Abstract
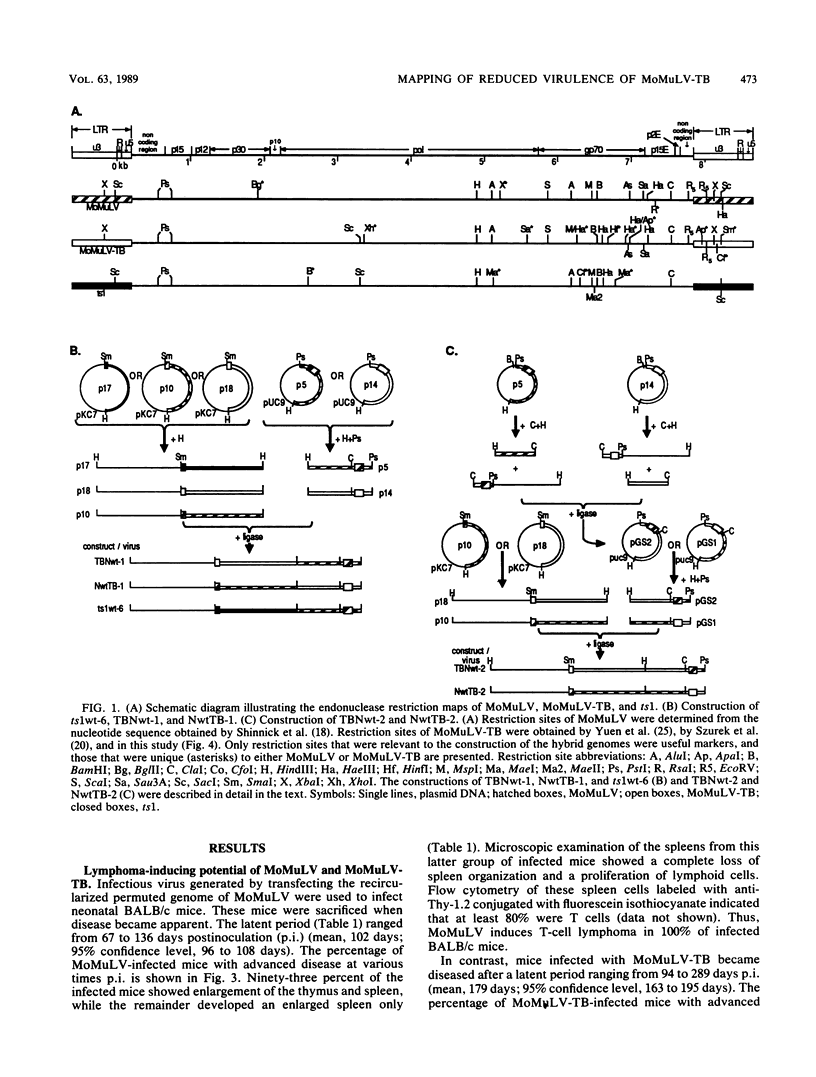
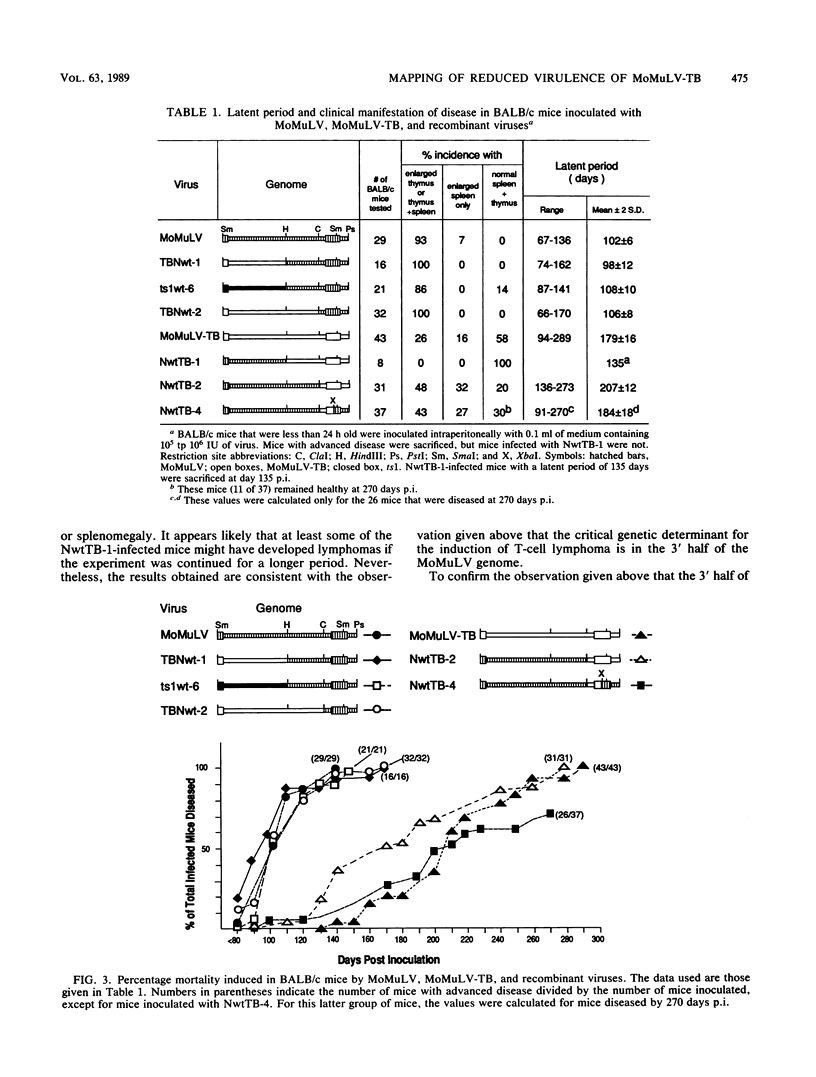
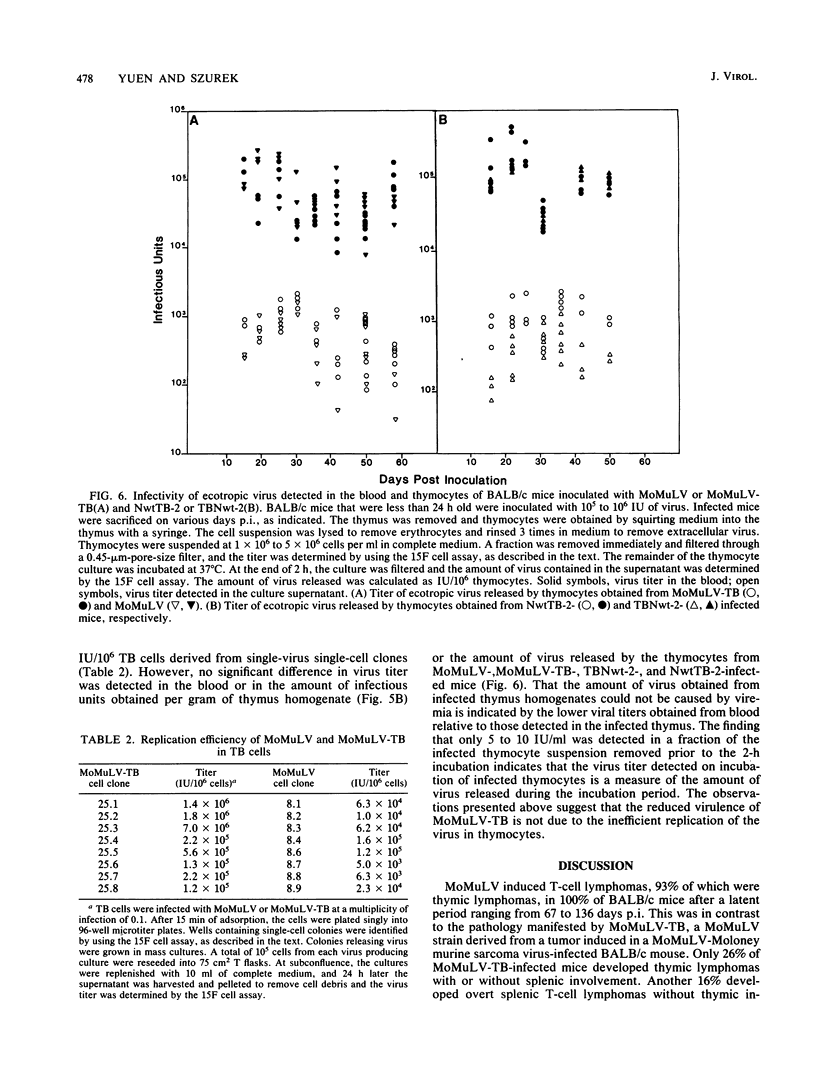
Chimeric constructs were generated by exchanging genomic fragments between the potent T-cell lymphoma inducer Moloney murine leukemia virus (MoMuLV) and its derivative MoMuLV-TB, which induces T-cell lymphoma after a relatively longer latent period. Analysis of the T-cell lymphoma-inducing potential of the hybrid viruses that were obtained localized the primary determinant critical to efficient T-cell lymphoma induction to the MoMuLV ClaI-XbaI fragment which comprises 48 nucleotides (nt) of p15E, p2E, the 3'-noncoding sequence, and 298 nt of U3. The 438-base-pair ClaI-XbaI fragments of MoMuLV and MoMuLV-TB differed in only 11 nt. Nine mutations were found within the enhancer. These mutations occurred within the two CORE, the two GRE-LVa, and two of the four NF1 nuclear factor-binding motifs. MoMuLV-TB replicated better than MoMuLV in thymus-bone marrow (TB) cells, a cultured cell line of lymphoid origin. In addition, MoMuLV-TB and NwtTB-2, a recombinant virus with the ClaI-SmaI fragment of MoMuLV-TB in a MoMuLV background, replicated in thymocytes as efficiently as did MoMuLV or TBNwt-2, the reciprocal recombinant virus, with the ClaI-SmaI fragment of MoMuLV in a MoMuLV-TB background. Like NwtTB-4, a recombinant virus with the ClaI-XbaI fragment of MoMuLV-TB in a MoMuLV background, NwtTB-2 induced lymphoma after a long latent period. The finding given above suggests that thymotropism is not the only factor that determines the T-cell lymphoma-inducing potential of MoMuLV. It appears likely that mutations in one or more of the MoMuLV-TB nuclear factor-binding motifs may have altered the interaction of the enhancer with specific nuclear factors; this, in turn, may affect the T-cell lymphoma-inducing potential of MoMuLV-TB.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALL J. K., HUH T. Y., MCCARTER J. A. ON THE STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION OF EPIDERMAL PAPILLOMATA IN MICE. Br J Cancer. 1964 Mar;18:120–123. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1964.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J., McCarter J. A., Sunderland S. M. Evidence for helper independent murine sarcoma virus. I. Segregation of replication-defective and transformation-defective viruses. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):268–284. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D., Haseltine W. A. Tissue-specific transcription preference as a determinant of cell tropism and leukaemogenic potential of murine retroviruses. