Abstract
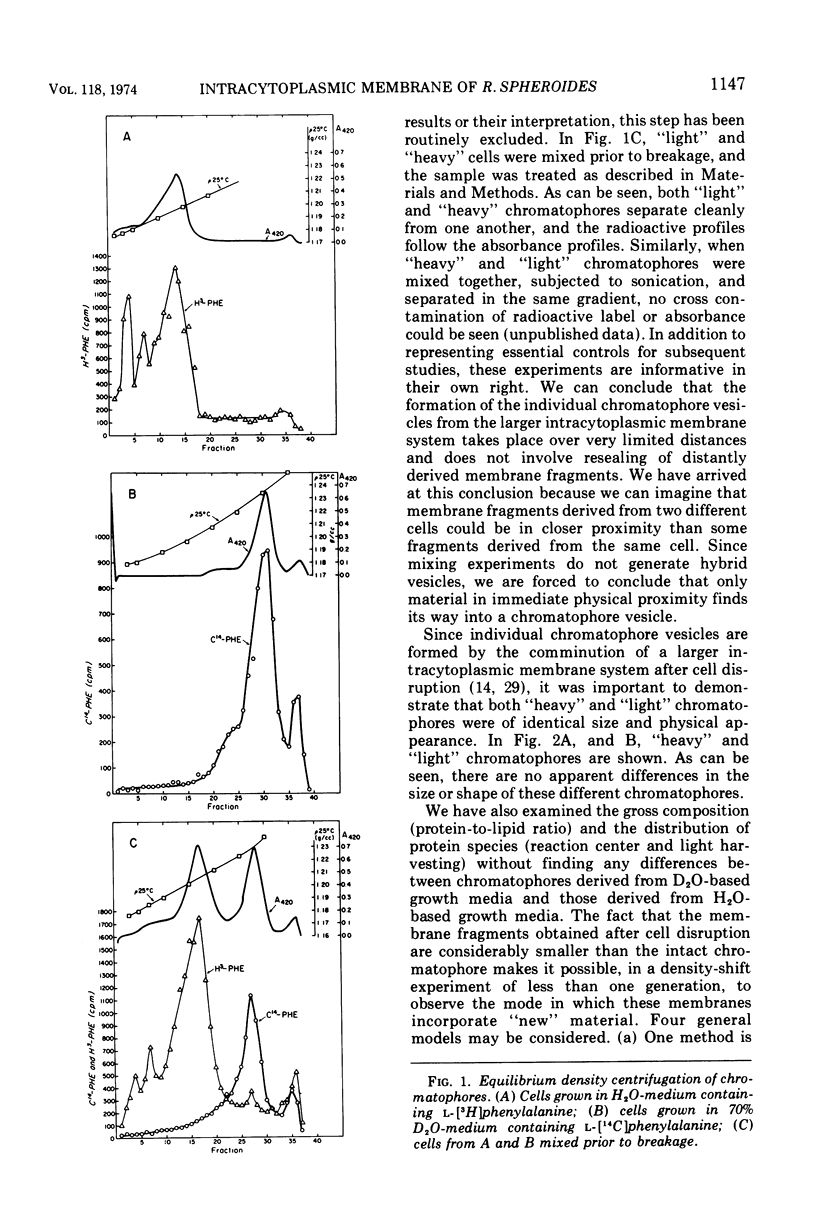
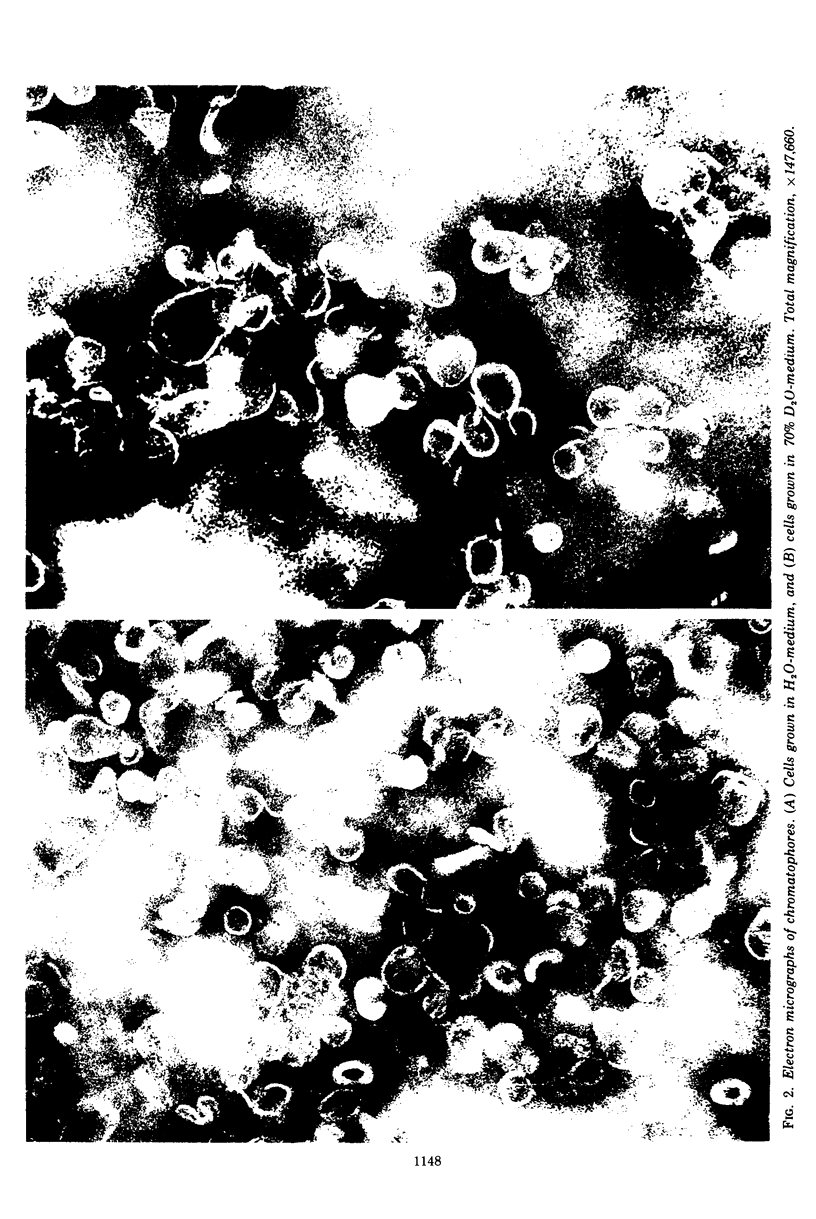
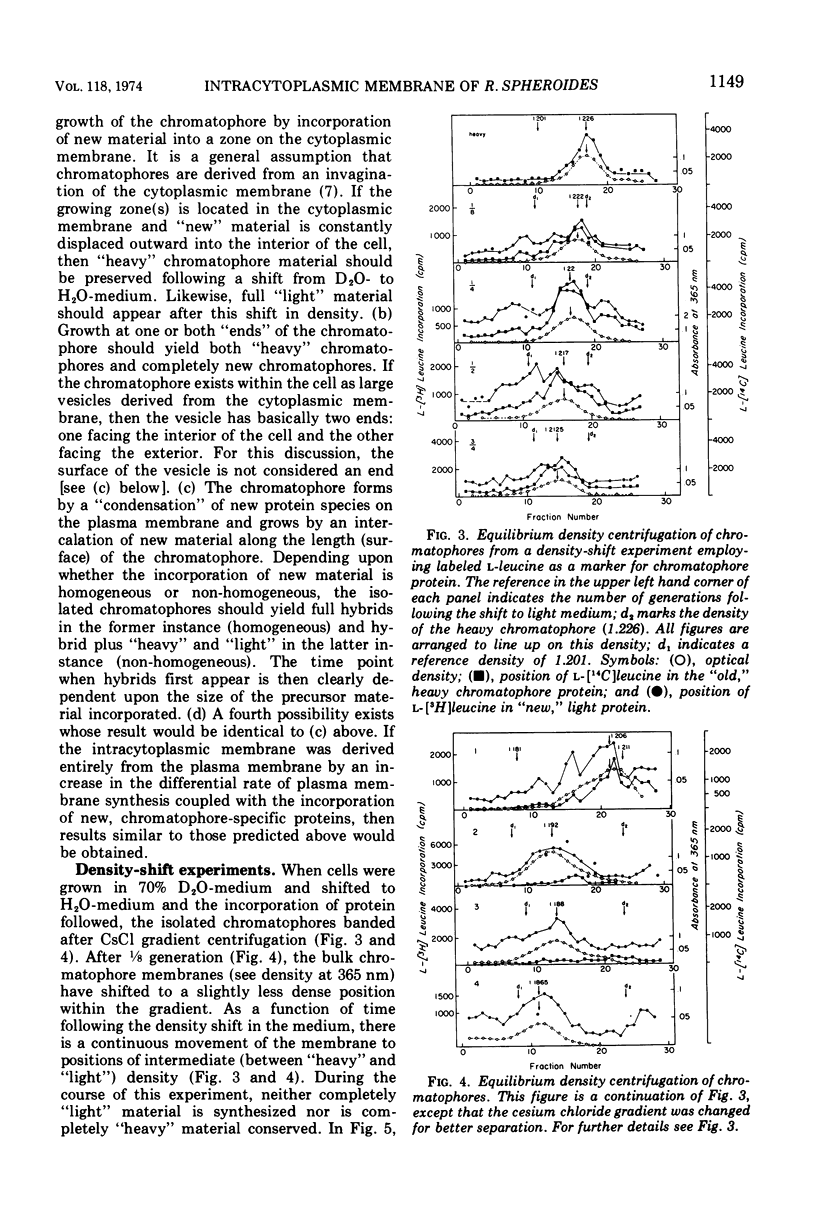
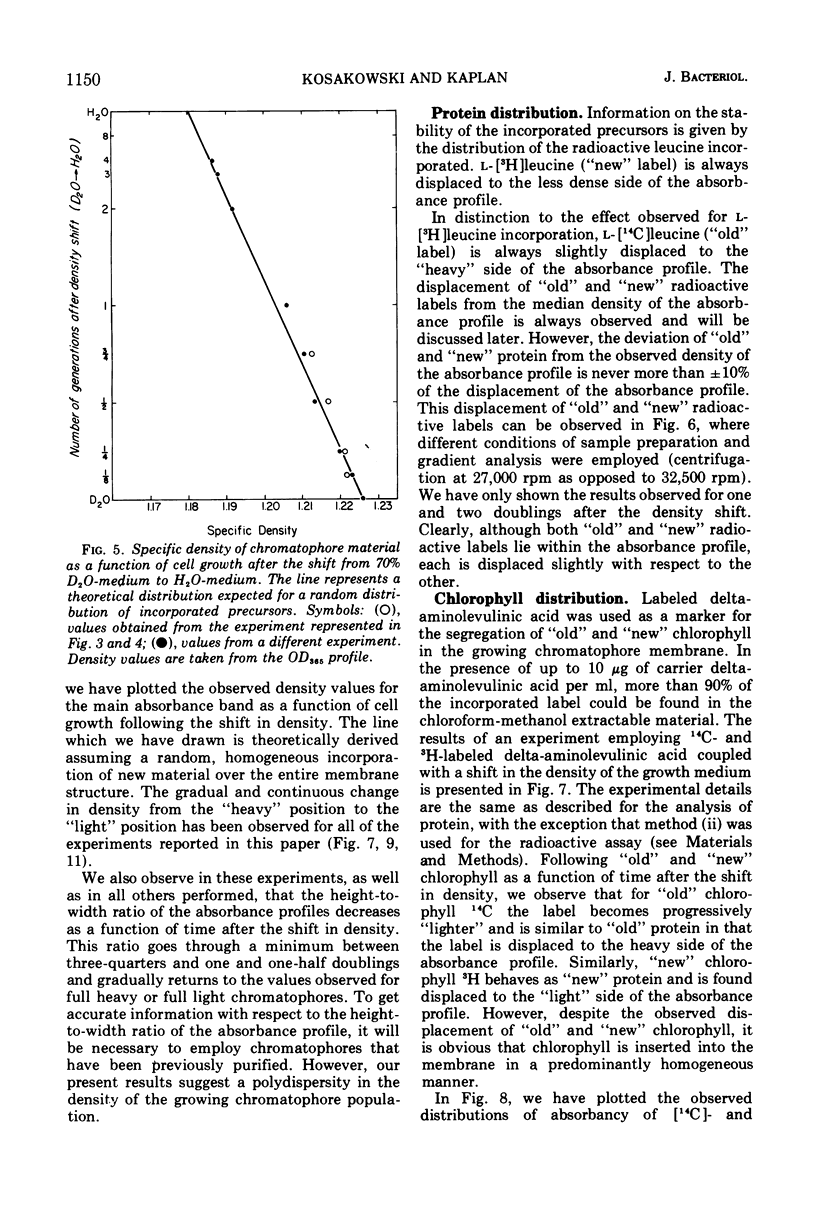
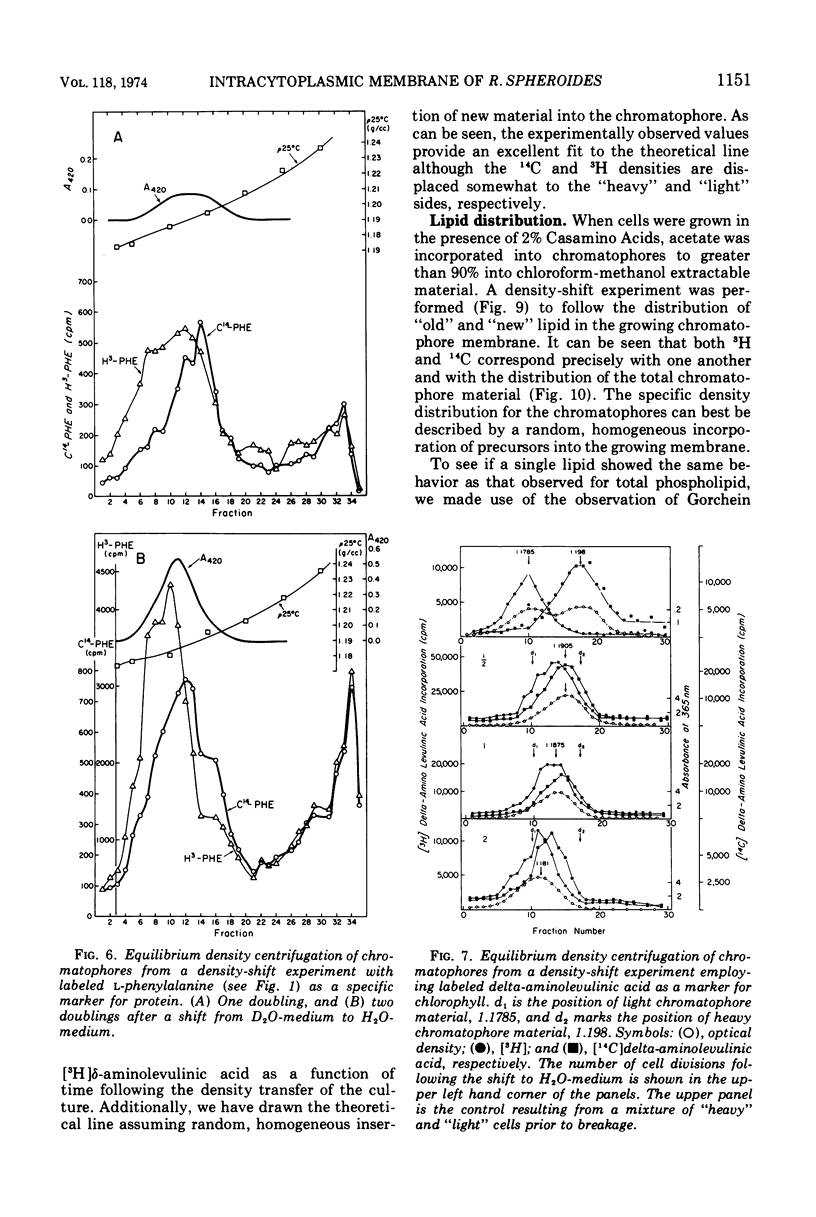
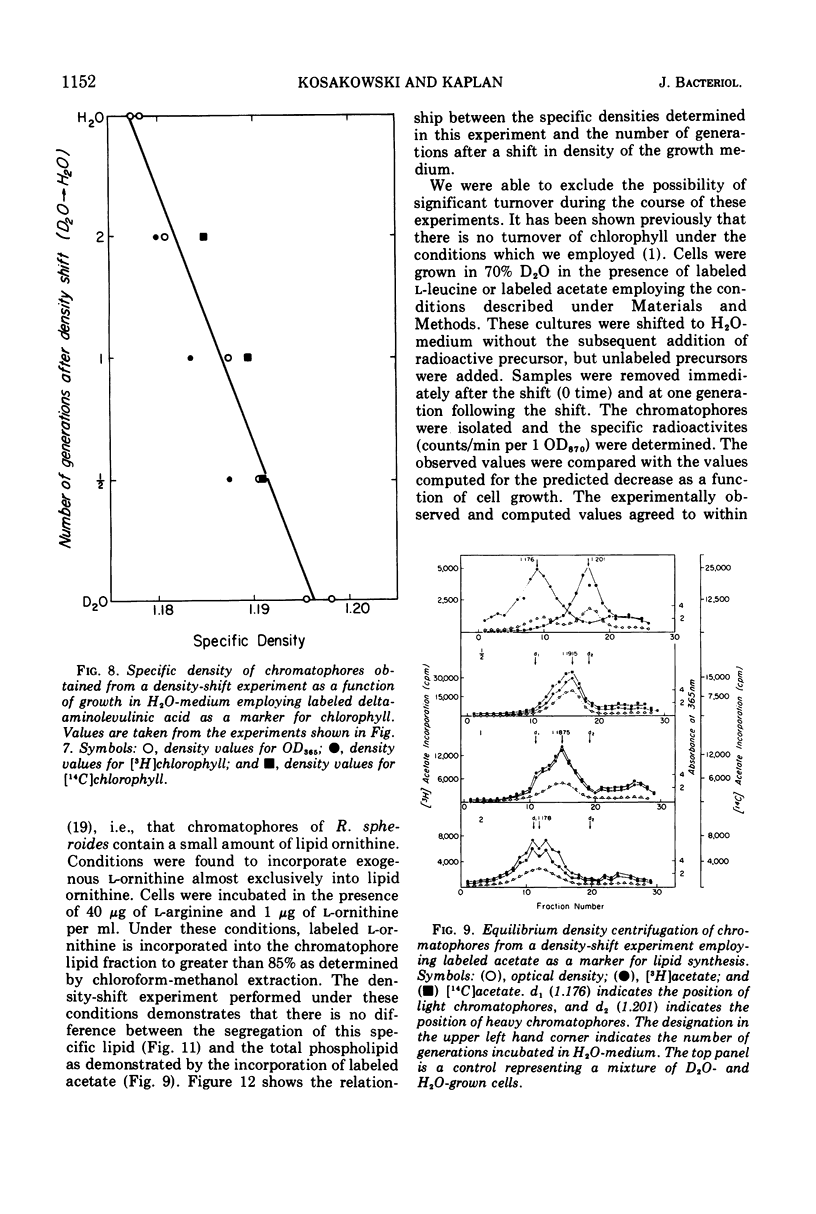
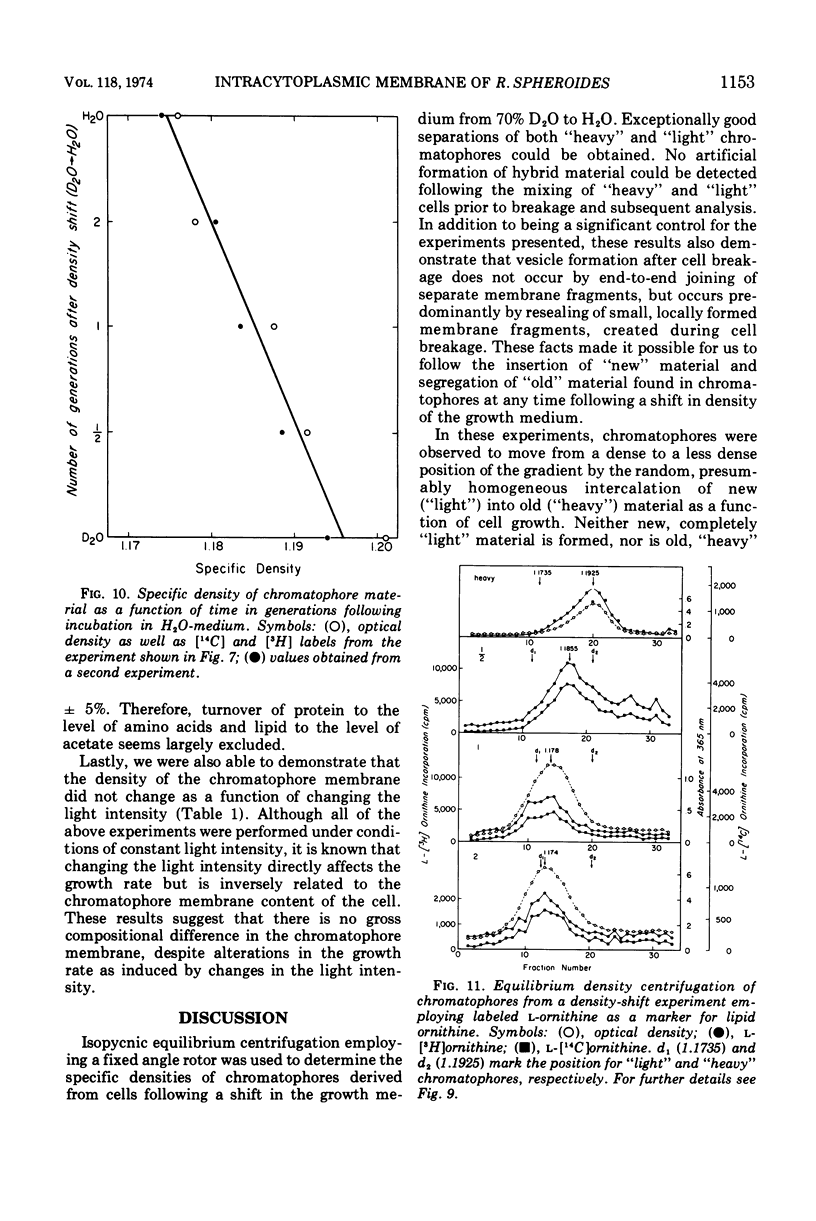
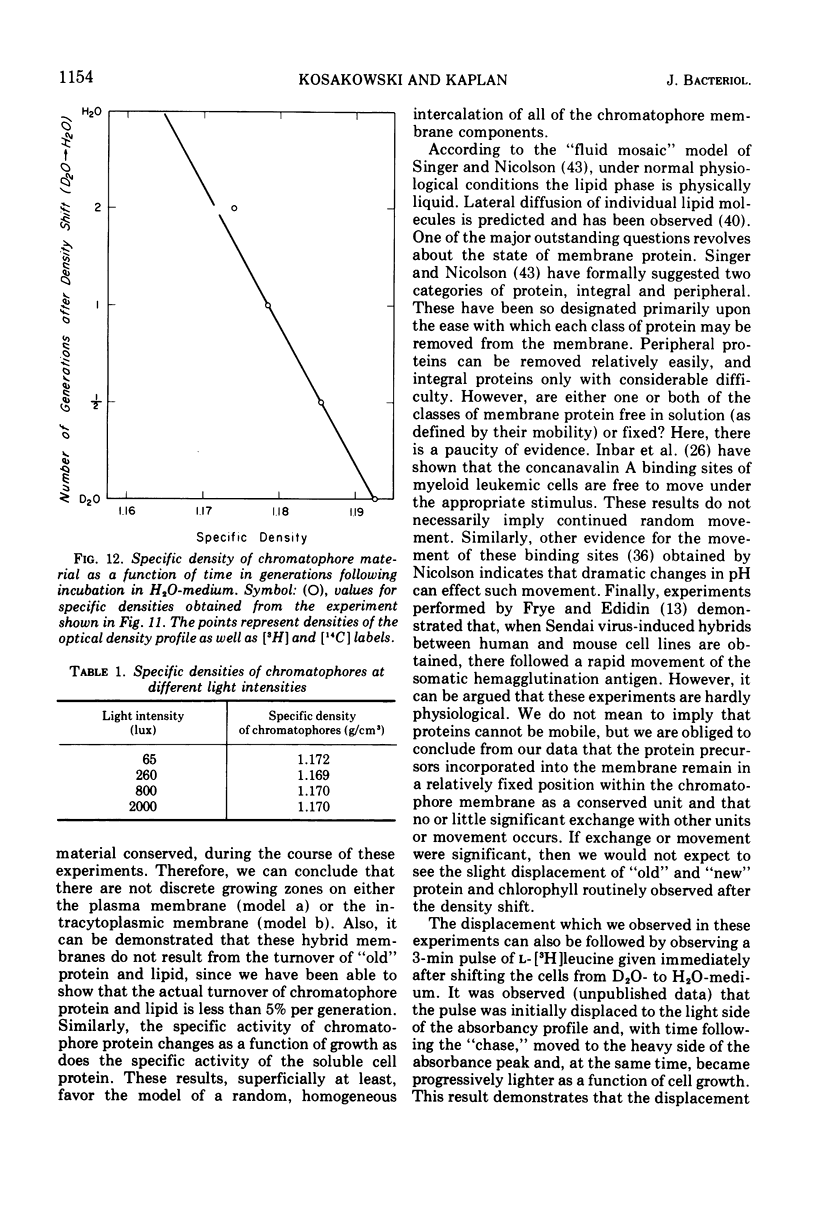
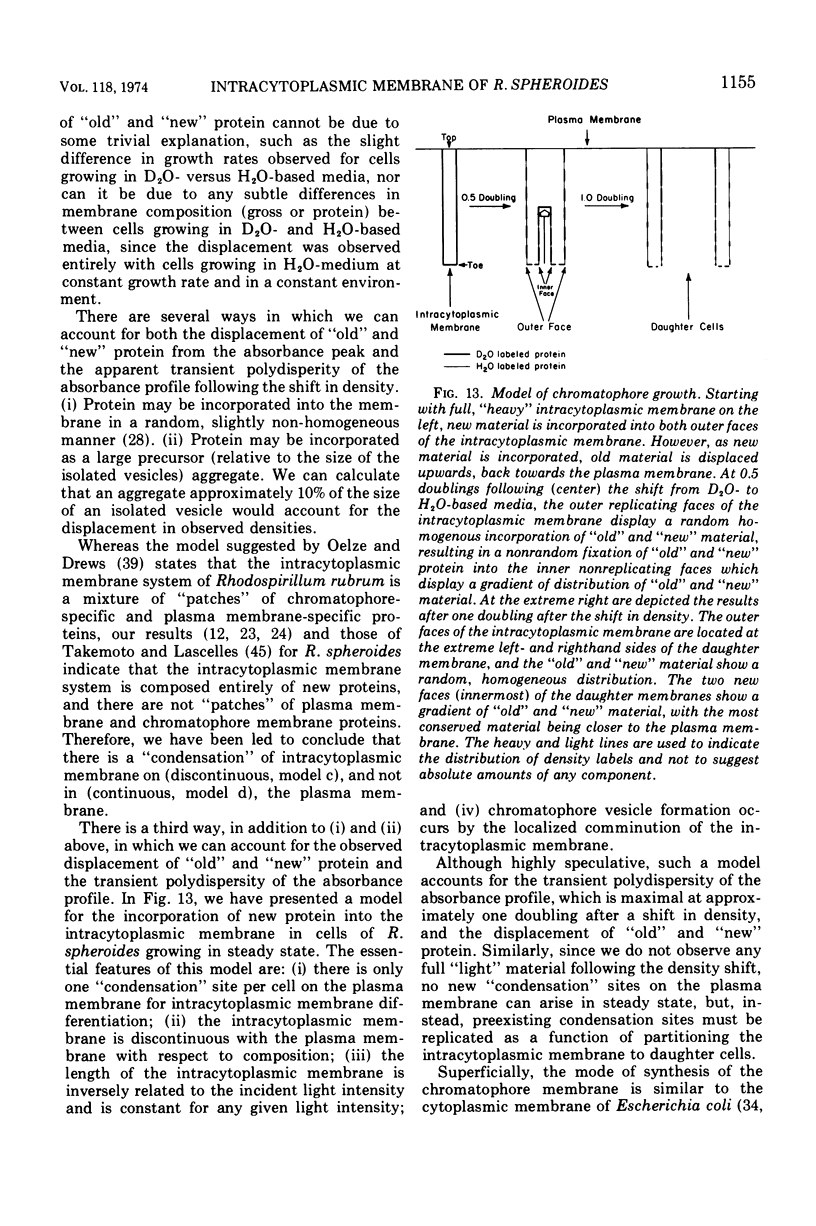
An equilibrium density gradient centrifugation study involving the separation of “old” and “new” membranes has been developed to determine the manner in which protein, lipid, and chlorophyll are incorporated into growing intracytoplasmic membranes (chromatophores) of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Chromatophores derived from cells grown in an H2O-medium had a density of 1.175 to 1.180 g/cm3 and were readily separable from chromatophores having a density of 1.220 to 1.230 isolated from cells grown in a 70% D2O-medium. After a shift from “D2O-” to “H2O”-based media, only hybrid chromatophores derived from a combination of “heavy” (old) and “light” (new) chromatophore material could be detected. The experimentally determined, median density values for the growing intracytoplasmic membrane system followed a theoretically determined profile which was calculated from the density of full “heavy” and full “light” material assuming random, homogeneous incorporation of new material into old membrane. The distribution of the radioactive labels for protein (leucine) and chlorophyll (delta-aminolevulinic acid) were identical and showed a reproducible displacement of the “old” material to the heavy side of the optical density at 365 nm (OD365) absorbance and a displacement of the “new” material to the light side of the OD365 absorbance profile. Specific phospholipid growth showed no displacement for either the “old” or “new” material from the median absorbance profile.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aagaard J., Sistrom W. R. Control of synthesis of reaction center bacteriochlorophyll in photosynthetic bacteria. Photochem Photobiol. 1972 Feb;15(2):209–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1972.tb06240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULL M. J., LASCELLES J. The association of protein synthesis with formation of pigments in some photosynthetic bacteria. Biochem J. 1963 Apr;87:15–28. doi: 10.1042/bj0870015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begg K. J., Donachie W. D. Topography of outer membrane growth in E. coli. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 12;245(141):38–39. doi: 10.1038/newbio245038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., PFENNIG N., KUNISAWA R. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF GREEN BACTERIA. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jul;22:207–225. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton R. K., Haselkorn R. Protein components of bacterial photosynthetic membranes. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 14;68(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90265-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton R. K., Sistrom W. R., Zaugg W. S. The role of a reaction center in photochemical activities of bacterial chromatophores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 22;102(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER W. D., CLINE G. B., ANDERSON N. G. DENSITY GRADIENT CENTRIFUGATION IN ANGLE-HEAD ROTORS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Dec;9:477–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feher G. Some chemical and physical properties of a bacterial reaction center particle and its primary photochemical reactants. Photochem Photobiol. 1971 Sep;14(3):373–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1971.tb06180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Kaplan S. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriochlorophyll-containing protein from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2732–2737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Kaplan S. Isolation and fractionation of the photosynthetic membranous organelles from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):465–473. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.465-473.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frye L. D., Edidin M. The rapid intermixing of cell surface antigens after formation of mouse-human heterokaryons. J Cell Sci. 1970 Sep;7(2):319–335. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson K. D. Electron microscopy of chromatophores of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):1059–1072. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.1059-1072.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson K. D., Segen B. J., Niederman R. A. Membranes of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. II. Precursor-product relations in anaerobically growing cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90251-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorchein A. Distribution and metabolism of ornithine in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jul 2;170(1020):265–278. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorchein A., Neuberger A., Tait G. H. Adaptation of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Aug 13;171(1022):111–125. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. W., Schaechter M. The mode of segregation of the bacterial cell membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Conti S. F., Fuller R. C. Effect of light intensity on the formation of the photochemical apparatus in the green bacterium Chloropseudomonas ethylicum. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):349–355. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.349-355.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. W., Kaplan S. Membrane proteins of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. 3. Isolation, purification, and characterization of cell envelope proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 11;307(2):301–316. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. W., Kaplan S. Membrane proteins of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. IV. Characterization of chromatophore proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 11;307(2):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. W., Kaplan S. Membrane proteins of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. V. Additional chemical characterization of a pigment-lipid-associated protein isolated from chromatophores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 11;307(2):332–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Ben-Bassat H., Fibach E., Sachs L. Mobility of carbohydrate-containing structures on the surface membrane and the normal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells to macrophages and granulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2577–2581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolchine G., Reiss-Husson F. Proteins of R. spheroides Y reaction center: gel electrophoresis and electrofocusing studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 25;48(2):333–340. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketchum P. A., Holt S. C. Isolation and characterization of the membranes from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;196(2):141–161. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASCELLES J. Adaptation to form bacteriochlorophyll in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides: changes in activity of enzymes concerned in pyrrole synthesis. Biochem J. 1959 Jul;72:508–518. doi: 10.1042/bj0720508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles J., Wertlieb D. Mutant strains of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides which form photosynthetic pigments aerobically in the dark. Growth characteristics and enzymic activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 2;226(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leal J., Marcovich H. Segregation of phage receptors T 6 during cell division in Escherichia coli K 12. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Apr;120(4):467–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin E. C., Hirota Y., Jacob F. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli. VI. Use of a methocel-autoradiographic method for the study of cellular division in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):375–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.375-385.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Dales S. Membrane synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. 3. The morphological localization of the sites of membrane synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1972 Oct;55(1):32–41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Anionic sites of human erythrocyte membranes. I. Effects of trypsin, phospholipase C, and pH on the topography of bound positively charged colloidal particles. J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):373–387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman R. A., Segen B. J., Gibson K. D. Membranes of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. I. Isolation and characterization of membrane fractions from extracts of aerobically and anaerobically grown cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):547–560. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90250-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelze J., Drews G. Membranes of photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 18;265(2):209–239. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Hill F. F., Lamnek-Hirsch I. Biogenesis of E. coli membrane: evidence for randomization of lipid phase. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 29;234(52):264–267. doi: 10.1038/newbio234264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Etude de la croissance de la membrane chez Bacillus subtilis au moyen de la distribution des flagelles. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Sep;121(3):271–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. The kinetics of the synthesis of photopigments in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Sep;28:607–616. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-4-607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M. A., Richards W. R. Evidence for the formation of membranous chromatophore precursor fractions in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov;45(4):863–870. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto J., Lascelles J. Coupling between bacteriochlorophyll and membrane protein synthesis in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):799–803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukagoshi N., Fielding P., Fox C. F. Membrane assembly in Escherichia coli. I. Segregation of preformed and newly formed membrane into daughter cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):497–502. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90629-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukagoshi N., Fox C. F. Transport system assembly and the mobility of membrane lipids in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 17;12(15):2822–2829. doi: 10.1021/bi00739a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORDEN P. B., SISTROM W. R. THE PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF BACTERIAL CHROMATOPHORE FRACTIONS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Oct;23:135–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G., Fox C. F. Membrane assembly in Escherichia coli. II. Segregation of preformed and newly formed membrane proteins into cells and minicells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):503–509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90630-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



