Abstract
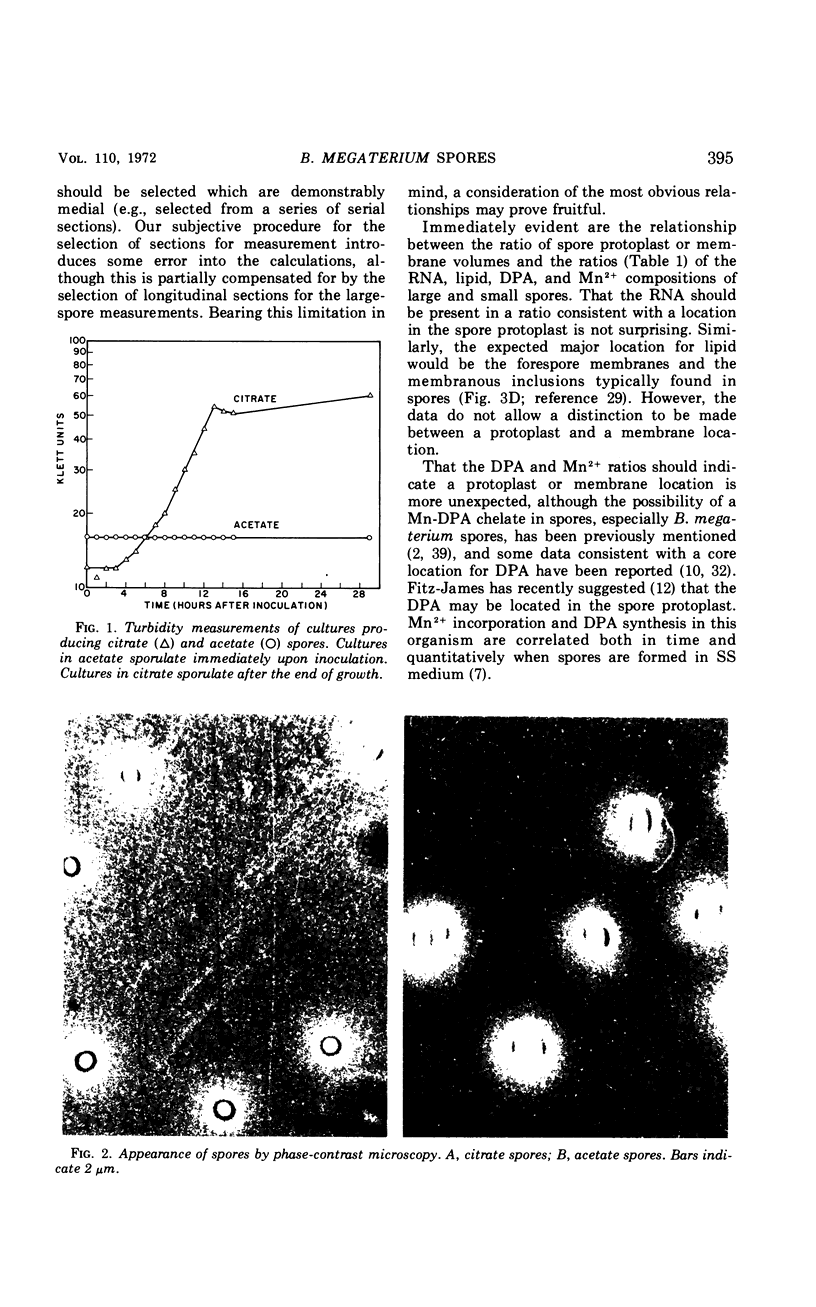
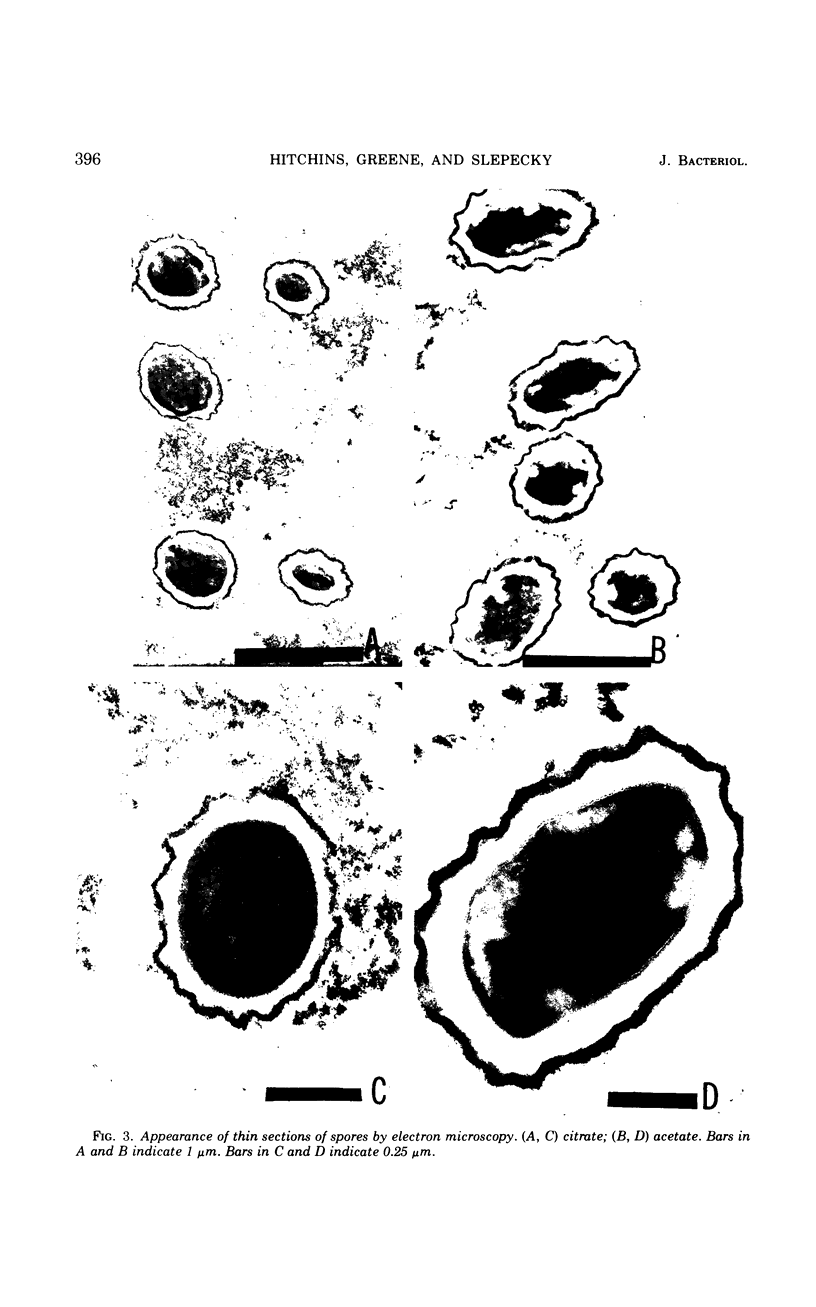
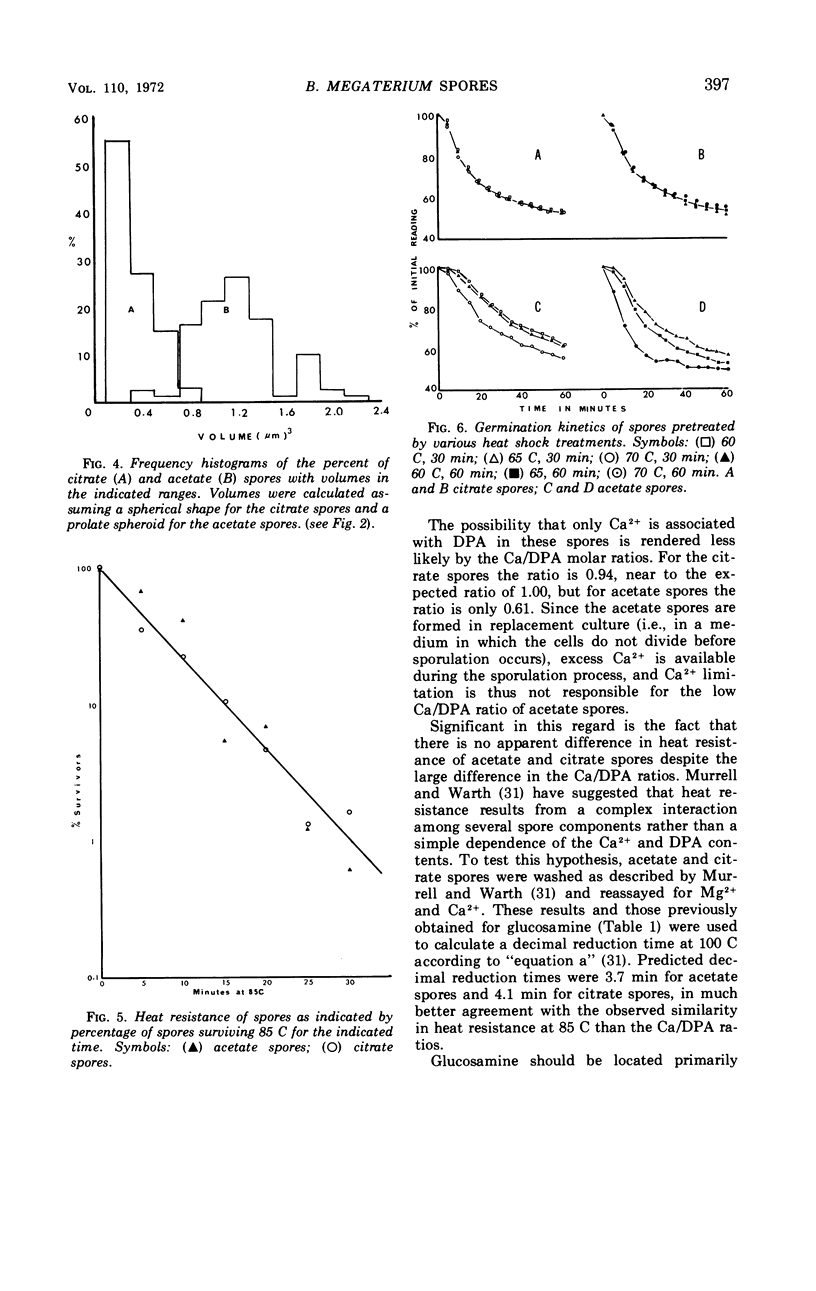
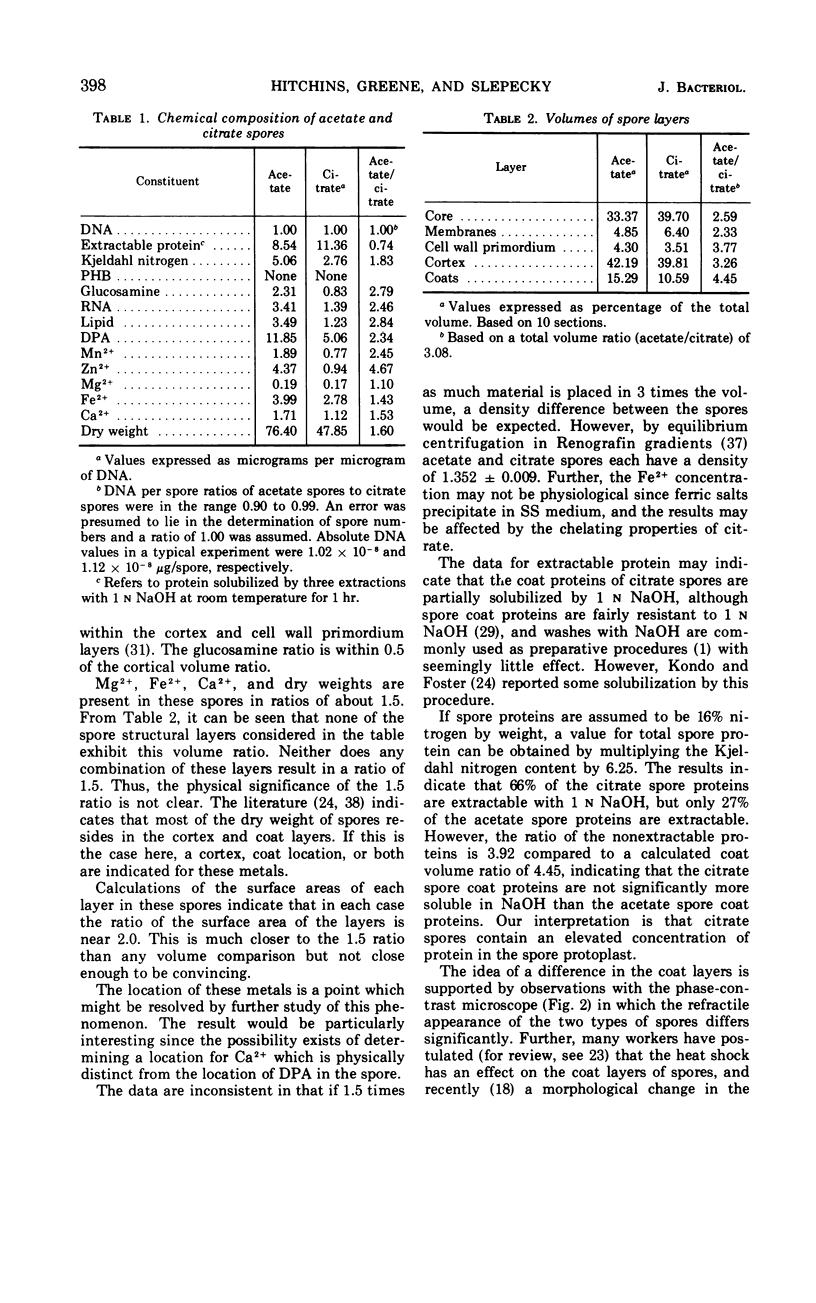
The size of the spores produced by Bacillus megaterium ATCC 19213 depended upon the nature of the carbon source present in the defined medium in which they were produced. Homogeneous preparations of small (0.38 μm3), nearly spherical spores were produced after batch culture in the presence of 2.8 mm citrate, and large (1.17 μm3), oblong spores were produced by replacement culture in the presence of 7.35 mm acetate. Large and small spores had approximately the same deoxyribonucleic acid content, density, and heat resistance. Large spores contained about 2.5 times the dipicolinic acid, glucosamine, ribonucleic acid, Mn2+, and lipid and about 1.5 times the Mg2+, Fe2+, Ca2+, and dry weight of small spores. Large spores were especially enriched in Zn2+ (4.5-fold). More protein (1.5-fold) was extracted from small spores with 1 n NaOH than from large spores, possibly indicating a difference in the spore coats, but large spores contained about twice the Kjeldahl nitrogen of small spores. A difference in the coats may account for the fact that, unlike small spores, large spores showed improved germination with increased times and temperature of heat shocking. The possibility of determining the location of some of these substances within the spore by comparing the compositional ratios with estimated volumes of specific spore layers is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson A. I., Fitz-James P. C. Biosynthesis of bacterial spore coats. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):199–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILEY G. F., KARP S., SACKS L. E. ULTRAVIOLET-ABSORPTION SPECTRA OF DRY BACTERIAL SPORES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:984–987. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.984-987.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK S. H., HASHIMOTO T., GERHARDT P. Calcium reversal of the heat susceptibility and dipicolinate deficiency of spores formed "endotrophically" in water. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Apr;6:213–224. doi: 10.1139/m60-023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERIOTTI G. A microchemical determination of desoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):297–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CESSI C., PILIEGO F. The determination of amino sugars in the presence of amino acids and glucose. Biochem J. 1960 Dec;77:508–510. doi: 10.1042/bj0770508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHURCH B. D., HALVORSON H., HARTMAN R. S., RAMSEY D. S. Population heterogeneity in the resistance of aerobic spores to ethylene oxide. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):242–247. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.242-247.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. Qualitative and quantitative colorimetric determination of heptoses. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):983–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H., Brown L. R., Rodgers G., Hsu Y. Bacillus subtilis mutant altered in spore morphology and in RNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):404–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnellan J. E., Jr, Setlow R. B. Thymine Photoproducts but not Thymine Dimers Found in Ultraviolet-Irradiated Bacterial Spores. Science. 1965 Jul 16;149(3681):308–310. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3681.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. C., YOUNG I. E. Comparison of species and yarieties of the genus Bacillus. Structure and nucleic acid content of spores. J Bacteriol. 1959 Dec;78:743–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.6.743-754.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitz-James P. C. Formation of protoplasts from resting spores. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1119–1136. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1119-1136.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortnagel P., Freese E. Inhibition of aconitase by chelation of transition metals causing inhibition of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5289–5295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTCHISON W. C., MUNRO H. N. The determination of nucleic acids in biological materials. A review. Analyst. 1961 Dec;86:768–813. doi: 10.1039/an9618600768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. S., Cox D. P. Effect of different nutritional conditions on the synthesis of tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1777–1787. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1777-1787.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoo T., Conti S. F. Ultrastructural changes associated with activation and germination of Bacillus cereus T spores. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):361–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.361-368.