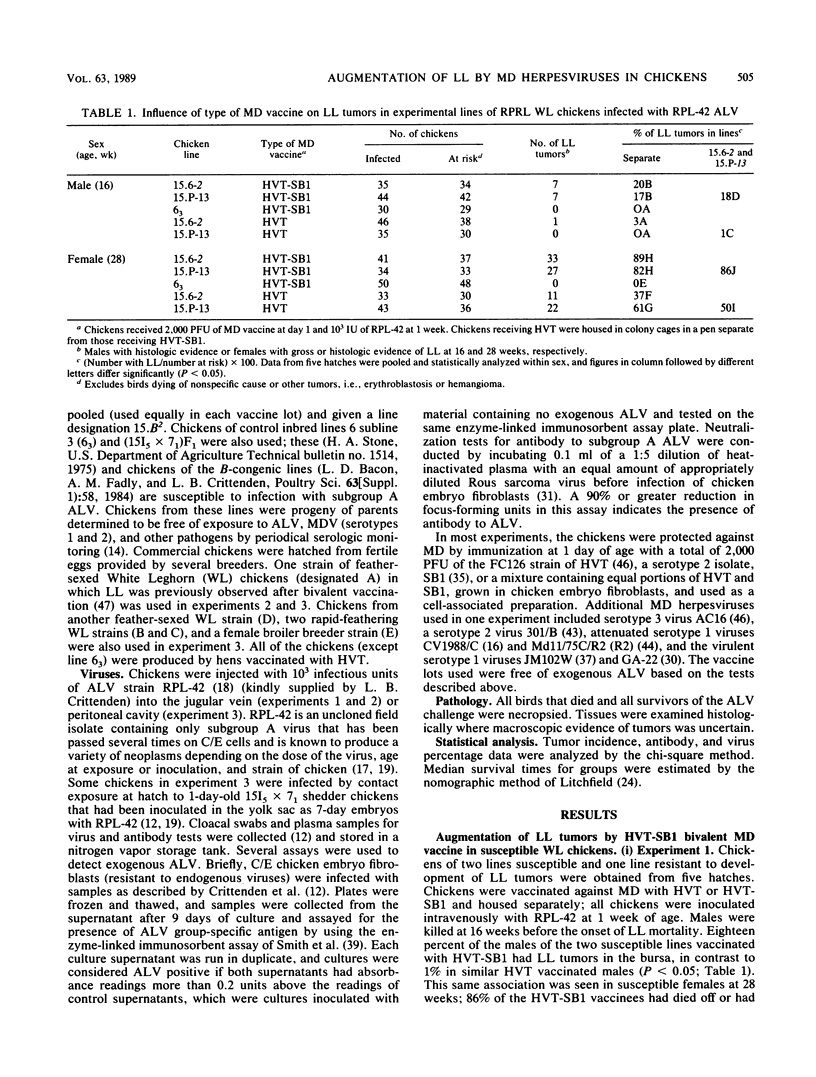
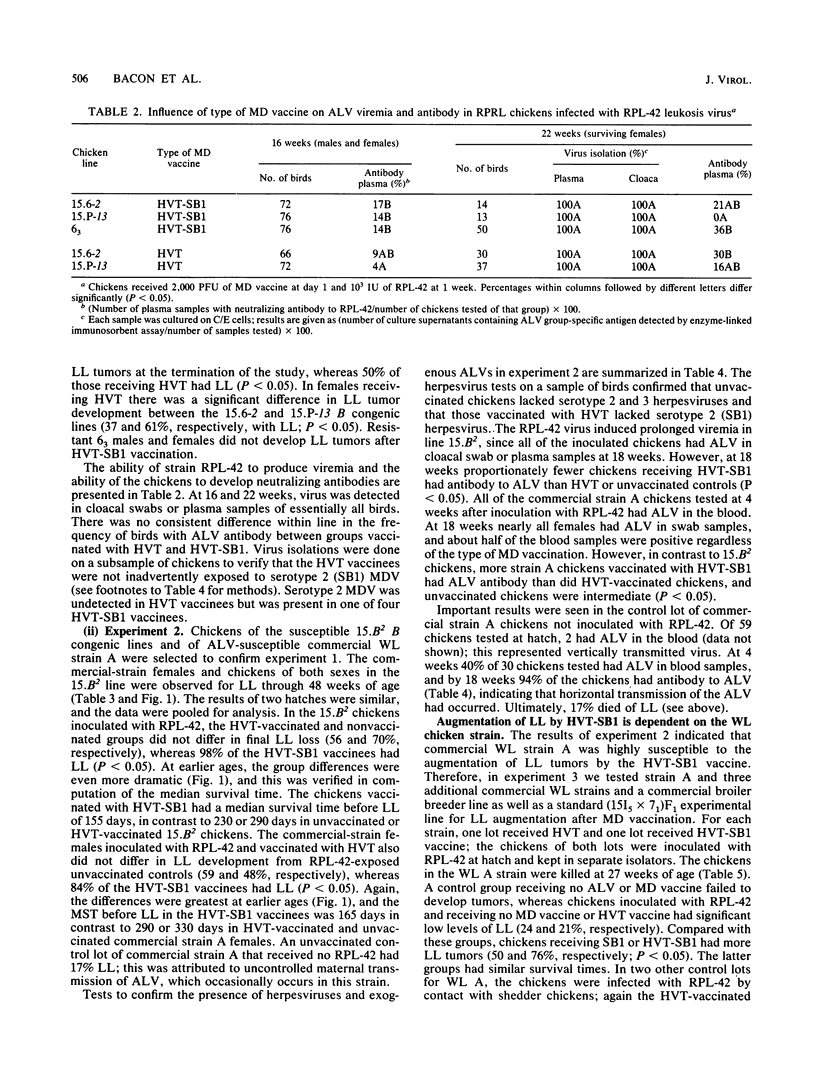
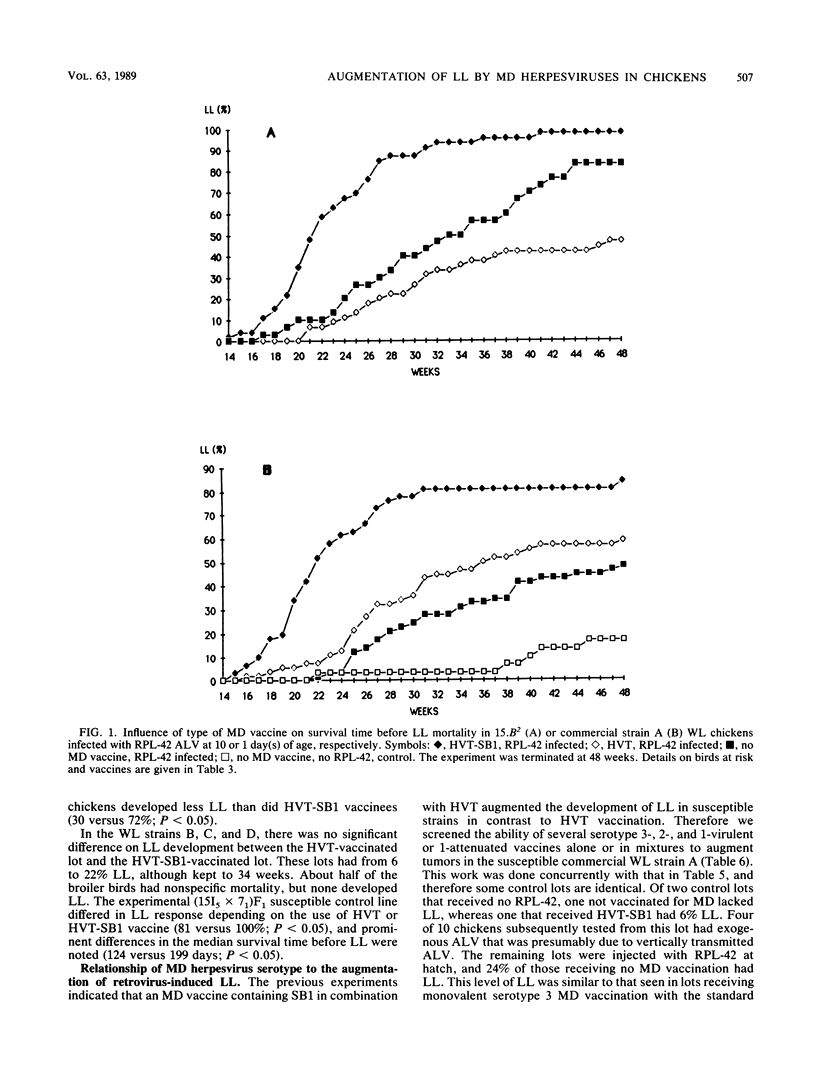
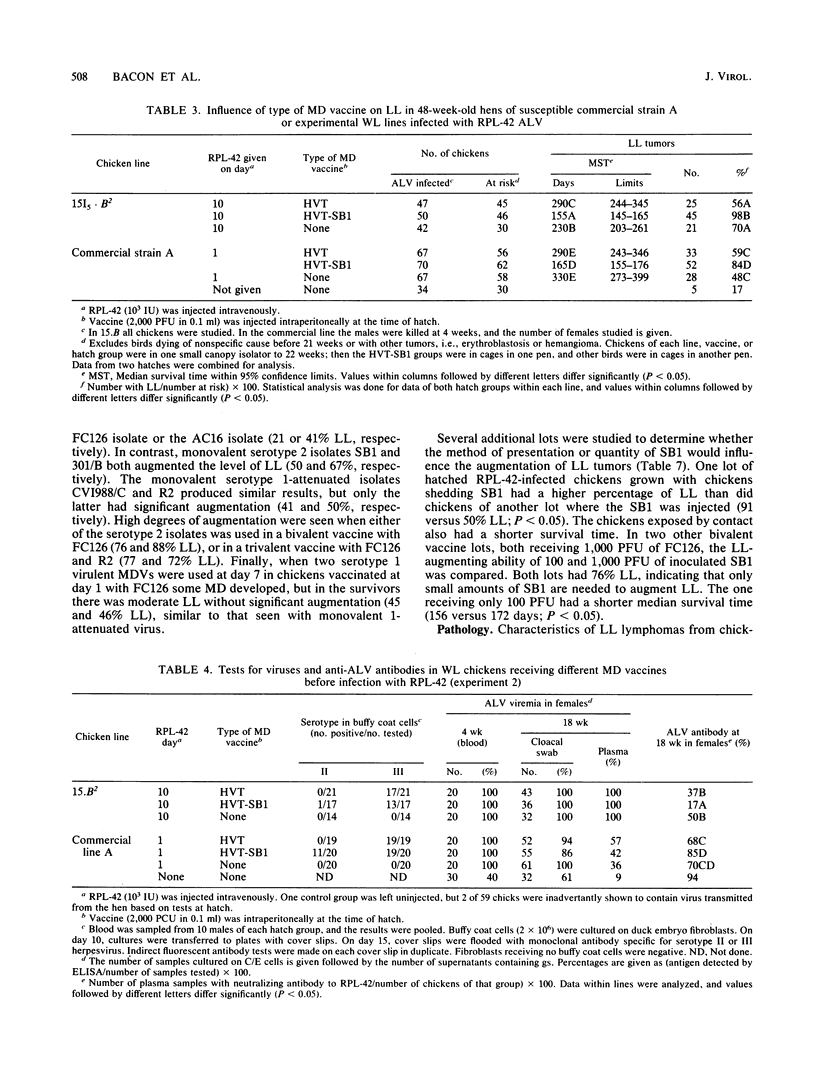
Abstract
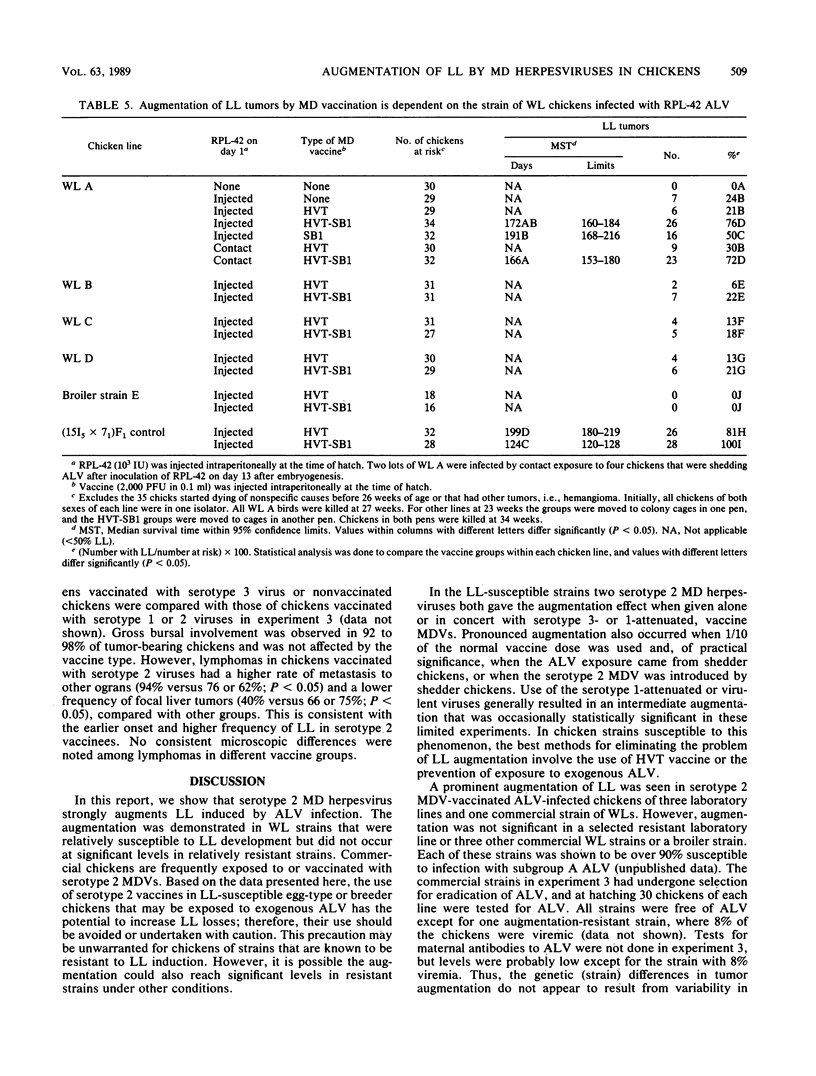
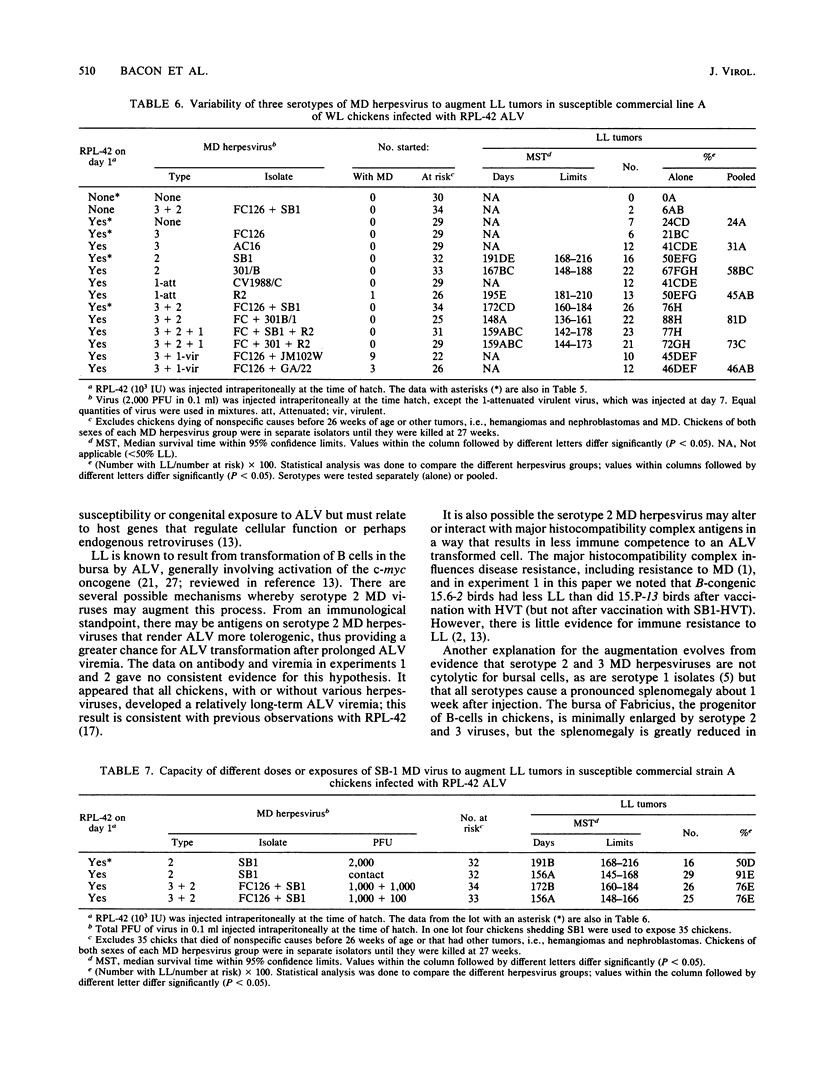
Our objective was to determine whether the cell-associated herpesvirus vaccines used in chickens to control Marek's disease tumors can augment development of lymphoid leukosis (LL) induced by exogenous avian leukosis virus (ALV). Various single or mixed Marek's disease vaccines were inoculated at day 1, and ALV was injected at 1 to 10 days, with chickens of several experimental or commercial strains. Development of LL was monitored at 16 to 48 weeks in various experiments. In several strains of chickens we repeatedly found that the widely used serotype 3 turkey herpesvirus vaccine did not augment LL in comparison with unvaccinated controls. However, LL development and incidence were prominently augmented in several chicken strains vaccinated with serotype 2 vaccines, used alone or as mixtures with other serotypes. In one chicken strain, augmentation was demonstrated after natural exposure to ALV or serotype 2 Marek's disease virus viremic shedder chickens. Augmentation of LL by virulent or attenuated Marek's disease viruses of serotype 1 was intermediate in effect. Serotype 2 Marek's disease virus augmentation of LL was prominent in three laboratory lines and one commercial strain of White Leghorns, but it was not observed in an LL-resistant laboratory line or four commercial strains susceptible to ALV infection. Chickens developed similar levels of viremia and neutralizing antibodies to ALV regardless of the presence of augmentation of LL, suggesting that the mechanism of enhanced LL did not result from differences in susceptibility or immune response to ALV. We postulate that the serotype 2 herpesviruses may augment LL through one of several possible influences on bursal cells that are subsequently transformed by exogenous ALV.