Abstract
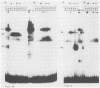
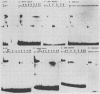
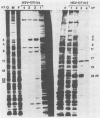
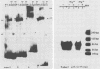
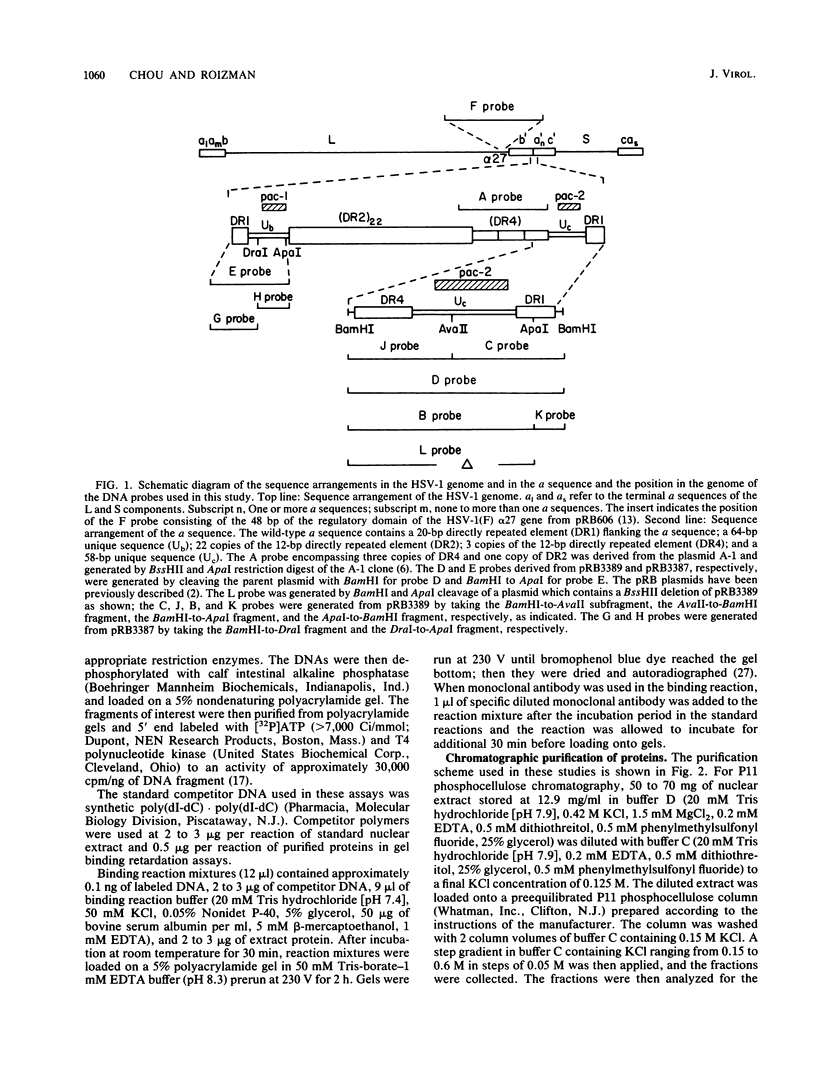
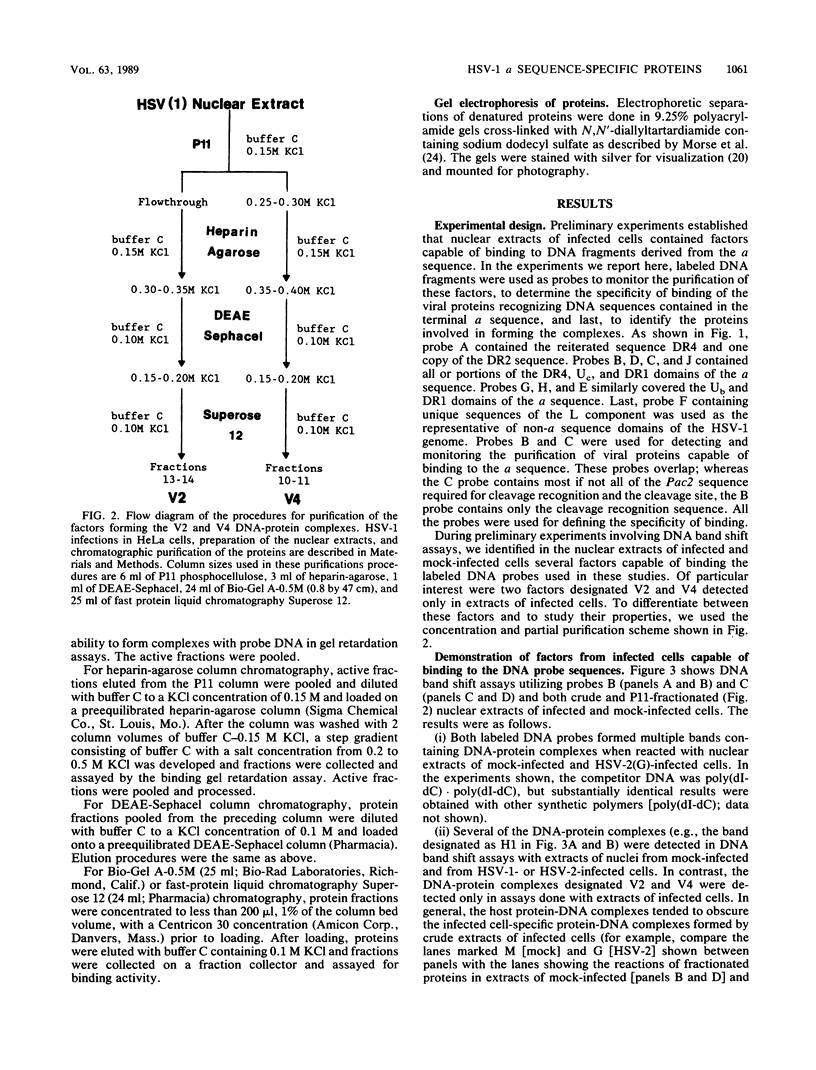
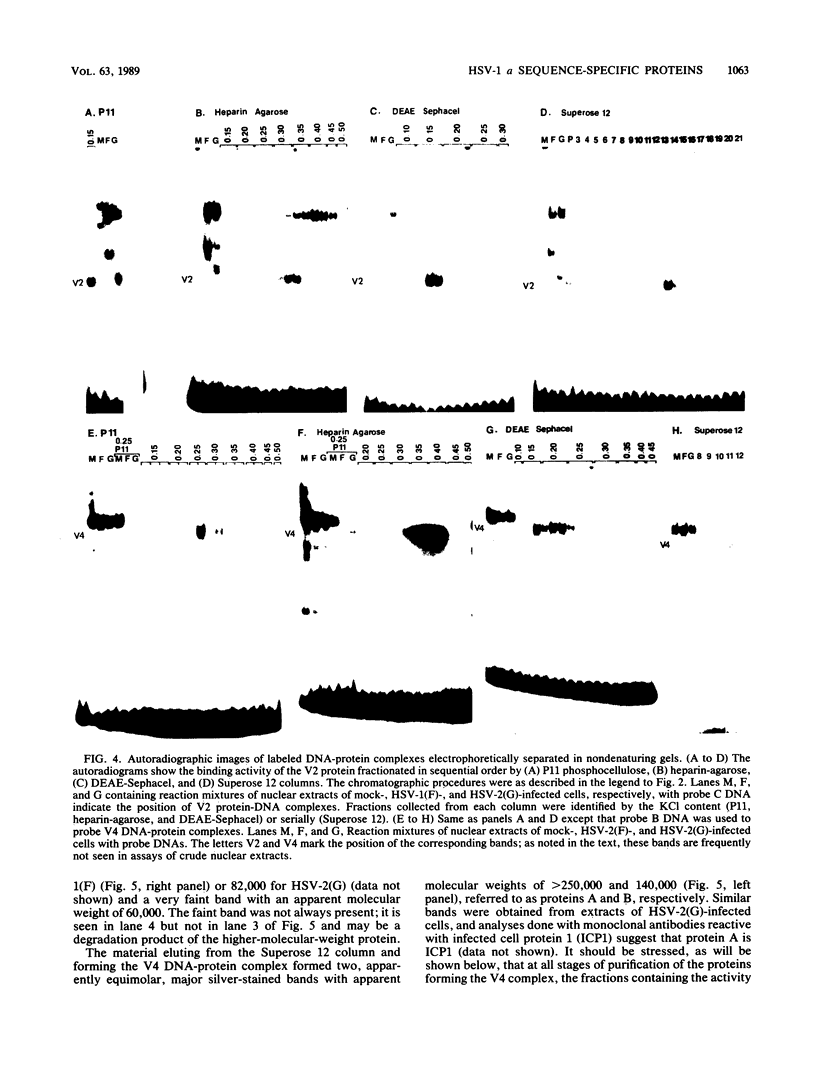
The terminal 500-base-pair alpha sequence of the herpes simplex virus 1 genome contains signals for cleavage (Pac1 and Pac2) of unit-length DNA molecules from concatemers in unique stretches of sequences designated Ub and Uc, respectively, and a cis site for cleavage designated DR1. We report that nuclear extracts from infected cells contain factors which form two DNA-virus-specific protein complexes with components of the a sequence. Purification of the factors forming the V2 complex yielded a protein with an apparent molecular weight of 82,000 binding to DNA in a non-sequence-specific manner. Addition of Mg2+ to the purified protein-DNA probe mixture resulted in exonucleolytic degradation of the DNA. The protein was identified as the virus-specific DNase with monoclonal antibody specific for the viral enzyme. The purification of the proteins forming the V4 complex yielded two proteins with molecular weights of greater than 250,000 and 140,000 corresponding to infected cell protein 1 and to an as yet unidentified protein, respectively. These proteins formed two DNA sequence-common bands with a number of DNA probes and one sequence-specific band with probes containing both Pac2 and DR1 but not with probes containing either site alone or Pac1 and DR1. Since the DNA probe containing Pac2 and DR1 inserted into viral genome or into amplicons induced specific cleavage of the DR1 sequence whereas the nonreactive probes failed to induce the cleavage, the formation of this sequence-specific DNA-protein complex is significant and may reflect a DNA-protein interaction essential for cleavage. The possible role of the proteins identified in this study for the cleavage-packaging of viral DNA into capsids is presented.
