Abstract
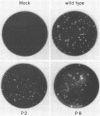
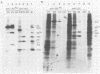
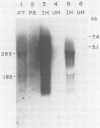
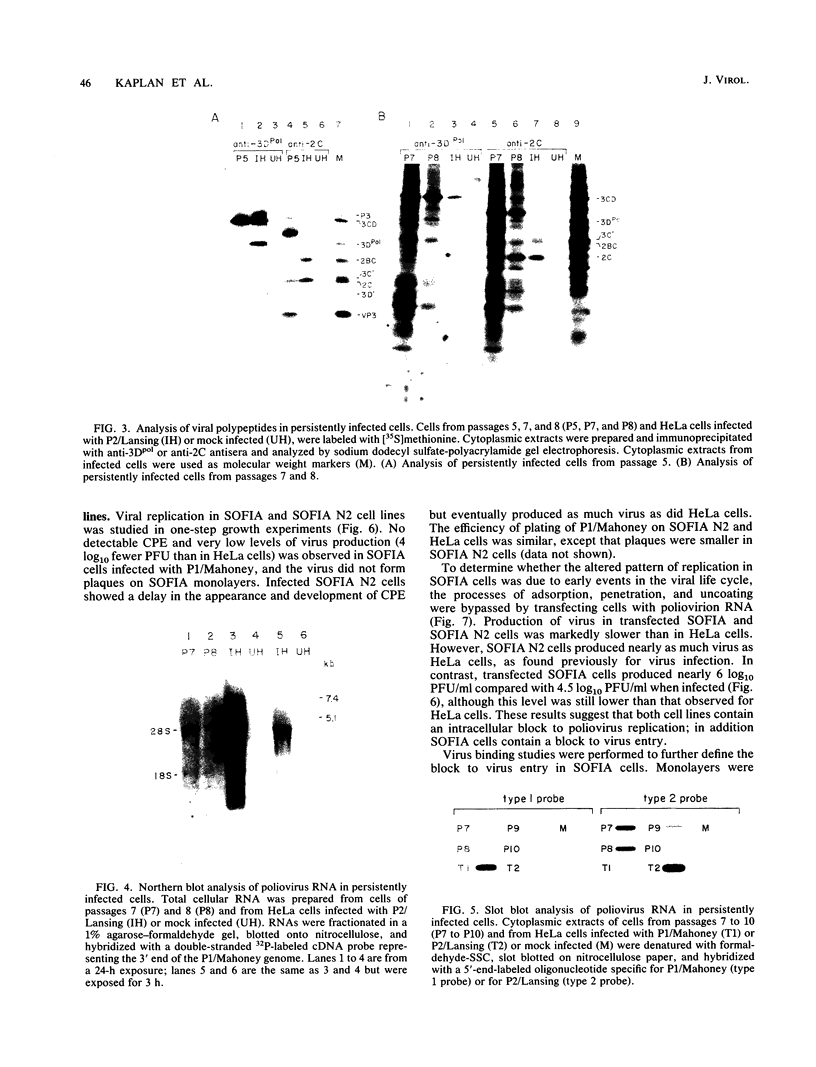
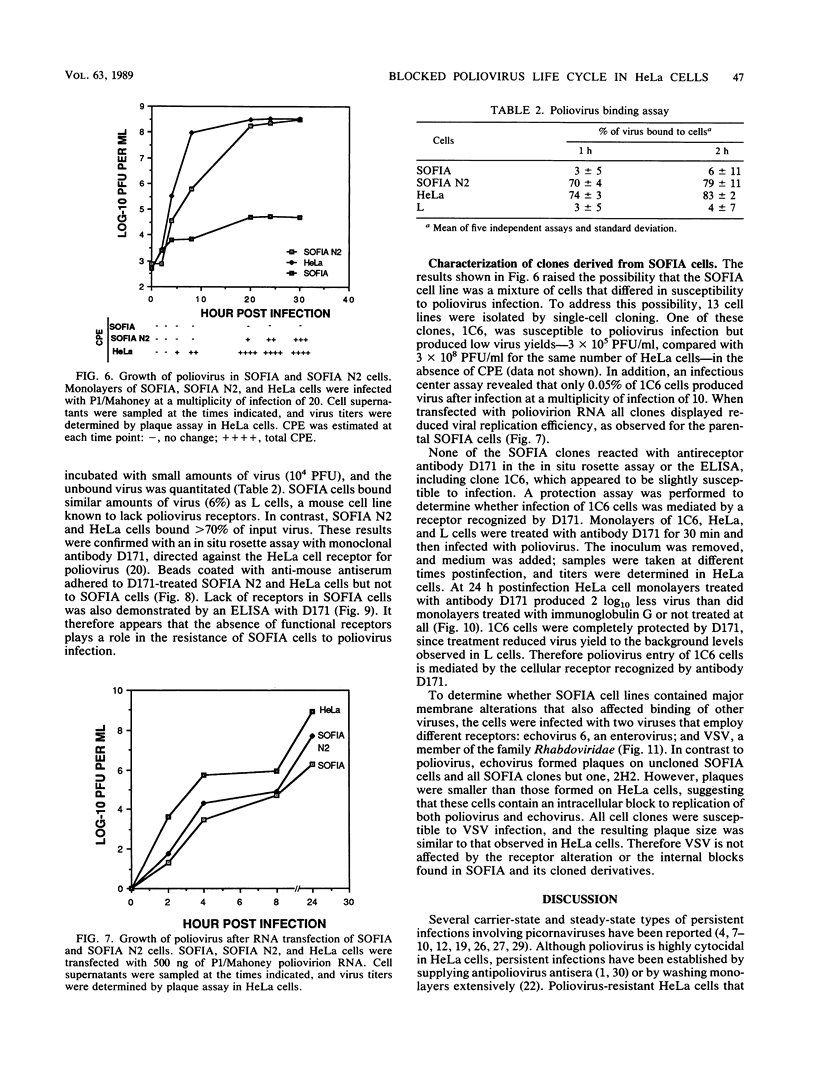
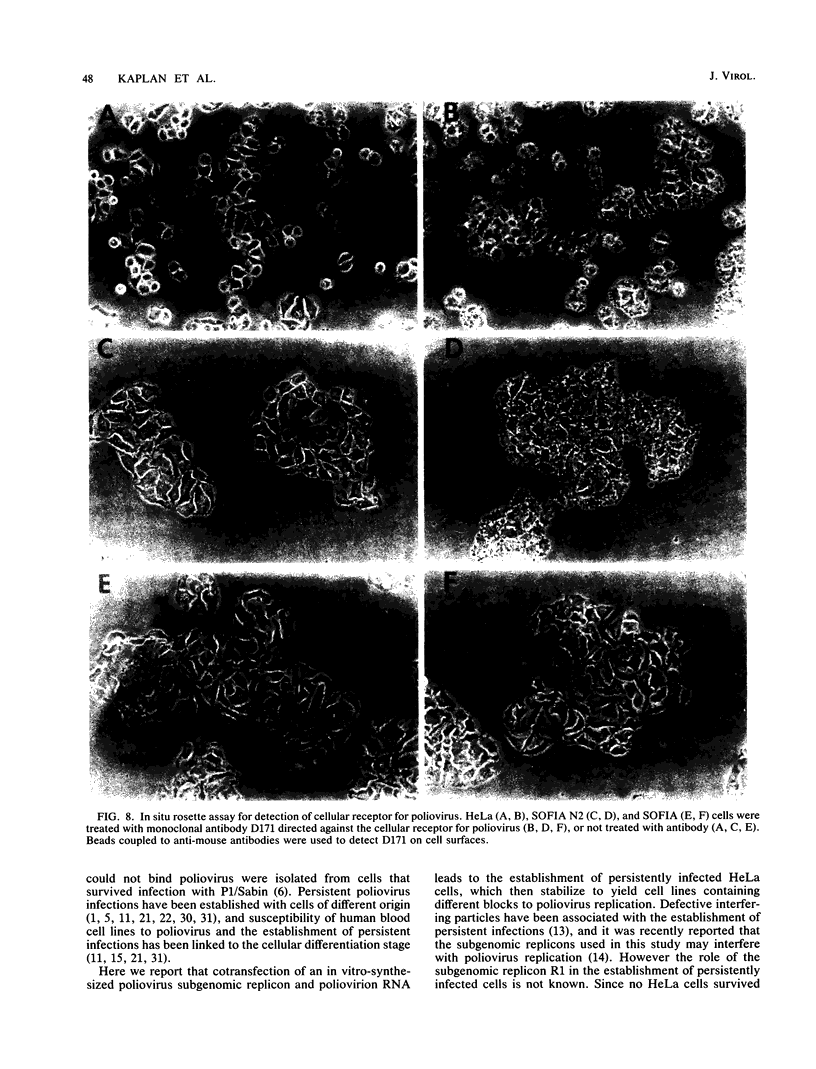
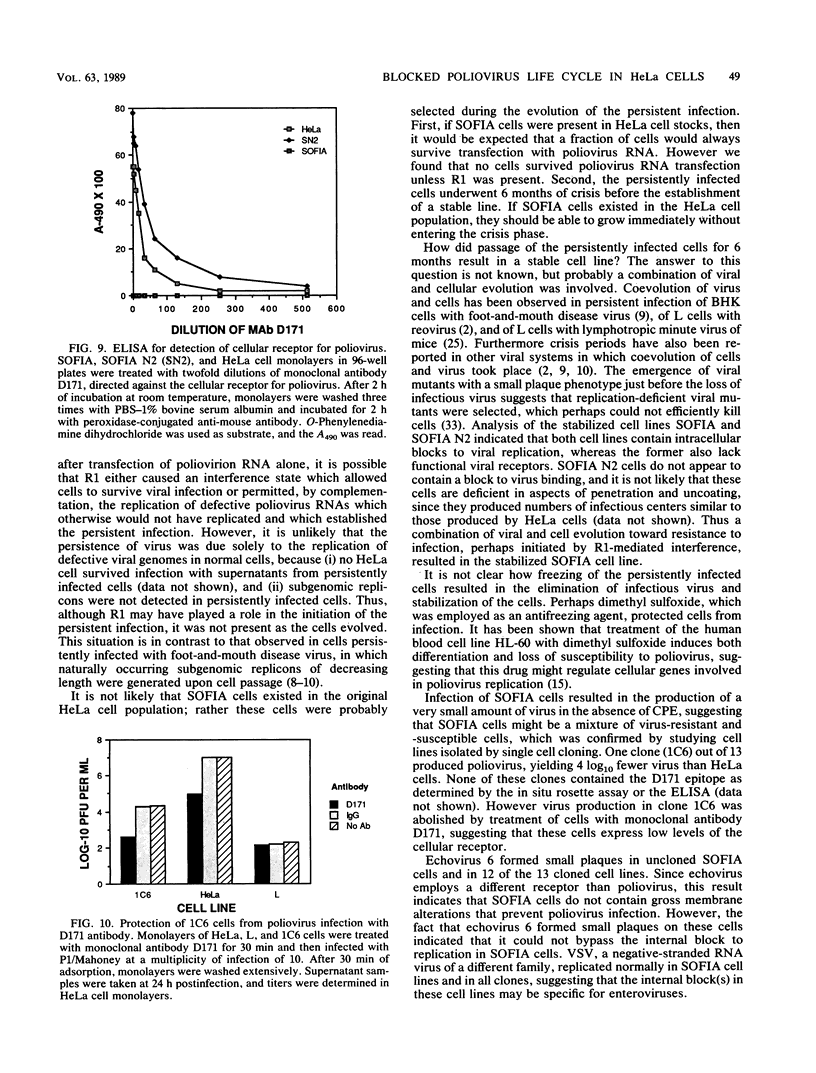
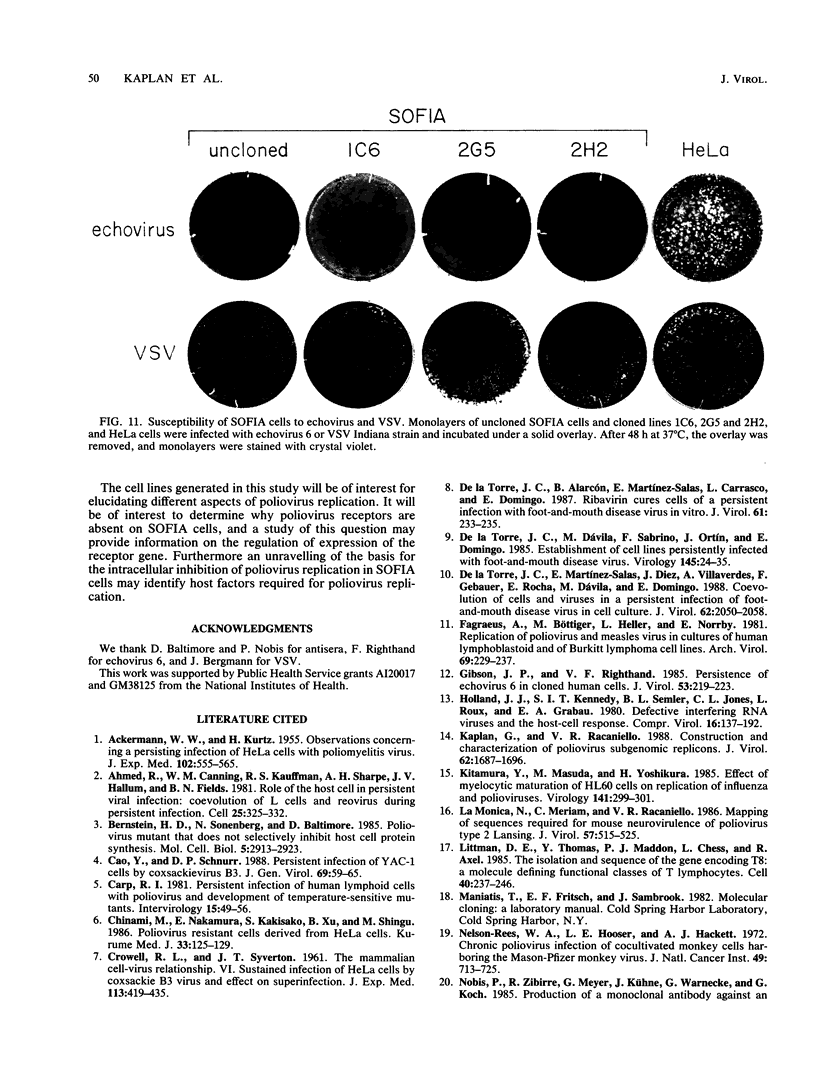
Cotransfection of poliovirus RNA and R1, a poliovirus subgenomic RNA containing a deletion of nearly all of the capsid region, resulted in surviving cells, in contrast to the complete cell death observed after transfection with viral RNA. Cells that survived the cotransfection grew into colonies, produced infectious poliovirus, and underwent cycles of cell lysis (crisis periods) where less than 1% of the cells survived, followed by periods of growth. Poliovirus evolved during the persistent infection as judged by changes in plaque size. After passage for 6 months, a stable line called SOFIA emerged that no longer produced infectious virus and did not contain viral proteins or viral RNA. Cells frozen in liquid N2 while still in crisis and recultured 4 months later (named SOFIA N2) were also stabilized. After infection with poliovirus, SOFIA N2 cells showed a delay in the development of cytopathic effect, viral production, and cellular death when compared with HeLa cells. In contrast, SOFIA cells did not develop cytopathic effect and produced 10,000 times less virus than SOFIA N2 or HeLa cells. Viral production was delayed in SOFIA and SOFIA N2 cells transfected with poliovirus RNA when compared with HeLa cells, suggesting the presence of an intracellular block to poliovirus replication. Analysis of the cellular receptor for poliovirus by virus binding, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and in situ rosette assays with an antireceptor monoclonal antibody showed that receptors were expressed in SOFIA N2 cells but not in SOFIA