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):159–162. doi: 10.1038/312159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. R., Chandy K. G., Brightman B. K., Gupta S., Fan H. Effects of nonleukemogenic and wild-type Moloney murine leukemia virus on lymphoid cells in vivo: identification of a preleukemic shift in thymocyte subpopulations. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):423–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.423-430.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. Mapping the viral sequences conferring leukemogenicity and disease specificity in Moloney and amphotropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):448–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.448-456.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. The tandem direct repeats within the long terminal repeat of murine leukemia viruses are the primary determinant of their leukemogenic potential. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):945–952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.945-952.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Eisenman R. N., McKnight S. L. Delineation of transcriptional control signals within the Moloney murine sarcoma virus long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1948–1958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. At least four viral genes contribute to the leukemogenicity of murine retrovirus MCF 247 in AKR mice. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):158–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.158-165.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Takimoto M., Adachi A., Kakuyama M., Kato S., Kakimi K., Fukuoka K., Ogiu T., Matsuyama M. Sequences responsible for erythroid and lymphoid leukemia in the long terminal repeats of Friend-mink cell focus-forming and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1861–1866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1861-1866.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Golemis E., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Disease specificity of nondefective Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses is controlled by a small number of nucleotides. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):693–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.693-700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter J. A., Ball J. K., Frei J. V. Lower limb paralysis induced in mice by a temperature-sensitive mutant of Moloney leukemia virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):179–183. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Signorelli K., Collins L. The envelope gene and long terminal repeat sequences contribute to the pathogenic phenotype of helper-independent Friend viruses. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):788–794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.788-794.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Gordon M. L., Goff S. P. Mutations in the gag gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus: effects on production of virions and reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):918–924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.918-924.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szurek P. F., Yuen P. H., Jerzy R., Wong P. K. Identification of point mutations in the envelope gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB temperature-sensitive paralytogenic mutant ts1: molecular determinants for neurovirulence. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):357–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.357-360.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Russ L. J., McCarter J. A. Rapid, selective procedure for isolation of spontaneous temperature-sensitive mutants of Moloney leukemia virus. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):424–431. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Soong M. M., Yuen P. H. Replication of murine leukemia virus in heterologous cells: interaction between ecotropic and xenotropic viruses. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):366–378. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F. K., Davison B., Chaffin K. Murine leukemia virus long terminal repeat sequences can enhance gene activity in a cell-type-specific manner. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2832–2835. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Malehorn D., Knupp C., Wong P. K. A 1.6-kilobase-pair fragment in the genome of the ts1 mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB that is associated with temperature sensitivity, nonprocessing of Pr80env, and paralytogenesis. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):364–373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.364-373.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Malehorn D., Nau C., Soong M. M., Wong P. K. Molecular cloning of two paralytogenic, temperature-sensitive mutants, ts1 and ts7, and the parental wild-type Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):178–185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.178-185.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Tzeng E., Knupp C., Wong P. K. The neurovirulent determinants of ts1, a paralytogenic mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB, are localized in at least two functionally distinct regions of the genome. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):59–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.59-65.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


