Abstract
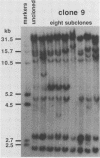
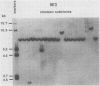
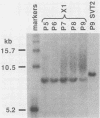
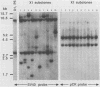
Frequencies of spontaneous DNA rearrangement within or near integrated simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA were measured in four transformed mouse and rat cell lines of independent origin and in five clones of the SV40-transformed mouse line SVT2. Rearrangements were detected as polymorphisms of restriction enzyme fragment length in subclones of the lines. At least 17% of the subclones of each line had detectable rearrangements. The rate of rearrangement was calculated to be at least 5 x 10(-3) events per cell per division. No rearrangements were detected in sequences of an immunoglobulin gene, part of the coding region of the mouse protein p53, and five proto-oncogenes. The possible role of recombination between duplicated segments of integrated SV40 DNA in generating rearrangements was studied in the five SVT2 clones, which differed in the number of duplications within a single SV40 DNA segment. The SVT2 clone that had no duplications, M3, became rearranged further at least as frequently as did closely related lines with one, two, or three duplications. Another line in this group that had one small duplication, X1, had a much higher frequency of rearrangement than did the others; integrated SV40 DNA of X1 became mostly rearranged within 100 cell divisions. The examples of M3 and X1 suggested that the high rate of rearrangement characteristic of integrated SV40 DNA was influenced more by the presence of particular sequences within or near integrated SV40 DNA than by the number or extent of duplicated sequences.
Full text
PDF

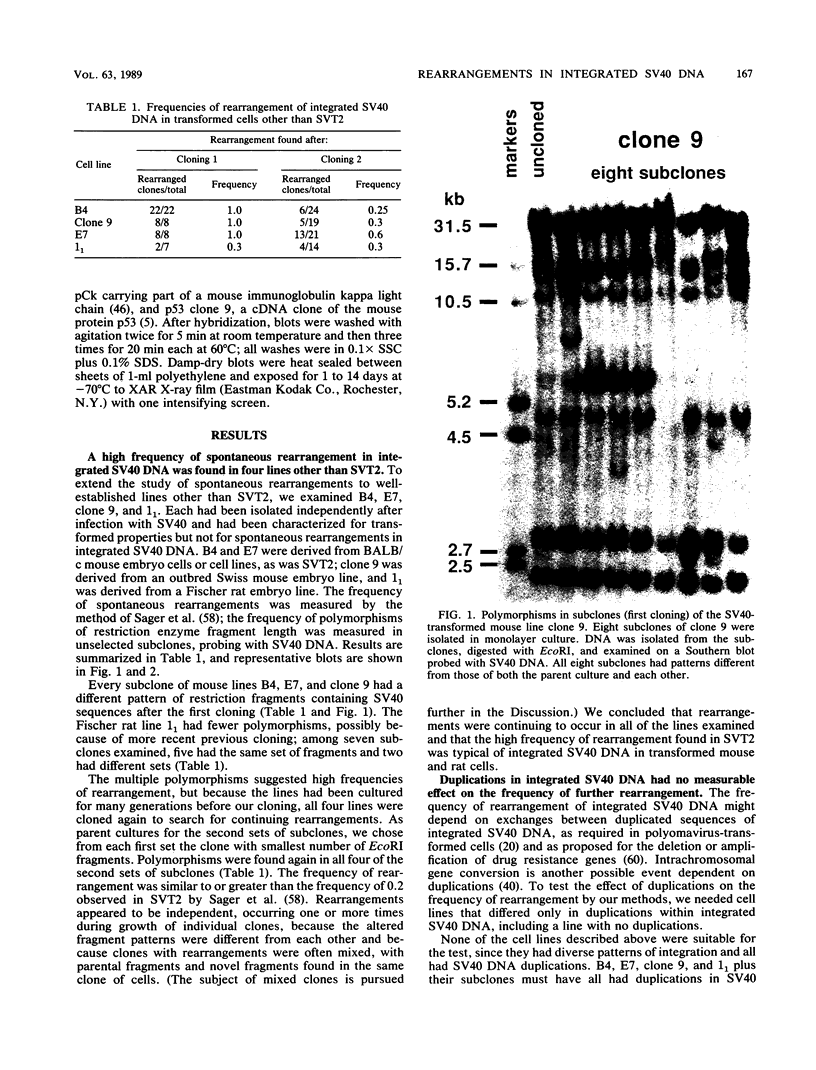
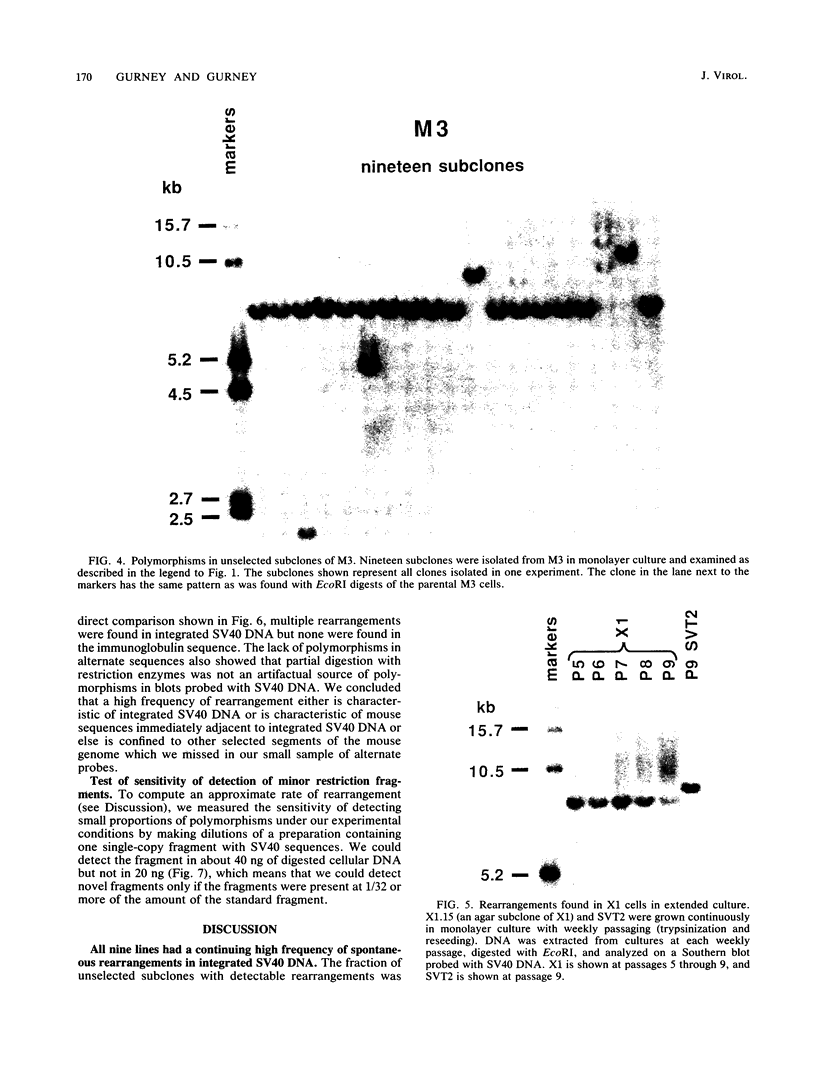
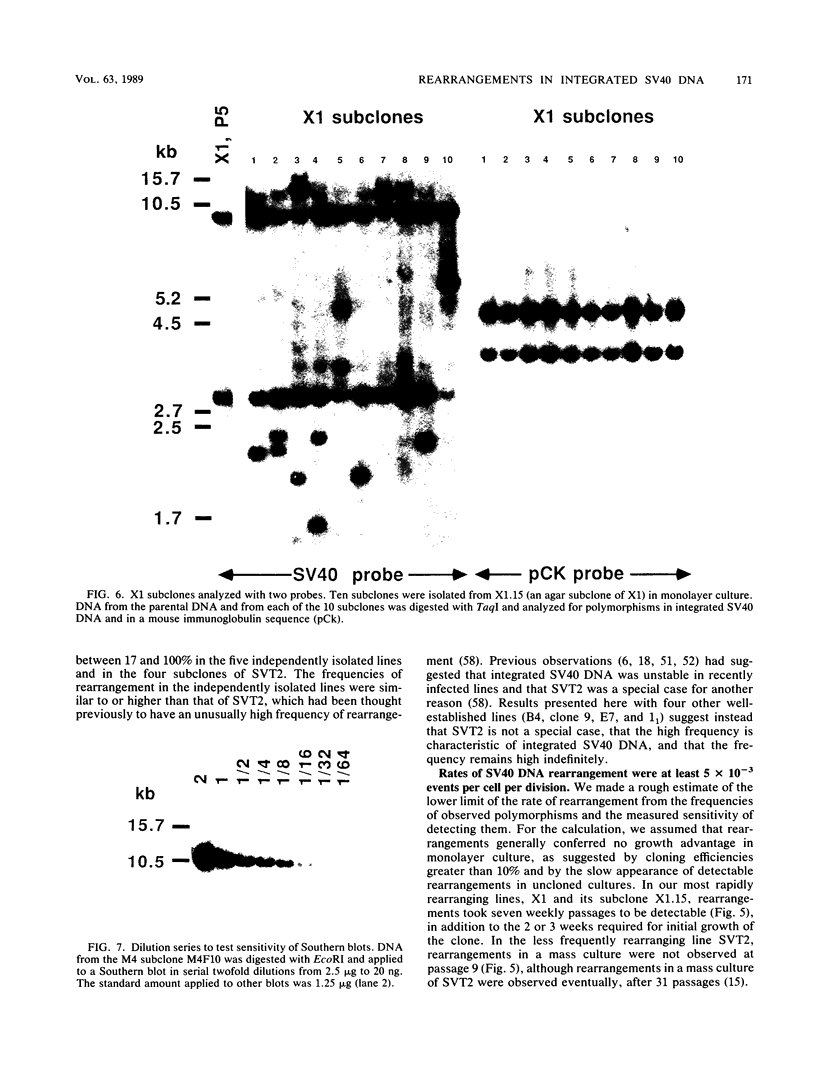



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Development of 3T3-like lines from Balb-c mouse embryo cultures: transformation susceptibility to SV40. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2):141–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baran N., Neer A., Manor H. "Onion skin" replication of integrated polyoma virus DNA and flanking sequences in polyoma-transformed rat cells: termination within a specific cellular DNA segment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):105–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basilico C., Gattoni S., Zouzias D., Valle G. D. Loss of integrated viral DNA sequences in polyomatransformed cells is associated with an active viral A function. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):645–659. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. A., Brockman W. W. Rearrangement of integrated viral DNA sequences in mouse cells transformed by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):872–879. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.872-879.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. A., Christensen J., Brockman W. W. Characterization of a T-antigen-negative revertant isolated from a mouse cell line which undergoes rearrangement of integrated simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):115–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.115-124.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birg F., Dulbecco R., Fried M., Kamen R. State and organization of polyoma virus DNA sequences in transformed rat cell lines. