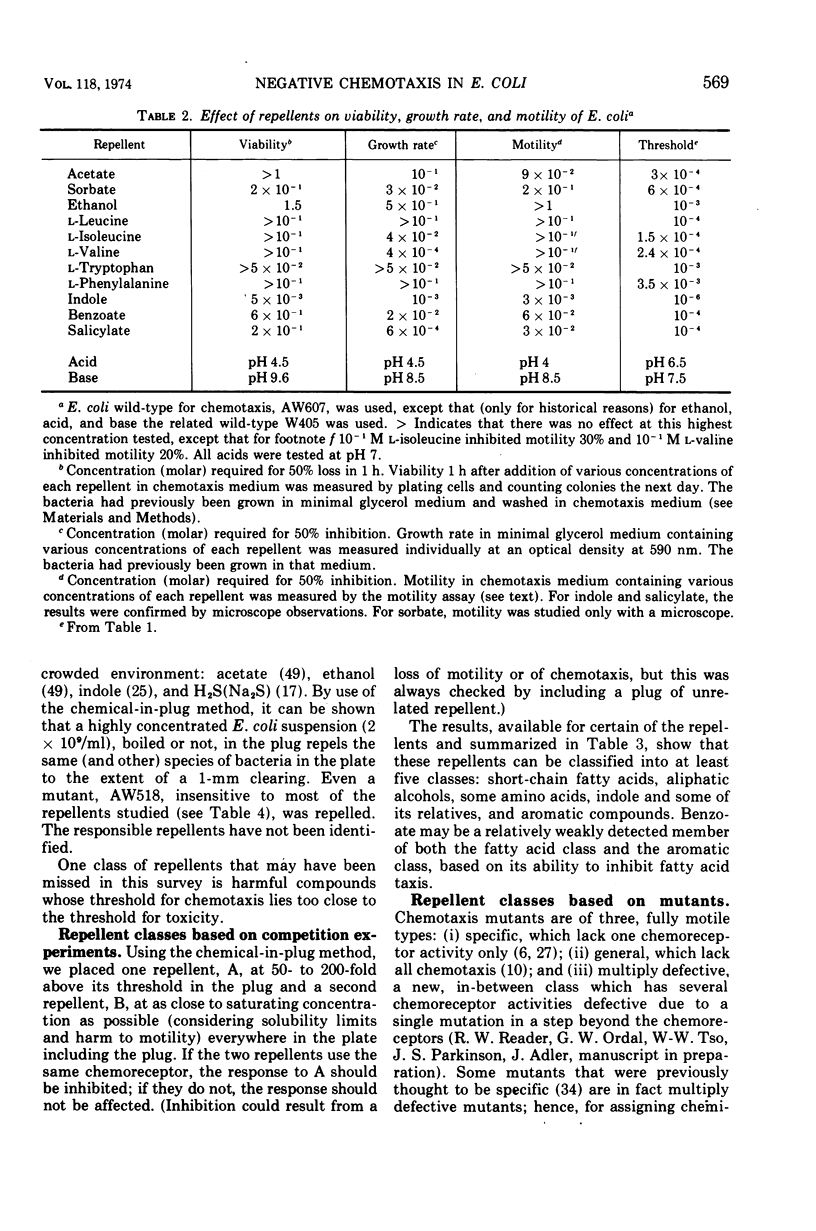
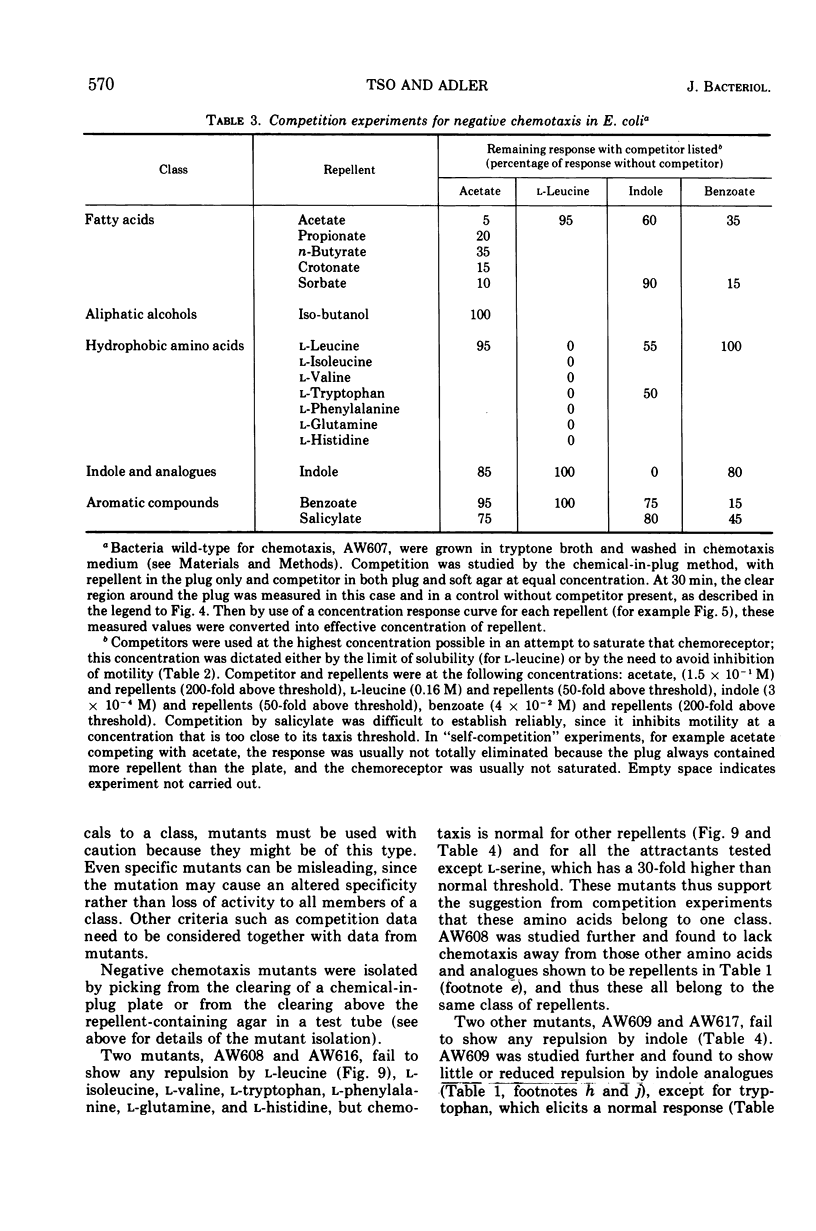
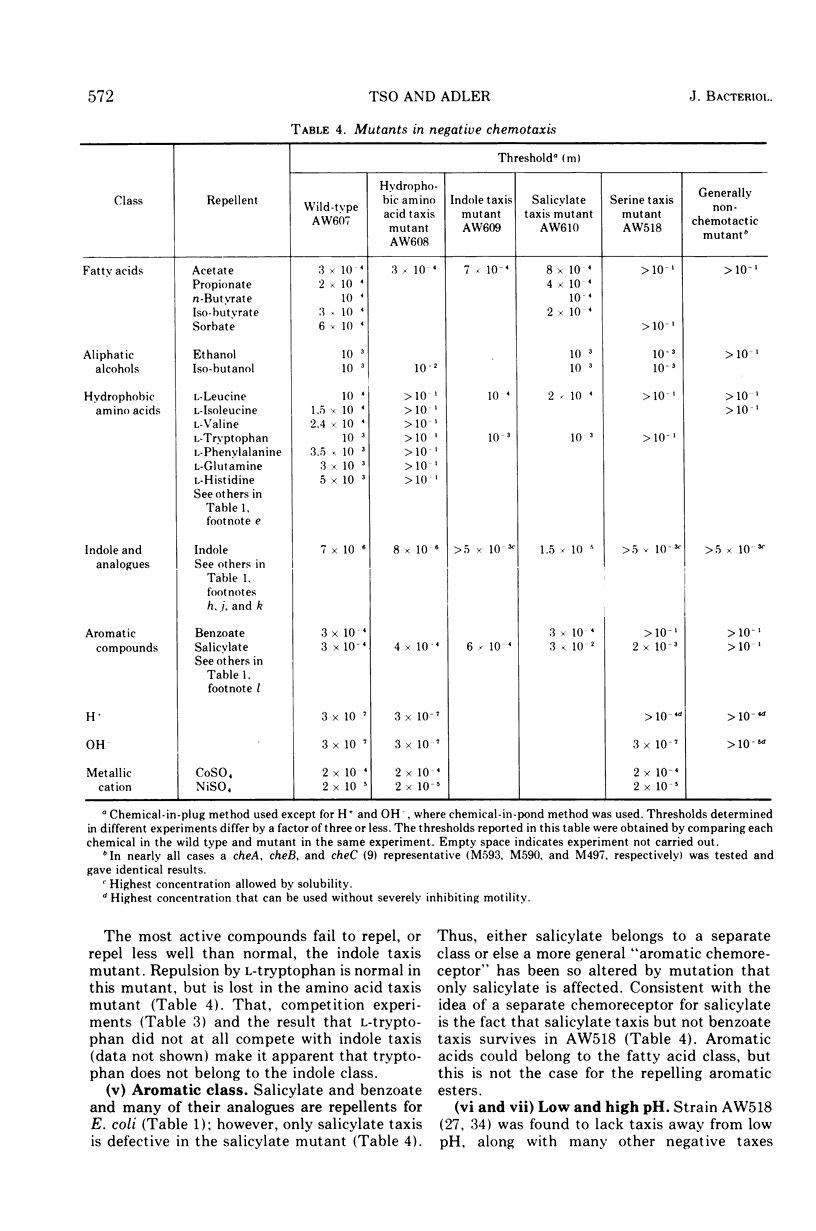
Several methods for detecting or measuring negative chemotaxis are described. Using these, we have surveyed a number of chemicals for their ability to repel Escherichia coli. Although most of the repellents are harmful compounds, harmfulness is neither necessary nor sufficient to make a compound a repellent. The repellents can be grouped into at least nine classes according to (i) competition experiments, (ii) mutants lacking certain of the negative taxes, and (iii) their chemical structure. The specificity of each class was studied. It is suggested that each class corresponds to a distinct chemoreceptor. Generally, non-chemotactic mutants lack both positive and negative chemotaxis, and l-methionine is required for both kinds of taxis. Repellents at very low concentrations are not attractants, and attractants at very high concentrations are not repellents.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABELSON P. H., ALDOUS E. Ion antagonisms in microorganisms; interference of normal magnesium metabolism by nickel, cobalt, cadmium, zinc, and manganese. J Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;60(4):401–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.4.401-413.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. Chemoreceptors in bacteria. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1588–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Science. 1966 Aug 12;153(3737):708–716. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3737.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Dahl M. M. A method for measuring the motility of bacteria and for comparing random and non-random motility. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):161–173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Hazelbauer G. L., Dahl M. M. Chemotaxis toward sugars in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):824–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.824-847.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Templeton B. The effect of environmental conditions on the motility of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):175–184. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksamit R., Koshland D. E., Jr A ribose binding protein of Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1348–1353. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90860-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J. Complementation of nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1969 Jan;61(1):61–66. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J., Dahl M. M. Nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):390–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.390-398.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARACCHINI O., SHERRIS J. C. The chemotactic effect of oxygen on bacteria. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Apr;77(2):565–574. doi: 10.1002/path.1700770228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROUS S. E., DEMOSS R. D. STUDIES ON TRYPTOPHAN PERMEASE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 6;73:623–637. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90332-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON R. K. On the interplay of environmental factors affecting taxis and motility in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1958;29(2):189–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00409860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D. The Isolation of Biochemically Deficient Mutants of Bacteria by Means of Penicillin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1949 Jan;35(1):1–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.35.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch R. N., Seymour W. F. Negative chemotaxis in bacteria. Life Sci II. 1970 Sep 22;9(18):1029–1037. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E., Sheu C. W., Galliers E. Function of lipophilic acids as antimicrobial food additives. Nature. 1973 Feb 2;241(5388):321–325. doi: 10.1038/241321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong C. E., Cirakoglu C., Willis R. C., Santy P. A. A simple preparative polyacrylamide disc gel electrophoresis apparatus: purification of three branched-chain amino acid binding proteins from Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jan;51(1):297–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90478-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong C. E., Weiner J. H. Purification of a leucine-specific binding protein from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 27;38(6):1076–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadó I., Horváth I. Amino acid sensitivity of strains derived from Escherichia coli K12. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1965;12(1):59–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guardiola J., Iaccarino M. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants altered in the transport of branched-chain amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1034–1044. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1034-1044.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Adler J. Role of the galactose binding protein in chemotaxis of Escherichia coli toward galactose. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 24;230(12):101–104. doi: 10.1038/newbio230101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Mesibov R. E., Adler J. Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis toward specific chemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1300–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INUI Y., AKEDO H. AMINO ACID UPTAKE BY ESCHERICHIA COLI GROWN IN PRESENCE OF AMINO ACIDS. EVIDENCE FOR REPRESSIBILITY OF AMINO ACID UPTAKE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 25;94:143–152. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAVITT R. I., UMBARGER H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. XI. Valine inhibition of the growth of Escherichia coli strain K-12. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:624–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.624-630.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. Linear Inheritance in Transductional Clones. Genetics. 1956 Nov;41(6):845–871. doi: 10.1093/genetics/41.6.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F. J., Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. 8. The transport of amino acids by membranes prepared from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):7844–7857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Adler J. Chemotaxis toward amino acids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):315–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.315-326.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Ordal G. W., Adler J. The range of attractant concentrations for bacterial chemotaxis and the threshold and size of response over this range. Weber law and related phenomena. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Aug;62(2):203–223. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Kennedy E. P. Magnesium transport in Escherichia coli. Inhibition by cobaltous ion. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):3042–3049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Kennedy E. P. Transport of magnesium by a repressible and a nonrepressible system in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1091–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Tanford C. The solubility of amino acids and two glycine peptides in aqueous ethanol and dioxane solutions. Establishment of a hydrophobicity scale. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2211–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Amino-acid-binding protein released from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5732–5734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmanian M., Claus D. R., Oxender D. L. Multiplicity of leucine transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1258–1266. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1258-1266.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMMONDS S., HARRIS J. I., FRUTON J. S. Inhibition of bacterial growth by leucine peptides. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jan;188(1):251–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour F. W., Doetsch R. N. Chemotactic responses by motile bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):287–296. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu C. W., Freese E. Lipopolysaccharide layer protection of gram-negative bacteria against inhibition by long-chain fatty acids. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):869–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.869-875.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Doetsch R. N. Studies on negative chemotaxis and the survival value of motility in Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):379–391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang N., Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Common mechanism for repellents and attractants in bacterial chemotaxis. Science. 1973 Jul 6;181(4094):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4094.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin M. J. Volatile fatty acids and the inhibition of Escherichia coli growth by rumen fluid. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jan;17(1):83–87. doi: 10.1128/am.17.1.83-87.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. Y., Mitchell R. Negative chemotaxis of marine bacteria to toxic chemicals. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jun;25(6):972–975. doi: 10.1128/am.25.6.972-975.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]