Abstract
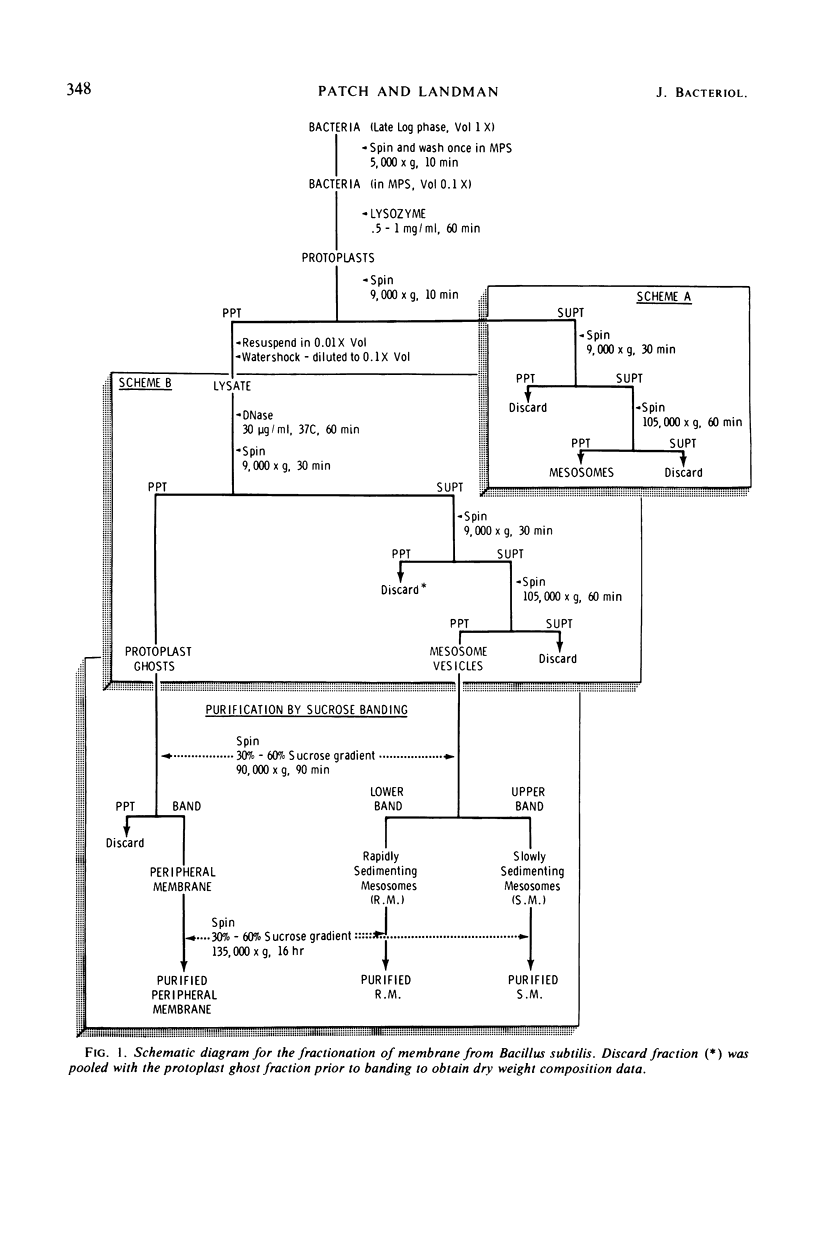
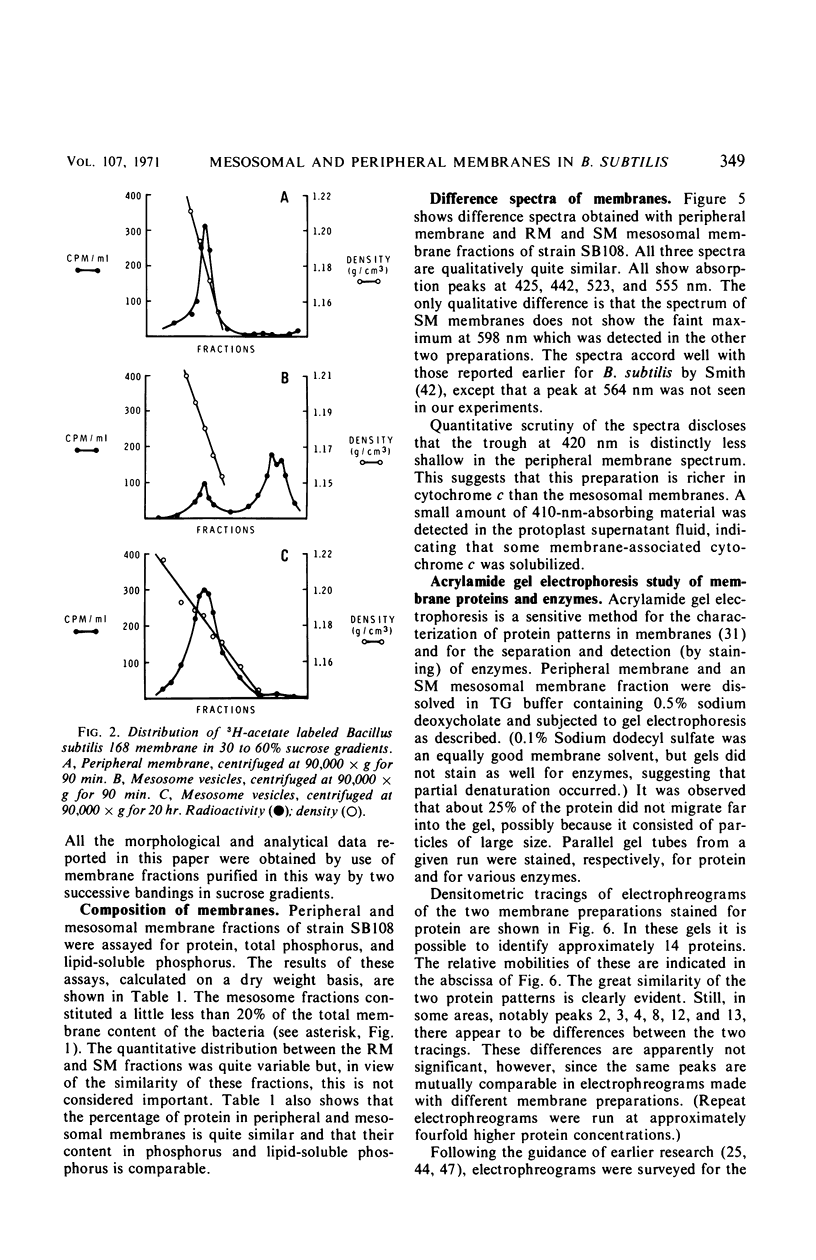
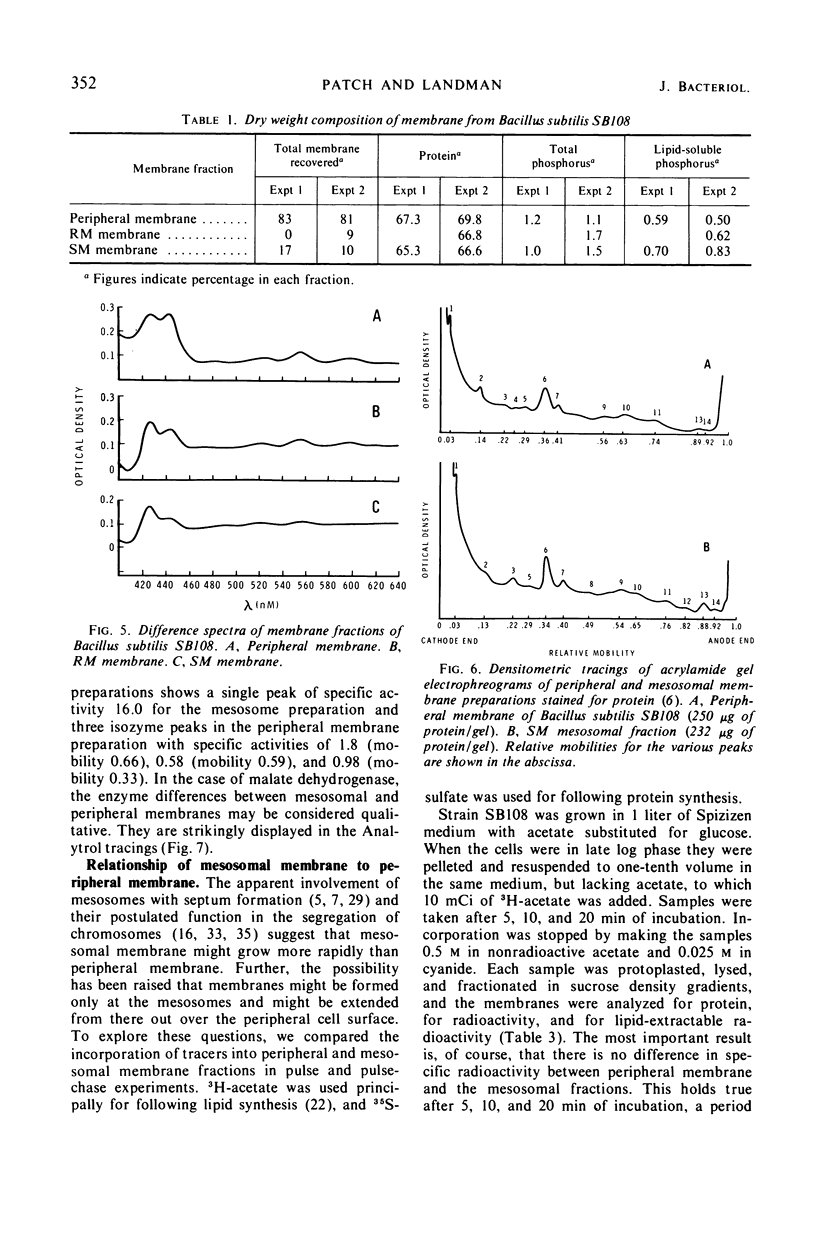
The membrane vesicle (beaded chain) portion of the mesosomes and peripheral (ghost) membrane of Bacillus subtilis were obtained by protoplast lysis and separated by differential and sucrose gradient centrifugation. Electron microscopy revealed that both fractions were satisfactorily homogeneous. Comparison of the two membrane preparations showed that they were similar with respect to total protein, total phosphorus, and lipid-soluble phosphorus content. Their protein patterns on acrylamide gel electrophreograms did not differ significantly. A possible point of distinction was revealed by a difference spectrum analysis of their cytochromes. The two preparations showed clear quantitative differences in all five of the enzyme activities assayed. Acrylamide gel electrophreograms of peripheral membrane stained for malate dehydrogenase showed four weak isozyme bands, whereas electrophreograms of mesosome membranes exhibited a single strong peak. (A survey of published data on enzymes in mesosome fractions shows a marked lack of correspondence between different species of bacteria.) Comparison of 3H-acetate incorporation into the two membrane fractions showed that both were labeled at the same rate. Similarly, 35SO4 was taken up by both fractions at a comparable rate and was chased from both comparably. Lipid and protein labeling thus indicates that mesosome vesicle membrane is not a precursor or special growing point of peripheral membrane.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARRIGONI O., SINGER T. P. Limitations of the phenazine methosulphate assay for succinic and related dehydrogenases. Nature. 1962 Mar 31;193:1256–1258. doi: 10.1038/1931256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRENNER S., HORNE R. W. A negative staining method for high resolution electron microscopy of viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:103–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN G. B., HILLIER J. Electron microscopy of ultra-thin sections of bacteria I. Cellular division in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1953 Sep;66(3):362–373. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.3.362-373.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellar D. J., Lundgren D. G., Slepecky R. A. Fine structure of Bacillus megaterium during synchronous growth. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1189–1205. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1189-1205.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. C. Participation of the cytoplasmic membrane in the growth and spore fromation of bacilli. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Oct;8:507–528. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. FATE OF THE MESOSOMES OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM DURING PROTOPLASTING. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1483–1491. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1483-1491.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrandes B., Chaix P., Ryter A. Localisation des cytochromes de Bacillus subtilis dans les structures mésosomiques. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1966 Nov 21;263(21):1632–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K., Murray R. G. Fine structure of Listeria monocytogenes in relation to protoplast formation. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):411–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.411-426.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K., Murray R. G. Fractionation and characterization of the plasma and mesosome membrane of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):426–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.426-440.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Deuel F. Proline uptake by disrupted membrane preparations from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):118–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90343-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Landman O. E. Retention of episomes during protoplasting and during propagation in the L state. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):398–404. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.398-404.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King E. J. The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1932;26(2):292–297. doi: 10.1042/bj0260292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDMAN O. E., HALLE S. ENZYMICALLY AND PHYSICALLY INDUCED INHERITANCE CHANGES IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Mol Biol. 1963 Dec;7:721–738. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landman O. E., Ryter A., Fréhel C. Gelatin-induced reversion of protoplasts of Bacillus subtilis to the bacillary form: electron-microscopic and physical study. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2154–2170. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2154-2170.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Morowitz H. J. Studies on membrane synthesis in Bacillus megaterium KM. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):441–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90256-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., JACOB F. ETUDE AU MICROSCOPE 'ELECTRONIQUE DES RELATIONS ENTRE M'ESOSOMES ET NOYAUX CHEZ BACILLUS SUBTILIS. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Nov 13;257:3060–3063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., LANDMAN O. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MESOSOME LOSS AND THE STABLE L STATE (OR PROTOPLAST STATE) IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:457–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.457-467.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaveley D. A., Rogers H. J. Some enzymic activities and chemical properties of the mesosomes and cytoplasmic membranes of Bacillus licheniformis 6346. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):67–79. doi: 10.1042/bj1130067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaveley D. A. The isolation and characterisation of cytoplasmic membranes and mesosomes of Bacillus licheniformis 6346. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Mar 27;30(6):649–655. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90562-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Bacterial growth and the cell envelope. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):194–214. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.194-214.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Electrophoretic patterns of membrane proteins of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.359-364.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Stein O., Razin S. Reassembly of Mycoplasma membranes disaggregated by detergents. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Apr;125(1):46–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90637-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Association of the nucleus and the membrane of bacteria: a morphological study. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Mar;32(1):39–54. doi: 10.1128/br.32.1.39-54.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Frehel C., Ferrandes B. Comportement des mésosomes lors de l'attaque de Bacillus subtilis par le lysozyme en milieu hyper- ou hypotonique. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Oct 23;265(17):1259–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCKER B. A. TRANSFORMATION OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS TO MOTILITY AND PROTOTROPHY: MICROMANIPULATIVE ISOLATION OF BACTERIA OF TRANSFORMED PHENOTYPE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:797–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.797-804.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STORCK R., WACHSMAN J. T. Enzyme localization in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jun;73(6):784–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.6.784-790.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R., Freer J. H. Composition of the membranes isolated from several Gram-positive bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 18;107(3):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G., Ghosh B. K., Lampen J. O. Localization of cell-bound penicillinase in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1329–1338. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1329-1338.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedar A. W., Burde R. M. The demonstration of the succinic dehydrogenase system in Bacillus subtilis using tetranitro--blue tetrazolium combined with techniques of electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1965 Oct;27(1):53–66. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tichy P., Landman O. E. Transformation in quasi spheroplasts of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):42–51. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.42-51.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C., BECKMAN H., BERGSTROM L. Localization of enzymes in Bacillus megaterium, strain M. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Jun;20(3):519–531. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-3-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG F. E., SPIZIZEN J. Physiological and genetic factors affecting transformation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81:823–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.823-829.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iterson W. Symposium on the fine structure and replication of bacteria and their parts. II. Bacterial cytoplasm. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Sep;29(3):299–325. doi: 10.1128/br.29.3.299-325.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]