Abstract
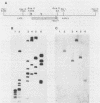
We have identified a region of human papillomavirus type 6 (HPV-6) DNA that hybridizes with human cellular DNA containing no detectable HPV DNA sequences. The region of hybridization has been localized to a segment of the viral long control region between the end of the L1 open reading frame and the late polyadenylation signal and is likely contained within a 94-base-pair insertion at nucleotide 7350 which is present in the cloned HPV-6b DNA used for these studies. Restriction fragments of HPV-6 DNA from seven patients suggested that this insert was present in these naturally occurring viral genomes as well. The presence of this insert was confirmed by direct sequence analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified segments from four naturally occurring HPV-6 genomes. By analogy with other systems, this insert and surrounding sequences may function to destabilize the HPV-6 late mRNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auborn K. J., Galli R. L., Dilorenzo T. P., Steinberg B. M. Identification of DNA-protein interactions and enhancer activity at the 5' end of the upstream regulatory region in human papillomavirus type 11. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90359-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Noe J. S. Transcriptional termination between bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV-1) early and late polyadenylation sites blocks late transcription in BPV-1-transformed cells. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3529–3534. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3529-3534.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., zur Hausen H. Human papillomaviruses in Buschke-Löwenstein tumors: physical state of the DNA and identification of a tandem duplication in the noncoding region of a human papillomavirus 6 subtype. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):963–966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.963-966.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasher M. S., Roman A. Alterations in the regulatory region of the human papillomavirus type 6 genome are generated during propagation in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3295–3300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3295-3300.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasher M. S., Roman A. Characterization of human papillomavirus type 6b DNA isolated from an invasive squamous carcinoma of the vulva. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90676-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulke R., Gross G. E., Pfister H. Duplication of enhancer sequences in human papillomavirus 6 from condylomas of the mamilla. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):284–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90245-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Baker C. C., Howley P. M. The genetics of bovine papillomavirus type 1. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:235–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. F., Groff D. E., Chirikjian J. G., Lancaster W. D. Isolation and characterization of a novel human papillomavirus type 6 DNA from an invasive vulvar carcinoma. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):353–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.353-356.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. F., Lancaster W. D., Han P., Lopez C. The noncoding region of HPV-6vc contains two distinct transcriptional enhancing elements. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. F., Sedlacek T. V., Hunt J., Jenson A. B., Kurman R. J., Lancaster W. D. Verrucous carcinoma of the vulva associated with an unusual type 6 human papillomavirus. Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Mar;67(3 Suppl):70S–75S. doi: 10.1097/00006250-198603001-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Dürst M., Demankowski C., Lattermann O., Zech R., Wolfsperger E., Suhai S., zur Hausen H. DNA sequence and genome organization of genital human papillomavirus type 6b. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2341–2348. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01744.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb D. H., Rogers R. E., Fife K. H. A one-step method for detecting and typing human papillomavirus DNA in cervical scrape specimens from women with cervical dysplasia. J Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;156(6):912–919. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.6.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers E. M., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Molecular cloning of viral DNA from human genital warts. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):932–935. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.932-935.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers E. M., Schneider A., Gross G., zur Hausen H. Analysis of benign and malignant urogenital tumors for human papillomavirus infection by labelling cellular DNA. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1986;174(6):281–286. doi: 10.1007/BF02123680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]