Abstract
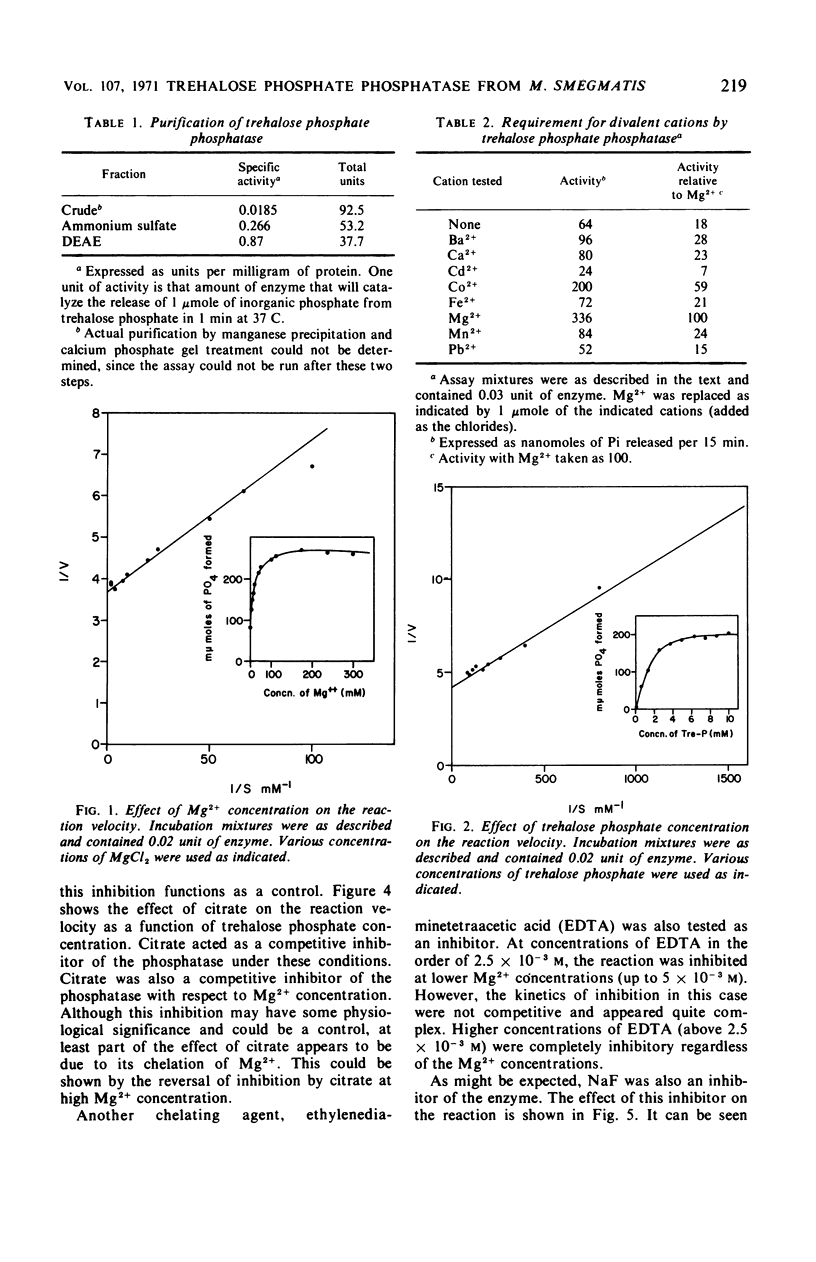
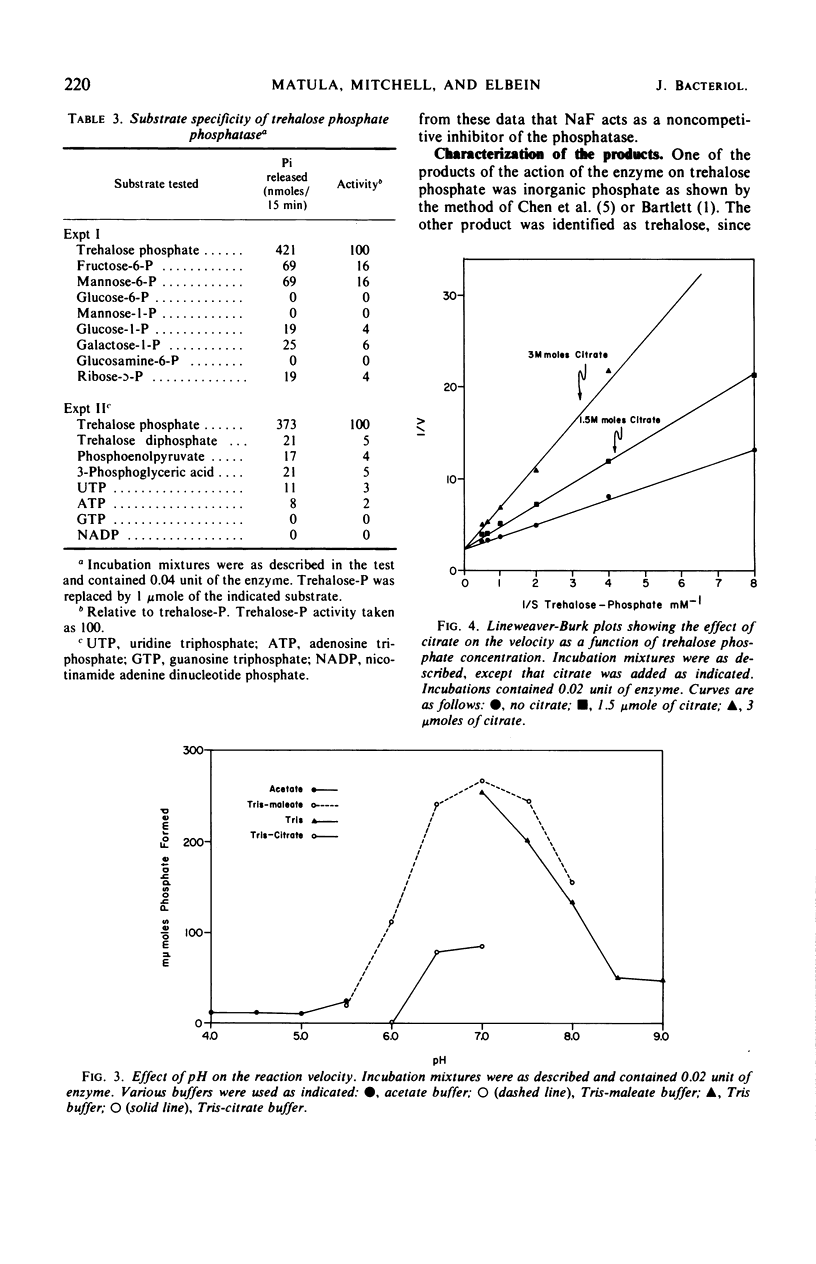
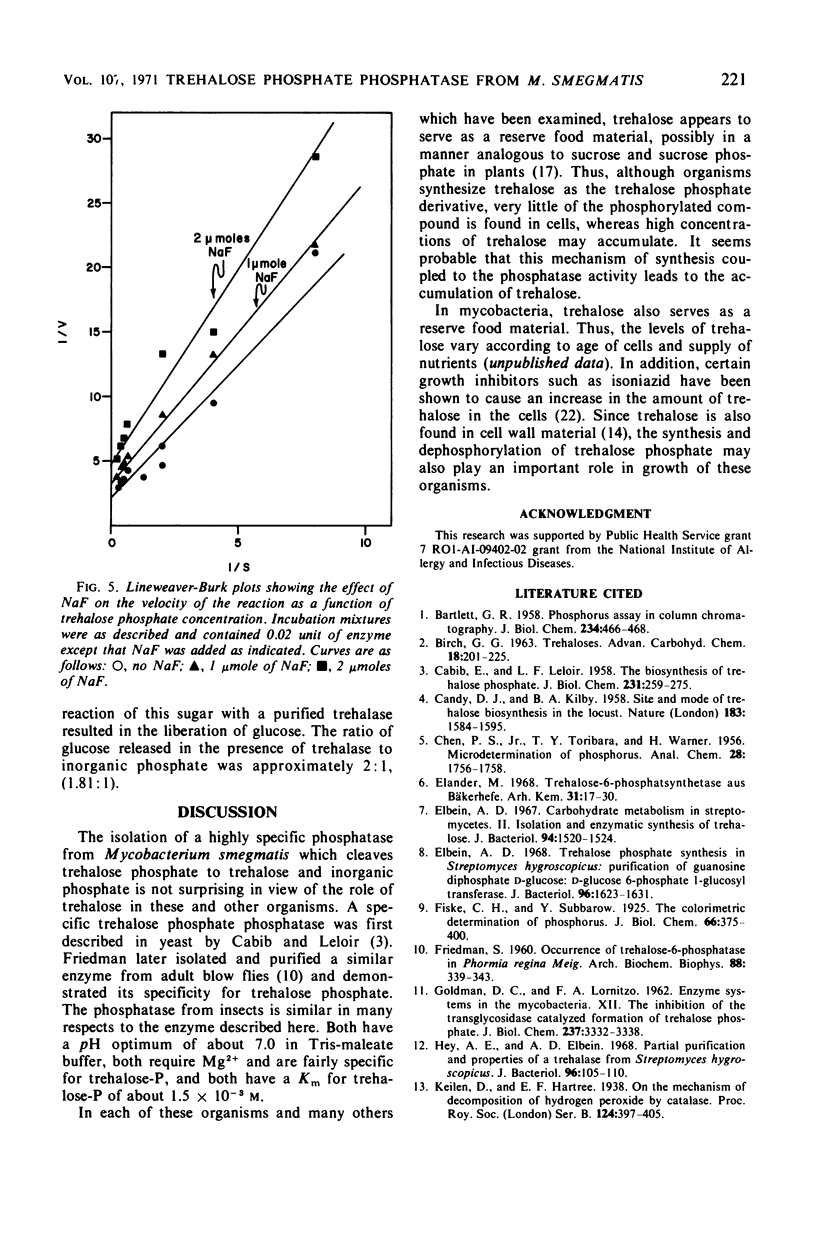
A specific trehalose phosphate phosphatase was purified approximately 50-fold from Mycobacterium smegmatis. The enzyme had a pH optimum of about 7.0 and was stimulated by Mg2+. The optimum concentration of Mg2+ was about 1.5 × 10−3m. Of other divalent cations tested, only Co2+ showed some activity. The Km for trehalose phosphate was found to be about 1.5 × 10−3m. The enzyme showed slight activity toward mannose-6-P and fructose-6-P but was inactive on a large number of other phosphorylated compounds. Citrate was a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme both with respect to trehalose phosphate concentration and Mg2+ concentration. This inhibition appears to be due to chelation of Mg2+ by this compound. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and NaF were also inhibitors of the enzyme, but these inhibitions were noncompetitive.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRCH G. G. TREHALOSES. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1963;18:201–225. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CABIB E., LELOIR L. F. The biosynthesis of trehalose phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):259–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANDY D. J., KILBY B. A. Site and mode of trehalose biosynthesis in the locust. Nature. 