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacon L. D., Ch'ng L. K., Spencer J., Benedict A. A., Fadly A. M., Witter R. L., Crittenden L. B. Tests of association of immunoglobulin allotype genes and viral oncogenesis in chickens. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(4):213–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00373015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon L. D. Influence of the major histocompatibility complex on disease resistance and productivity. Poult Sci. 1987 May;66(5):802–811. doi: 10.3382/ps.0660802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calneck B. W., Payne L. N. Lack of correlation between Marena tumor induction and expression of endogenous avian RNA tumor virus genome. Int J Cancer. 1976 Feb 15;17(2):235–244. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Adldinger H. K., Kahn D. E. Feather follicle epithelium: a source of enveloped and infectious cell-free herpesvirus from Marek's disease. Avian Dis. 1970 May;14(2):219–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Carlisle J. C., Fabricant J., Murthy K. K., Schat K. A. Comparative pathogenesis studies with oncogenic and nononcogenic Marek's disease viruses and turkey herpesvirus. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Apr;40(4):541–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Schat K. A., Peckham M. C., Fabricant J. Field trials with a bivalent vaccine (HVT and SB-1) against Marek's disease. Avian Dis. 1983 Jul-Sep;27(3):844–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Shek W. R., Schat K. A. Latent infections with Marek's disease virus and turkey herpesvirus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Mar;66(3):585–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill A. E., Biggs P. M. Agent of Marek's disease in tissue culture. Nature. 