Abstract
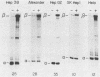
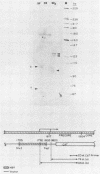
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) enhancer and the core gene promoter regulate the expression of the core and polymerase genes, as well as of the 3.5-kilobase pregenomic RNA. RNA analysis and chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene expression by plasmids carrying the HBV enhancer linked to the heterologous beta-globin or simian virus 40 early promoter demonstrated that the HBV enhancer is 3- to 20-fold preferentially expressed in human liver cells. Core gene promoter activity was mapped to a 100-base-pair fragment which was shown to be sufficient for accurate initiation of transcription. The partial tissue specificity of this promoter was demonstrated by transient transfection into various cell lines with a plasmid containing the core gene promoter linked to the heterologous simian virus 40 enhancer. When the HBV core gene promoter was examined under the control of the HBV enhancer, there was high tissue specificity in that activity could be observed only in differentiated human liver cells. These results suggest that the strict tissue specificity of HBV gene expression is determined by the combinatorial action of these two elements.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Promoter occlusion: transcription through a promoter may inhibit its activity. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):939–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90456-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla G. A., Siddiqui A. The hepatitis B virus enhancer modulates transcription of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene from an internal location. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1437–1441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1437-1441.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Enders G., Sprengel R., Peters N., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Expression of the precore region of an avian hepatitis B virus is not required for viral replication. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3322–3325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3322-3325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De-Medina T., Faktor O., Shaul Y. The S promoter of hepatitis B virus is regulated by positive and negative elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2449–2455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfassi E. Broad specificity of the hepatitis B enhancer function. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. H., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. 5'-terminal sequences influence the segregation of ground squirrel hepatitis virus RNAs into polyribosomes and viral core particles. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):35–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.35-41.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. H., Ganem D., Varmus H. Mapping the major transcripts of ground squirrel hepatitis virus: the presumptive template for reverse transcriptase is terminally redundant. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):297–308. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faktor O., De-Medina T., Shaul Y. Regulation of hepatitis B virus S gene promoter in transfected cell lines. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90476-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Bich-Thuy L. T., Stafford J., Queen C. Synergism between immunoglobulin enhancers and promoters. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):383–385. doi: 10.1038/322383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameel S., Siddiqui A. The human hepatitis B virus enhancer requires trans-acting cellular factor(s) for activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):710–715. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker M., Galle P., Schaller H. Expression and replication of the hepatitis B virus genome under foreign promoter control. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10117–10132. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Berg P. Effects of the position of the simian virus 40 enhancer on expression of multiple transcription units in a single plasmid. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2593–2601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möröy T., Etiemble J., Trépo C., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Transcription of woodchuck hepatitis virus in the chronically infected liver. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1507–1514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Shepard A., Herr W. Discrete elements within the SV40 enhancer region display different cell-specific enhancer activities. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Piatak M., Weissman S. M. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's. I. Genomic localization of 3' and 5' termini and two major splices in mRNA from transformed and lytically infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):279–296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.279-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roossinck M. J., Jameel S., Loukin S. H., Siddiqui A. Expression of hepatitis B viral core region in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1393–1400. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Rutter W. J., Laub O. A human hepatitis B viral enhancer element. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):427–430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Rall L. B., Laub O., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B virus encodes an RNA polymerase III transcript. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1774–1782. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treinin M., Laub O. Identification of a promoter element located upstream from the hepatitis B virus X gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):545–548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Green M. R., Maniatis T. cis and trans activation of globin gene transcription in transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannice J. L., Levinson A. D. Properties of the human hepatitis B virus enhancer: position effects and cell-type nonspecificity. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1305–1313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1305-1313.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will H., Reiser W., Weimer T., Pfaff E., Büscher M., Sprengel R., Cattaneo R., Schaller H. Replication strategy of human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.904-911.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Shirakata Y., Kobayashi M., Koike K. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) particles are produced in a cell culture system by transient expression of transfected HBV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2678–2682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]