cells. Echovirus 6, an enterovirus which uses a different cellular receptor, formed small plaques on SOFIA cells. Vesicular stomatitis virus formed plaques of similar size on SOFIA and HeLa cells, suggesting that the intracellular block was specific for enteroviruses. Cotransfection of the subgenomic replicon R1 with poliovirion RNA therefore resulted in the selection of HeLa cell variants containing blocks to poliovirus replication at the level of receptor and within the cell.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERMANN W. W., KURTZ H. Observations concerning a persisting infection of HeLa cells with poliomyelitis virus. J Exp Med. 1955 Nov 1;102(5):555–565. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.5.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed R., Canning W. M., Kauffman R. S., Sharpe A. H., Hallum J. V., Fields B. N. Role of the host cell in persistent viral infection: coevolution of L cells and reovoirus during persistent infection. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWELL R. L., SYVERTON J. T. The mammalian cell-virus relationship. VI. Sustained infection of HeLa cells by Coxsackie B3 virus and effect on superinfection. J Exp Med. 1961 Feb 1;113:419–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y., Schnurr D. P. Persistent infection of YAC-1 cells by coxsackievirus B3. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):59–65. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp R. I. Persistent infection of human lymphoid cells with poliovirus and development of temperature-sensitive mutants. Intervirology. 1981;15(1):49–56. doi: 10.1159/000149214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinami M., Nakamura E., Kakisako S., Xu B., Shingu M. Poliovirus resistant cells derived from HeLa cells. Kurume Med J. 1986;33(3):125–129. doi: 10.2739/kurumemedj.33.