Abstract
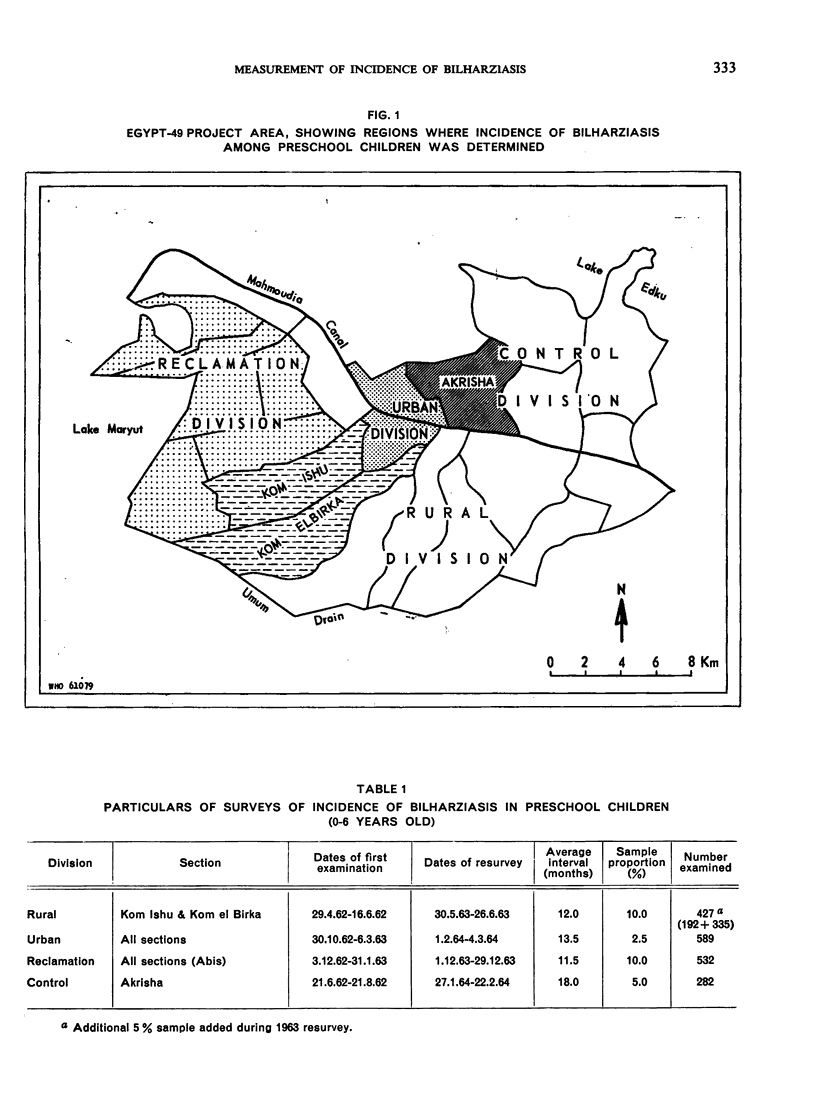
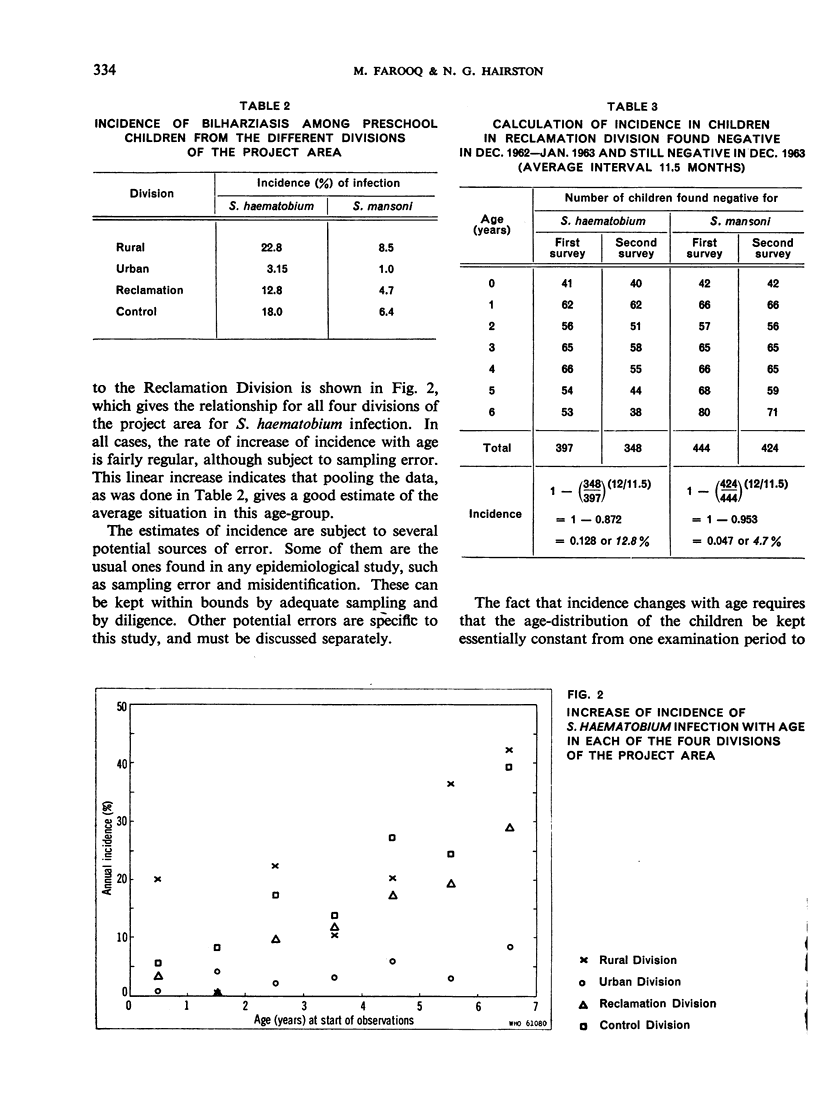
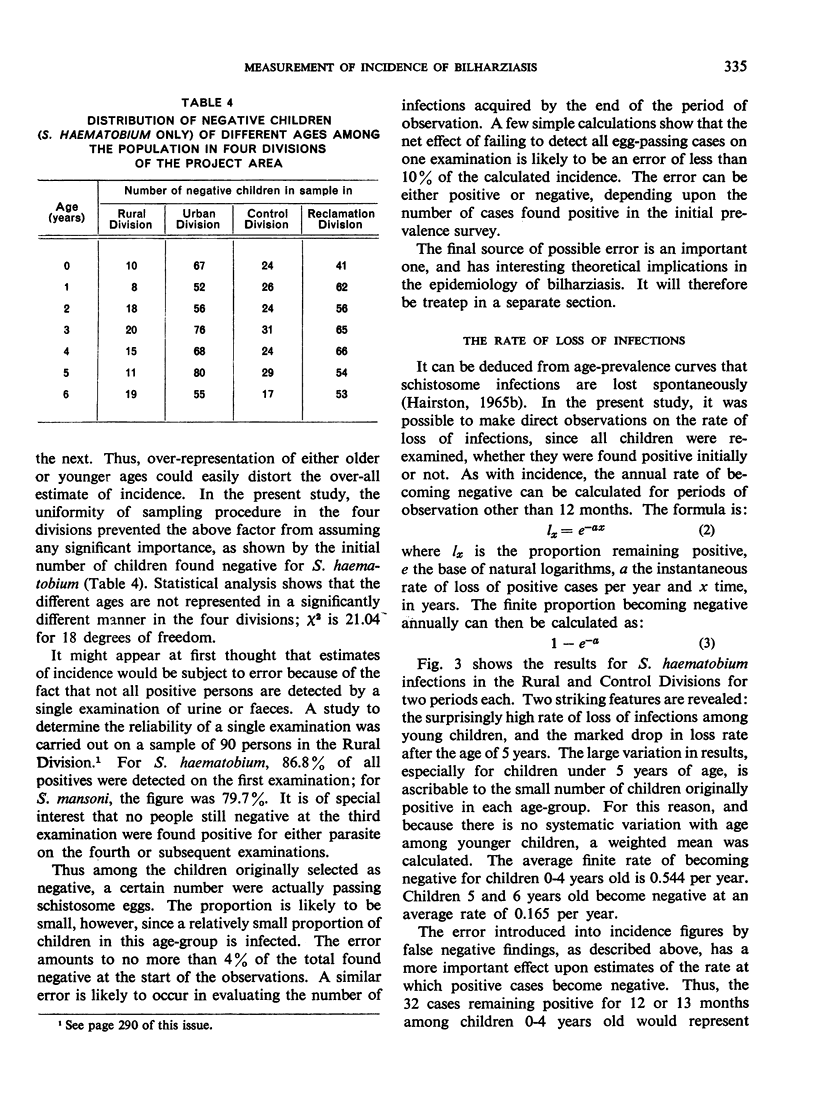
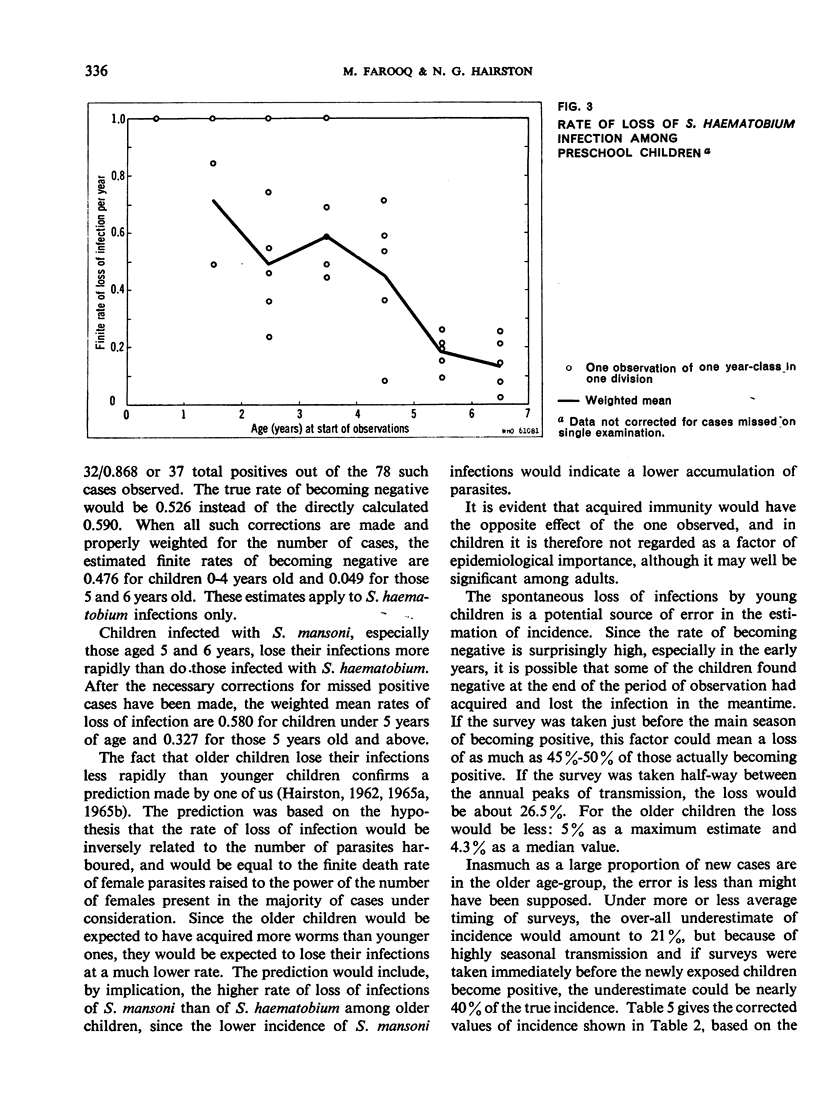
The measurement of incidence, or the rate at which people become positive, for Schistosoma haematobium and S. mansoni was carried out in four parts of the Egypt-49 project area near Alexandria. For S. haematobium, rates as high as 22.8% per year were found for children 0-6 years old in a rural area; in the same area, the incidence of S. mansoni was 8.5% per year. The true incidence is underestimated because many cases become negative spontaneously. This loss rate of S. haematobium cases is 0.476 per year for children 0-4 years old, and 0.049 per year for those aged 5 and 6 years; for S. mansoni, the rates are 0.580 and 0.327, respectively. Despite the error, incidence is the most accurate and sensitive method of assessing the success of control operations, and is an important measurable parameter in epidemiology.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hairston N. G. An analysis of age-prevalence data by catalytic models. A contribution to the study of bilharziasis. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;33(2):163–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hairston N. G. On the mathematical analysis of schistosome populations. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;33(1):45–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PESIGAN T. P., FAROOQ M., HAIRSTON N. G., JAUREGUI J. J., GARCIA E. G., SANTOS A. T., SANTOS B. C., BESA A. A. Studies on Schistosoma japonicum infection in the Philippines. 1. General considerations and epidemiology. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;18(3):345–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