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):633–648. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.633-648.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanck G., Chen S., Pollack R. Integration, loss, and reacquisition of defective viral DNA in SV40-transformed mouse cell lines. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):413–428. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Stringer J., Mitchison T., Sambrook J. Integration and excision of SV40 DNA from the chromosome of a transformed cell. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. Studies on simian virus 40 excision from cellular chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):709–719. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., DeRose M. L., Gaudray P., Moore C. M., Needham-Vandevanter D. R., Von Hoff D. D., Wahl G. M. Double minute chromosomes can be produced from precursors derived from a chromosomal deletion. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1525–1533. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., Gaudray P., De Rose M. L., Emery J. F., Meinkoth J. L., Nakkim E., Subler M., Von Hoff D. D., Wahl G. M. Characterization of an episome produced in hamster cells that amplify a transfected CAD gene at high frequency: functional evidence for a mammalian replication origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1740–1750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Simmons D. T., Martin M. A., Mora P. T. Identification and partial characterization of new antigens from simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.463-471.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Blanck G., Pollack R. Reacquisition of a functional early region by a mouse transformant containing only defective simian virus 40 DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):666–670. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Grass D. S., Blanck G., Hoganson N., Manley J. L., Pollack R. E. A functional simian virus 40 origin of replication is required for the generation of a super T antigen with a molecular weight of 100,000 in transformed mouse cells. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):492–502. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.492-502.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chepelinsky A. B., Chiu N. H., Zannis-Hadjopoulos M., Wang S. S., Martin R. G. Flat revertants of temperature-insensitive transformants induced by simian virus 40 tsA mutants lose their ability to express T-antigen. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):992–994. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.992-994.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Rigby P. W. Cloning and characterization of the integrated viral DNA from three lines of SV40-transformed mouse cells. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):547–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantuoni V., Dailey L., Basilico C. Amplification of integrated viral DNA sequences in polyoma virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3850–3854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantuoni V., Dailey L., Valle G. D., Basilico C. Requirements for excision and amplification of integrated viral DNA molecules in polyoma virus-transformed cells. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):617–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.617-628.