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagraeus A., Böttiger M., Heller L., Norrby E. Replication of poliovirus and measles virus in cultures of human lymphoblastoid and of Burkitt lymphoma cell lines. Arch Virol. 1981;69(3-4):229–237. doi: 10.1007/BF01317338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. P., Righthand V. F. Persistence of echovirus 6 in cloned human cells. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):219–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.219-223.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R. Construction and characterization of poliovirus subgenomic replicons. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1687–1696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1687-1696.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Masuda M., Yoshikura H. Effect of myelocytic maturation of HL60 cells on replication of influenza and polioviruses. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):299–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Meriam C., Racaniello V. R. Mapping of sequences required for mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):515–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.515-525.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R., Thomas Y., Maddon P. J., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and sequence of the gene encoding T8: a molecule defining functional classes of T lymphocytes. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson-Rees W. A., Hooser L. E., Hackett A. J. Chronic poliovirus infection of cocultivated monkey cells harboring the Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):713–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobis P., Zibirre R., Meyer G., Kühne J., Warnecke G., Koch G. Production of a monoclonal antibody against an epitope on HeLa cells that is the functional poliovirus binding site. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2563–2569. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Toda G., Oka H., Nomoto A., Yoshikura H. Poliovirus infection of established human blood cell lines: relationship between the differentiation stage and susceptibility of cell killing. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):238–245. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90403-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PACSA S. Poliovirus-carrying lines of HeLa cells: their establishment and sensitivity to viruses. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1961;8:329–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Meriam C. Poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutant containing a single nucleotide deletion in the 5'-noncoding region of the viral RNA. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):498–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Tal J. Coevolution of cells and virus as a mechanism for the persistence of lymphotropic minute virus of mice in L-cells. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):424–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.424-430.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Richards O. C., Green J., Ehrenfeld E. Characterization of a cell culture persistently infected with the DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1118–1122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1118-1122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEMOTO K. K., HABEL K. Virus-cell relationship in a carrier culture of HeLa cells and Coxsackie A9 virus. Virology. 1959 Jan;7(1):28–44. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticehurst J. R., Racaniello V. R., Baroudy B. M., Baltimore D., Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of hepatitis A virus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5885–5889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M., DULBECCO R. Properties of a HeLa cell culture with increased resistance to poliomyelitis virus. Virology. 1958 Jun;5(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Hofmann L., Wurster K. G., Flehmig B. Persistent infection of human fibroblasts by hepatitis A virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):609–615. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. E. Susceptibility of human lymphoblasts (RPMI 7466) to viral infections in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Mar;130(3):702–710. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E., Kuhn R. J., Pincus S., Yang C. F., Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Takeda N. Molecular events leading to picornavirus genome replication. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;7:251–276. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_7.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre J. C., Alarcón B., Martínez-Salas E., Carrasco L., Domingo E. Ribavirin cures cells of a persistent infection with foot-and-mouth disease virus in vitro. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):233–235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.233-235.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre J. C., Dávila M., Sobrino F., Ortín J., Domingo E. Establishment of cell lines persistently infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):24–35. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre J. C., Martínez-Salas E., Diez J., Villaverde A., Gebauer F., Rocha E., Dávila M., Domingo E. Coevolution of cells and viruses in a persistent infection of foot-and-mouth disease virus in cell culture. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2050–2058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2050-2058.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]