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchins A. D., Kahn A. J., Slepecky R. A. Interference contrast and phase contrast microscopy of sporulation and germination of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1811–1817. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1811-1817.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka H., Gillis J. R., Slepecky R. A. Synchronous growth and sporulation of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1624–1630. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1624-1630.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN F. W., LUND A. J., ANDERSON L. E. Colorimetric assay for dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores. Science. 1958 Jan 3;127(3288):26–27. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3288.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo M., Foster J. W. Chemical and electron microscope studies on fractions prepared from coats of Bacillus spores. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 May;47(2):257–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korch C. T., Doi R. H. Electron microscopy of the altered spore morphology of a ribonucleic acid polymerase mutant of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1110–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1110-1118.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAW J. H., SLEPECKY R. A. Assay of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:33–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.33-36.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce S. M., Fitz-James P. C. Spore refractility in variants of Bacillus cereus treated with actinomycin D. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.337-344.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., MAALOE O., KJELDGAARD N. O. Dependency on medium and temperature of cell size and chemical composition during balanced grown of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Dec;19(3):592–606. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-3-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLEPECKY R., FOSTER J. W. Alterations in metal content of spores of Bacillus megaterium and the effect on some spore properties. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):117–123. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.117-123.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slepecky R. A., Law J. H. SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION OF POLY-beta-HYDROXYBUTYRIC ACID IN CONNECTION WITH SPORULATION OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82(1):37–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.37-42.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TINELLI R. Etude de la biochimie de la sporulation chez Bacillus megaterium. I. Composition des spores obtenues par carence des différents substrats carbonés. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1955 Feb;88(2):212–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamir H., Gilvarg C. Density gradient centrifugation for the separation of sporulating forms of bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 10;241(5):1085–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDLE J. J., SACKS L. E. Electron paramagnetic resonance of managanese(II) and copper(II) in spores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 19;66:173–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