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Chen E. Y., Smith D. H., Levinson A. D. Identification and nucleotide sequence of a human locus homologous to the v-myc oncogene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):722–725. doi: 10.1038/301722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drobetsky E., Meuth M. Increased mutational rates in Chinese hamster ovary cells serially selected for drug resistance. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1882–1885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Defeo D., Shih T. Y., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Tsuchida N., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. The p21 src genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses originate from divergent members of a family of normal vertebrate genes. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):506–511. doi: 10.1038/292506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluck M. M., Benjamin T. L. Comparisons of two early gene functions essential for transformation in polyoma virus and SV-40. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):205–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulotto E., Knights C., Stark G. R. Hamster cells with increased rates of DNA amplification, a new phenotype. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Gurney T., Jr Density dependent inhibition of both growth and T-antigen expression in revertants isolated from simian virus 40-transformed mouse SVT2 cells. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):667–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.667-671.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney T., Jr, Woolf M. J., Abplanalp L. J., McKittrick N. H., Dietz J. N., Cole B. C. Elimination of Mycoplasma hyorhinis infections from four cell lines. In Vitro. 1981 Nov;17(11):993–996. doi: 10.1007/BF02618424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn P., Kapp L. N., Morgan W. F., Painter R. B. Chromosomal changes without DNA overproduction in hydroxyurea-treated mammalian cells: implications for gene amplification. Cancer Res. 1986 Sep;46(9):4607–4612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J. B., Murphy D., Defendi V. Instability of integrated viral DNA in mouse cells transformed by simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1736–1740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J., Murphy D., Defendi V. Amplification and rearrangement of integrated SV40 DNA sequences accompany the selection of anchorage-independent transformed mouse cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketner G., Kelly T. J., Jr Structure of integrated simian virus 40 DNA in transformed mouse cells. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 5;144(2):163–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., May E., Cassingena R., May P. Simian virus 40-transformed cells express new species of proteins precipitable by anti-simian virus 40 tumor serum. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):472–483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.472-483.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S. Carcinogen-mediated amplification of viral DNA sequences in simian virus 40-transformed Chinese hamster embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6144–6148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt A., Chen S., Blanck G., George D., Pollack R. E. Two integrated partial repeats of simian virus 40 together code for a super-T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):742–750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liskay R. M., Stachelek J. L. Evidence for intrachromosomal gene conversion in cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchionni M. A., Roufa D. J. Replication of viral DNA sequences integrated within the chromatin of SV40-transformed Chinese hamster lung cells. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90307-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani B. D., Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in a single cell cycle in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1901–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Hiwasa T., Oda K. I. Characterization of flat revertant cells isolated from simian virus 40-transformed mouse and rat cells which contain multiple copies of viral genomes. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1028–1043. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1028-1043.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Oda K. Two types of deletion within integrated viral sequences mediate reversion of simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):479–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.479-489.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz B. Herpes simplex virus infection generates large tandemly reiterated simian virus 40 DNA molecules in a transformed hamster cell line. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1427–1434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1427-1434.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Jeltsch J. M., Gannon F. Characterization of a gene encoding a 115 K super T antigen expressed by a SV40-transformed rat cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4111–4128. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Kress M., Daya-Grosjean L., Monier R., May P. Mapping of the viral mRNA encoding a super-T antigen of 115,000 daltons expressed in simian virus 40-transformed rat cell lines. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):24–35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.24-35.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P., Resche-Rigon M., Borde J., Breugnot C., May E. Conversion through homologous recombination of the gene encoding Simian virus 40 115,000-molecular-weight super T antigen to a gene encoding a normal-size large T antigen variant. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1141–1151. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougneau E., Birg F., Rassoulzadegan M., Cuzin F. Integration sites and sequence arrangement of SV40 DNA in a homogeneous series of transformed rat fibroblast lines. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):917–927. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90569-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounts P., Kelly T. J., Jr Rearrangements of host and viral DNA in mouse cells transformed by simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):431–460. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill F. J. Control of nuclear division in sv40 and adenovirus type 12 transformed mouse 3t3 cells. Int J Cancer. 1975 May 15;15(5):715–723. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad I., Zouzias D., Basilico C. State of the viral DNA in rat cells transformed by polyoma virus. I. Virus rescue and the presence of nonintergrated viral DNA molecules. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):436–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.436-444.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Devare S. G., Reddy E. P., Aaronson S. A. In vivo identification of the transforming gene product of simian sarcoma virus. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1131–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.6293053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Buck L. B., Axel R. A structure for amplified DNA. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Anisowicz A., Howell N. Genomic rearrangements in a mouse cell line containing integrated SV40 DNA. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Botchan M., Gallimore P., Ozanne B., Pettersson U., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Viral DNA sequences in cells transformed by simian virus 40, adenovirus type 2 and adenovirus type 5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):615–632. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sherwood S. W., Hill A. B., Johnston R. N. Overreplication and recombination of DNA in higher eukaryotes: potential consequences and biological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Jones K. W. The use of heparin as a simple cost-effective means of controlling background in nucleic acid hybridization procedures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5627–5638. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Smith R., Paucha E. Characterization of different tumor antigens present in cells transformed by simian virus 40. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):335–346. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg B., Pollack R., Topp W., Botchan M. Isolation and characterization of T antigen-negative revertants from a line of transformed rat cells containing one copy of the SV40 genome. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):19–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayalaxmi, Evans H. J., Ray J. H., German J. Bloom's syndrome: evidence for an increased mutation frequency in vivo. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):851–853. doi: 10.1126/science.6879180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Baltimore D. Cellular RNA homologous to the Abelson murine leukemia virus transforming gene: expression and relationship to the viral sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):773–779. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. T., Schultz R. A., Chang C. C., Wade M. H., Trosko J. E. Elevated spontaneous mutation rate in Bloom syndrome fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3133–3137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. F., Dulbecco R. Production of SV40 virus in heterokaryons of transformed and susceptible cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1396–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock D. M., Cooper I. A. Evidence for double replication of chromosomal DNA segments as a general consequence of DNA replication inhibition. Cancer Res. 1981 Jun;41(6):2483–2490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouzias D., Prasad I., Basilico C. State of the viral DNA in rat cells transformed by polyma virus. II. Identification of the cells containing nonintegrated viral DNA and the effect of viral mutations. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):142–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.142-150.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]