1959 Jun 6;183(4675):1594–1595. doi: 10.1038/1831594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Carbohydrate metabolism in streptomycetes. II. Isolation and enzymatic synthesis of trehalose. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1520–1524. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1520-1524.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Trehalose phosphate synthesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus: purification of guanosine diphosphate D-glucose: D-glucose-6-phosphate 1-glucosyl-transferase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1623–1631. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1623-1631.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN S. Occurrence of trehalose-6-phosphatase in Phormia regina Meig. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Jun;88:339–343. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN D. S., LORNITZO F. A. Enzyme systems in the mycobacteria. XII. The inhibition of the transglycosidase-catalyzed formation of trehalose 6-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3332–3338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey A. E., Elbein A. D. Partial prufication and properties of a trehalase from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.105-110.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Patterson B. W., Lapp D., Elbein A. D. Trehalose phosphate synthesis from uridine diphosphate glucose or guanosine diphosphate glucose. Activation of uridine diphosphate-glucose: trehalose phosphate synthetase by polynucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3728–3731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD D. L., WONG R. Y. A CHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF TREHALOSE 6-PHOSPHATE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 11;86:390–392. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENDICINO J. Sucrose phosphate synthesis in wheat germ and green leaves. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3347–3352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY T. A., WYATT G. R. THE ENZYMES OF GLYCOGEN AND TREHALOSE SYNTHESIS IN SILK MOTH FAT BODY. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1500–1508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Sussman M. Trehalose synthesis in the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 10;122(2):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0926-6593(66)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDER F., BRENNAN P. THE ACCUMULATION OF FREE TREHALOSE BY MYCOBACTERIA EXPOSED TO ISONIAZID. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 19;90:442–444. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYATT G. R., KALE G. F. The chemistry of insect hemolymph. II. Trehalose and other carbohydrates. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Jul 20;40(6):833–847. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.6.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