1967 Jul 29;215(5100):528–530. doi: 10.1038/215528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill A. E., Payne L. N., Chubb R. C. Immunization against Marek's disease using a live attenuated virus. Nature. 1969 Feb 22;221(5182):744–747. doi: 10.1038/221744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden L. B., Eagen D. A., Gulvas F. A. Assays for endogenous and exogenous lymphoid leukosis viruses and chick helper factor with RSV(--) cell lines. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):379–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.379-386.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden L. B., Witter R. L., Okazaki W., Neiman P. E. Lymphoid neoplasms in chicken flocks free of infection with exogenous avian tumor viruses. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jul;63(1):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. G., Kenney S. C., Kamine J., Pagano J. S., Huang E. S. Immediate-early gene region of human cytomegalovirus trans-activates the promoter of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8642–8646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadly A. M., Okazaki W. Studies of avian leukosis virus infection in chickens from a commercial breeder flock. Poult Sci. 1982 Jun;61(6):1055–1060. doi: 10.3382/ps.0611055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadly A. M., Okazaki W., Witter R. L. Hatchery-related contact transmission and short- term small-group-rearing as related to lymphoid-leukosis-virus-eradication programs. Avian Dis. 1981 Jul-Sep;25(3):667–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel J. W., Farrow W. M., Prickett C. O., Smith M. E., Campbell W. F., Groupè V. Responses of isolator-derived and conventional chickens to Marek's disease herpesvirus and avian leukosis virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 May;52(5):1491–1497. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.5.1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakovleva L. S., Mazurenko N. P. Increased susceptibility of leukemia-infected chickens to Marek's disease. Neoplasma. 1979;26(4):393–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITCHFIELD J. T., Jr A method for rapid graphic solution of time-per cent effect curves. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1949 Dec;97(4):399-408, 3 tab. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. F., Liu X., Witter R. L. Monoclonal antibodies with specificity for three different serotypes of Marek's disease viruses in chickens. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):1003–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi L., Newcomb E. W., Dalla-Favera R. Pathogenesis of Burkitt lymphoma: expression of an activated c-myc oncogene causes the tumorigenic conversion of EBV-infected human B lymphoblasts. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90556-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Bednarik D. P., Raj N. B., Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Pitha P. M. Herpes simplex virus type-1 can reactivate transcription of latent human immunodeficiency virus. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):67–70. doi: 10.1038/325067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P., Wolf C., Enrietto P. J., Cooper G. M. A retroviral myc gene induces preneoplastic transformation of lymphocytes in a bursal transplantation assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):222–226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki W., Purchase H. G., Burmester B. R. Protection against Marek's disease by vaccination with a herpesvirus of turkeys. Avian Dis. 1970 May;14(2):413–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W. P., Kufe D., Schlom J., Frankel J. W., Prickett C. O., Groupé V., Spiegelman S. Biological and biochemical evidence for an interaction between Marek's disease herpesvirus and avian leukosis virus in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3175–3178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchase H. G., Burmester B. R., Cunningham C. H. Pathogenicity and Antigenicity of Clones from Strains of Marek's Disease Virus and the Herpesvirus of Turkeys. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):295–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.295-303.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. A VIRUS IN CHICK EMBRYOS WHICH INDUCES RESISTANCE IN VITRO TO INFECTION WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Aug;46(8):1105–1119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.8.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schat K. A., Calnek B. W. Characterization of an apparently nononcogenic Marek's disease virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 May;60(5):1075–1082. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.5.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schat K. A., Calnek B. W., Fabricant J. Influence of the bursa of Fabricius on the pathogenesis of Marek's disease. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):199–207. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.199-207.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen P. F., Smith E. J., Bacon L. D. The ontogeny of blood cells, complement, and immunoglobulins in 3- to 12-week-old 15I5-B congenic white Leghorn chickens. Poult Sci. 1984 Jun;63(6):1083–1093. doi: 10.3382/ps.0631083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. J., Witter R. L., Nazerian K., Burmester B. R. Studies on the etiology of Marek's disease. I. Propagation of the agent in cell culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):173–177. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter R. L. Characteristics of Marek's disease viruses isolated from vaccinated commercial chicken flocks: association of viral pathotype with lymphoma frequency. Avian Dis. 1983 Jan-Mar;27(1):113–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter R. L., Lee L. F., Okazaki W., Purchase H. G., Burmester B. R., Luginbuhl R. E. Oncogenesis by Marek's disease herpesvirus in chickens lacking expression of endogenous (gs, chick helper factor, Rous-associated virus-O) and exogenous avian RNA tumor viruses. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jul;55(1):215–218. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.1.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter R. L., Nazerian K., Purchase H. G., Burgoyne G. H. Isolation from turkeys of a cell-associated herpesvirus antigenically related to Marek's disease virus. Am J Vet Res. 1970 Mar;31(3):525–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter R. L. New serotype 2 and attenuated serotype 1 Marek's disease vaccine viruses: comparative efficacy. Avian Dis. 1987 Oct-Dec;31(4):752–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter R. L., Sharma J. M., Chase W. B., Halvorson D. A., Sivanandan V. Field trials to test the efficacy of polyvalent Marek's disease vaccines in layer and broiler breeder chickens. Poult Sci. 1985 Dec;64(12):2280–2286. doi: 10.3382/ps.0642280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer G. F., Groenendal J. E., Boerrigter H. M., Kok G. L., Pol J. M. Protective efficacy of Marek's disease virus (MDV) CVI-988 CEF65 clone C against challenge infection with three very virulent MDV strains. Avian Dis. 1986 Apr-Jun;30(2):276–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