Full text
PDF



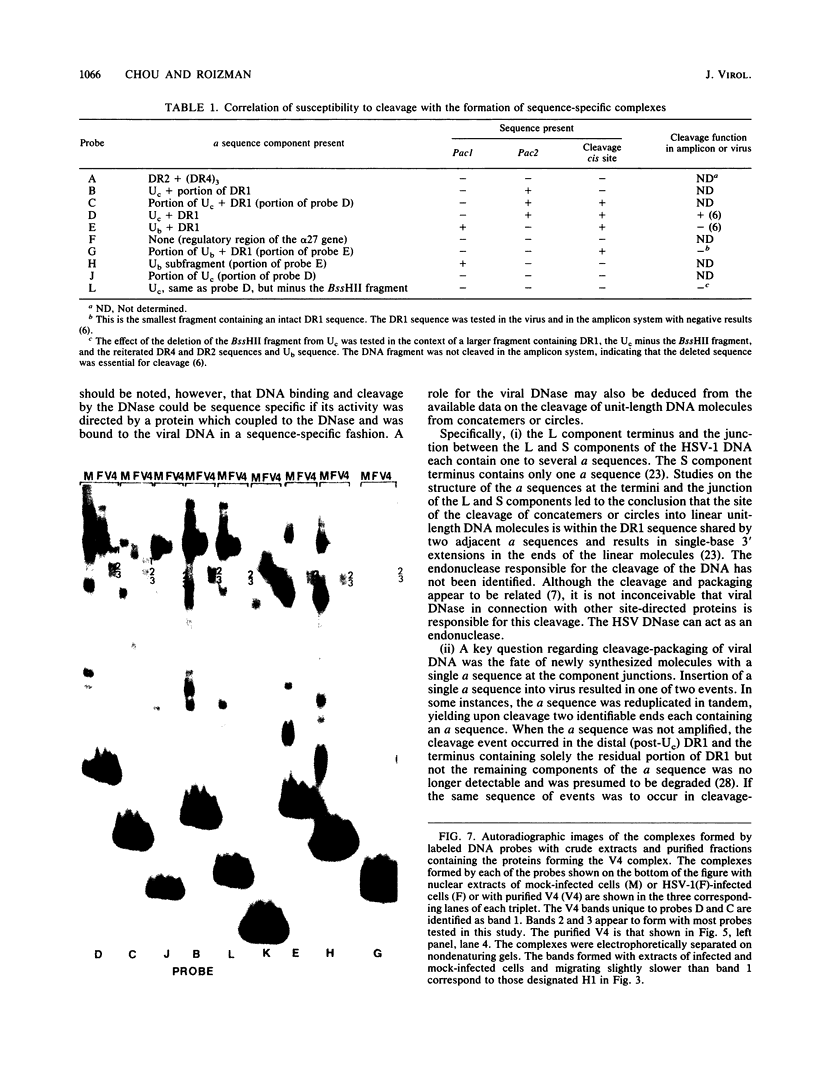


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batterson W., Furlong D., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VIII. further characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant defective in release of viral DNA and in other stages of the viral reproductive cycle. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):397–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.397-407.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. Isomerization of herpes simplex virus 1 genome: identification of the cis-acting and recombination sites within the domain of the a sequence. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):803–811. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The terminal a sequence of the herpes simplex virus genome contains the promoter of a gene located in the repeat sequences of the L component. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):629–637. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.629-637.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J. Structure of the genome termini of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Nov;65(Pt 11):1969–1977. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-11-1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Wilkie N. M. Nucleotide sequences of the joint between the L and S segments of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):315–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deiss L. P., Chou J., Frenkel N. Functional domains within the a sequence involved in the cleavage-packaging of herpes simplex virus DNA. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):605–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.605-618.