Abstract
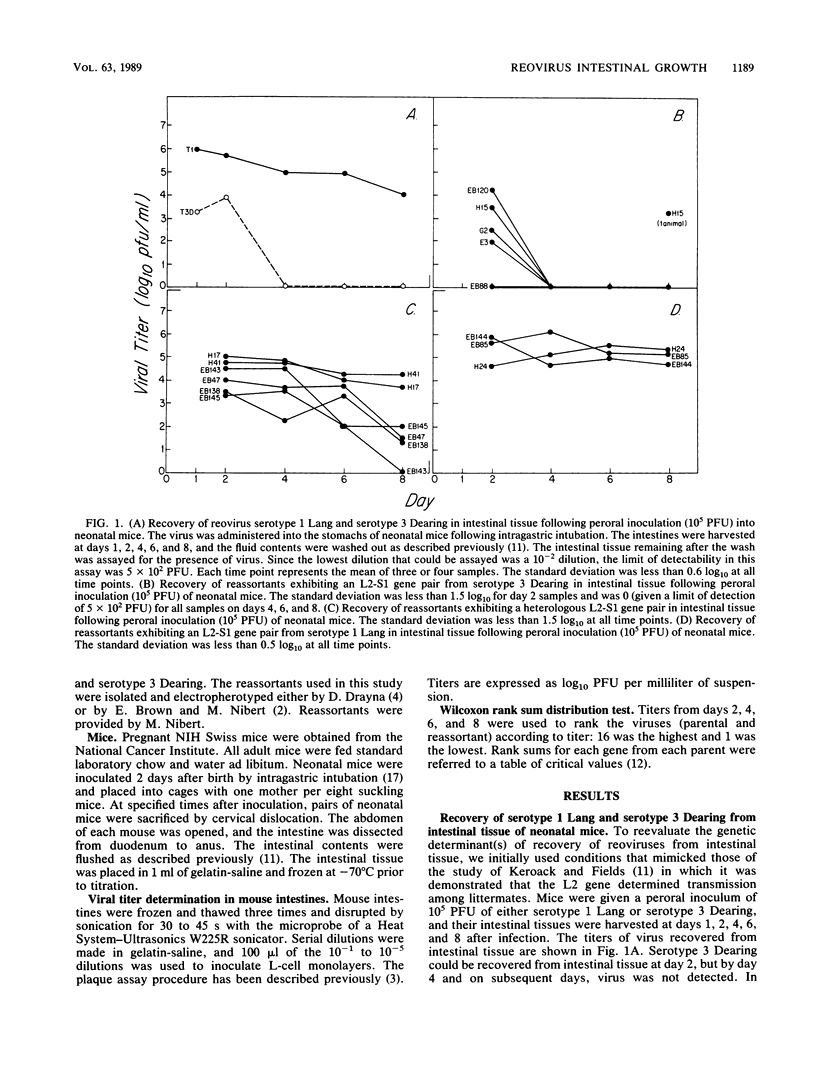
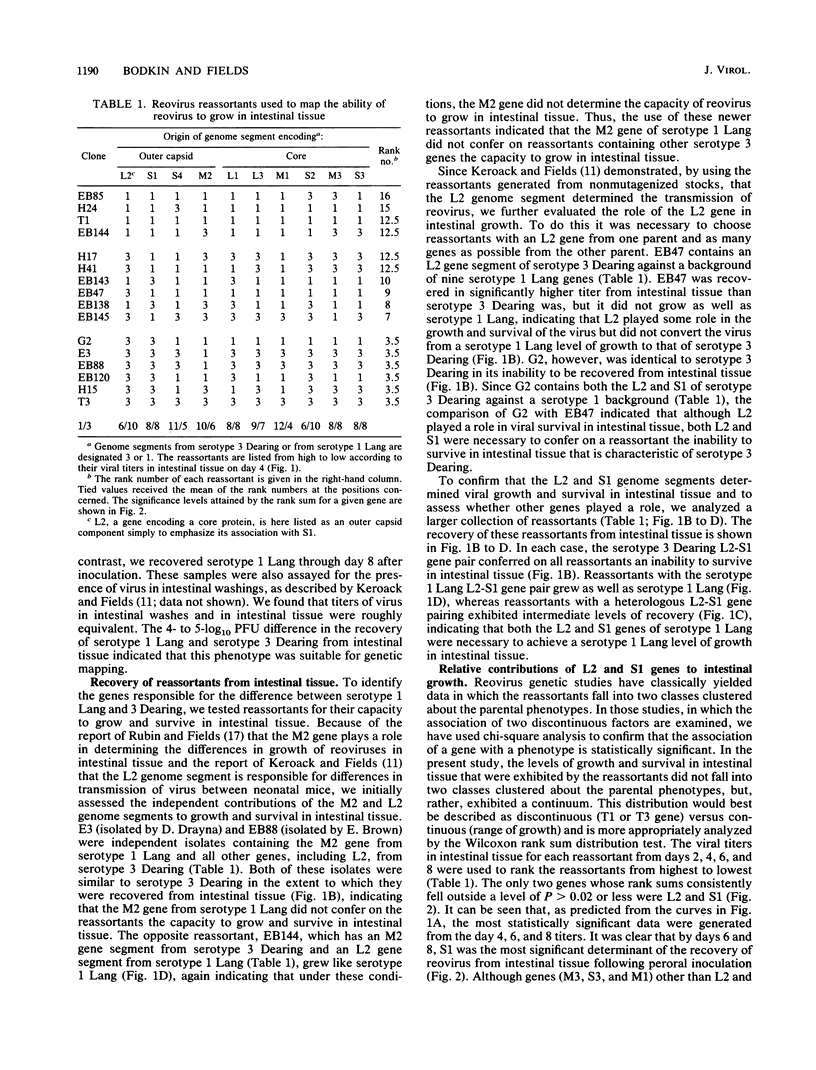
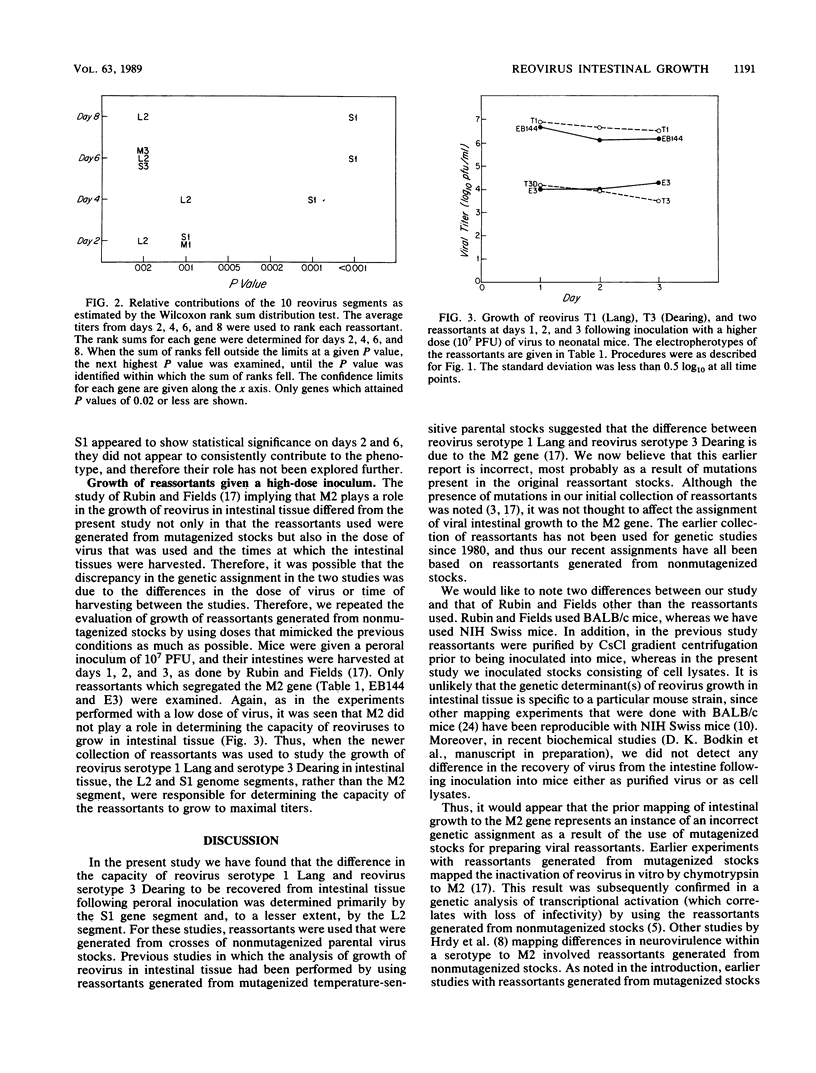
Reovirus serotype 1 Lang can be recovered in high titer from the intestines of neonatal mice up to day 8 after peroral inoculation. By contrast, reovirus serotype 3 Dearing cannot be recovered from intestinal tissue past day 4 after peroral inoculation. This difference between the two reoviruses was mapped by using reassortants generated from nonmutagenized laboratory stocks. When the L2 and S1 genes of reovirus serotype 3 Dearing were present in reassortants, the reassortants behaved like serotype 3 Dearing in exhibiting a decreased capacity to be recovered from intestinal tissue. Likewise, viruses which contained the L2 and S2 genes from serotype 1 Lang exhibited an enhanced capacity to grow and survive, which is characteristic of serotype 1 Lang. Thus, the capacity of reovirus to survive in intestinal tissue was determined by the L2 and S1 genes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassel-Duby R., Jayasuriya A., Chatterjee D., Sonenberg N., Maizel J. V., Jr, Fields B. N. Sequence of reovirus haemagglutinin predicts a coiled-coil structure. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):421–423. doi: 10.1038/315421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Use of an aberrant polypeptide as a marker in three-factor crosses: further evidence for independent reassortment as the mechanism of recombination between temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):345–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Fields B. N. Activation and characterization of the reovirus transcriptase: genetic analysis. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):110–118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.110-118.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Fields B. N. Genetic studies on the mechanism of chemical and physical inactivation of reovirus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Nov;63(Pt 1):149–159. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong D. B., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Sigma 1 protein of mammalian reoviruses extends from the surfaces of viral particles. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):246–256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.246-256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Spindler K., Horodyski F., Grabau E., Nichol S., VandePol S. Rapid evolution of RNA genomes. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1577–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.7041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdy D. B., Rubin D. H., Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus neurovirulence: role of the M2 gene in avirulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1298–1302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Studies on the effect of chymotrypsin on reovirions. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):700–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye K. M., Spriggs D. R., Bassel-Duby R., Fields B. N., Tyler K. L. Genetic basis for altered pathogenesis of an immune-selected antigenic variant of reovirus type 3 (Dearing). J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.90-97.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keroack M., Fields B. N. Viral shedding and transmission between hosts determined by reovirus L2 gene. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1635–1638. doi: 10.1126/science.3012780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustoe T. A., Ramig R. F., Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus. III. Assignment of the double-stranded RNA-positive mutant groups A, B, and G to genome segments. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Genome RNAs and polypeptides of reovirus serotypes 1, 2, and 3. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):726–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.726-733.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus. II. Assignment of the double-stranded RNA-negative mutant groups C, D, and E to genome segments. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):531–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozhon E. J., Gensemer P., Shope R. E., Bishop D. H. Attenuation of virulence of a bunyavirus involving an L RNA defect and isolation of LAC/SSH/LAC and LAC/SSH/SSH reassortants. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):125–138. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90659-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus virulence. Role of the M2 gene. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):853–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. Reovirus inhibition of cellular RNA and protein synthesis: role of the S4 gene. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus. 1. Correlation of genome RNAs between serotypes 1, 2, and 3. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., LaFiandra A. J. Transcription by infectious subviral particles of reovirus. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):698–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.698-706.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturzenbecker L. J., Nibert M., Furlong D., Fields B. N. Intracellular digestion of reovirus particles requires a low pH and is an essential step in the viral infectious cycle. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2351–2361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2351-2361.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler K. L., McPhee D. A., Fields B. N. Distinct pathways of viral spread in the host determined by reovirus S1 gene segment. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):770–774. doi: 10.1126/science.3016895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Drayna D., Averill D. R., Jr, Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus virulence: role of the S1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5744–5748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Fields B. N. Neutralization of reovirus: the gene responsible for the neutralization antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1305–1310. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Fields B. N. Identification of the gene coding for the hemagglutinin of reovirus. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):581–584. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