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deiss L. P., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus amplicon: cleavage of concatemeric DNA is linked to packaging and involves amplification of the terminally reiterated a sequence. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):933–941. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.933-941.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann P. J., Cheng Y. C. The deoxyribonuclease induced after infection of KB cells by herpes simplex virus type 1 or type 2. I. Purification and characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3557–3562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann P. J. Mechanism of degradation of duplex DNA by the DNase induced by herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):1005–1014. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.1005-1014.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Alpha 4, the major regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus type 1, is stably and specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes and of selected other viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Host cell proteins bind to the cis-acting site required for virion-mediated induction of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):71–75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaster S., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. II. Characterization of the virion protein kinase and of the polypeptides phosphorylated in the virion. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):798–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.798-811.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight J. L., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Binding of the virion protein mediating alpha gene induction in herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells to its cis site requires cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7061–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Deiss L. P., Frenkel N. Nucleotide sequence and structural features of a novel US-a junction present in a defective herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):140–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.140-146.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Post L. E., Roizman B. Molecular engineering of the herpes simplex virus genome: insertion of a second L-S junction into the genome causes additional genome inversions. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Structure and role of the herpes simplex virus DNA termini in inversion, circularization and generation of virion DNA. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poffenberger K. L., Roizman B. A noninverting genome of a viable herpes simplex virus 1: presence of head-to-tail linkages in packaged genomes and requirements for circularization after infection. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):587–595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.587-595.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B. The structure and isomerization of herpes simplex virus genomes. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmuza S. L., Smiley J. R. Signals for site-specific cleavage of HSV DNA: maturation involves two separate cleavage events at sites distal to the recognition sequences. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):793–802. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Kwong A., Frenkel N. Site-specific cleavage/packaging of herpes simplex virus DNA and the selective maturation of nucleocapsids containing full-length viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1423–1427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]