Abstract
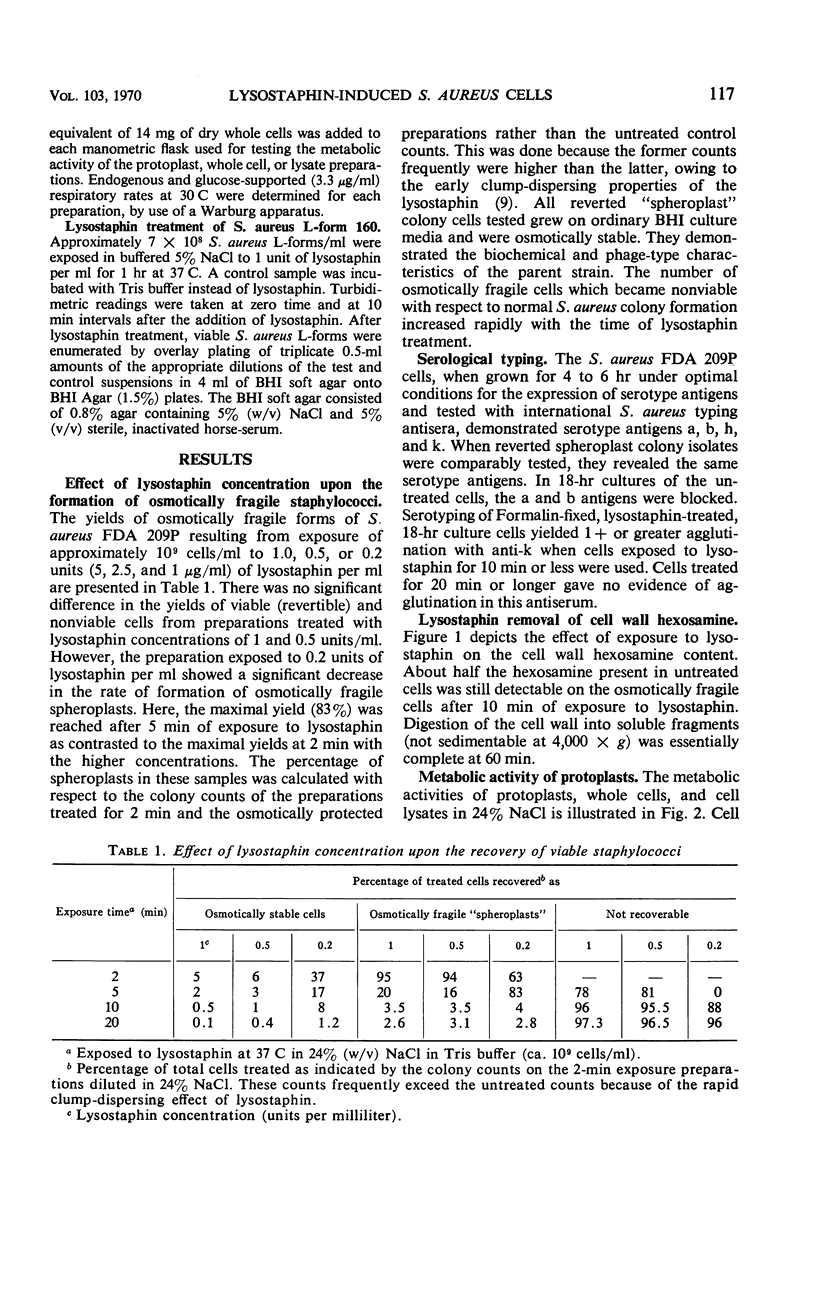
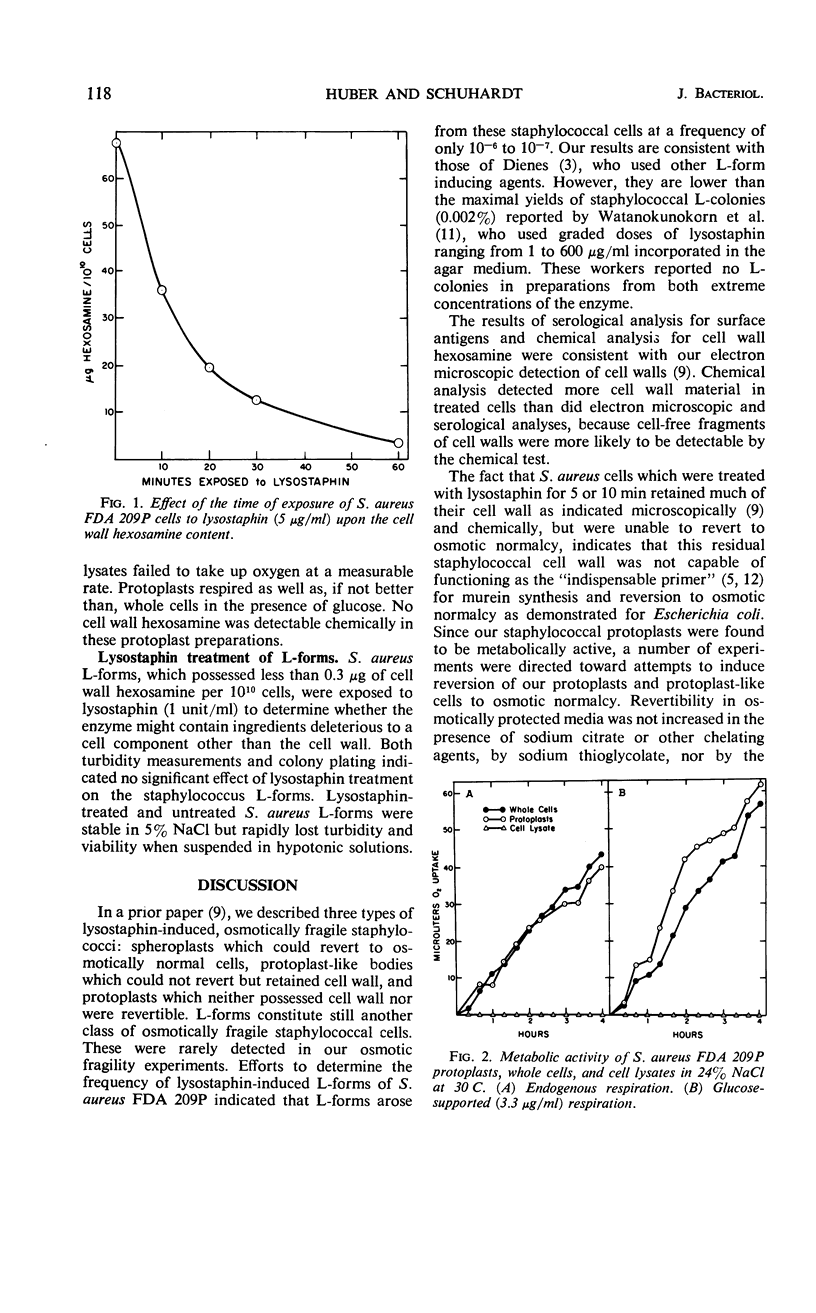
Staphylococcus aureus FDA 209P cells when suspended in 24% (w/v) NaCl were rendered osmotically fragile by exposure to lysostaphin for time intervals ranging from 2 to 60 min. Such cells were analyzed chemically and serologically for evidence of residual cell wall material, were plated in hypertonic sucrose medium to determine revertibility to normal, and were subjected to manometric studies to determine metabolic capabilities. Most of the cells (95%) which were exposed to lysostaphin (0.5 or 1.0 unit/ml) for 2 min, although osmotically fragile, retained their cell wall hexosamine and were capable of reverting to osmotically normal cells when plated in hypertonic medium. Cells exposed to lysostaphin for 5 and 10 min also retained much of their cell wall hexosamine, but lost their ability to revert to normal staphylococci. Cells exposed to lysostaphin for 2 to 10 min continued to react with staphylococcus anti-k antiserum. Complete removal of cell wall hexosamine was attained only after exposure to lysostaphin for 20 min or more; these cells failed to react with k antiserum. Lysostaphin-induced L-type colonies were extremely rare in our experiments, even if incubation times and media were optimal for their detection. Lysostaphin-induced staphylococcal protoplasts were as active metabolically in manometric studies as were untreated staphylococci.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHEN J. O., SMITH P. B. SEROLOGICAL TYPING OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. II. TYPING BY SLIDE AGGLUTINATION AND COMPARISON WITH PHAGE TYPING. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1364–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1364-1371.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes L. Morphology and reproductive processes of the L forms of bacteria. I. Streptococci and staphylocci. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):693–702. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.693-702.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDMAN O. E., HALLE S. ENZYMICALLY AND PHYSICALLY INDUCED INHERITANCE CHANGES IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Mol Biol. 1963 Dec;7:721–738. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., HANCOCK R. A fractionation procedure for studies of the synthesis of cell-wall mucopeptide and of other polymers in cells of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:249–258. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER C. A., SCHUHARDT V. T. LYSOSTAPHIN: A NEW BACTERIOLYTIC AGENT FOR THE STAPHYLOCOCCUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:414–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER C. A., SCHUHARDT V. T. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF LYSOSTAPHIN--A LYTIC AGENT FOR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 15;97:242–250. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuhardt V. T., Huber T. W., Pope L. M. Electron microscopy and viability of lysostaphin-induced staphylococcal spheroplasts, protoplast-like bodies, and protoplasts. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):396–401. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.396-401.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuhardt V. T., Klesius P. H. Osmotic fragility and viability of lysostaphin-induced staphylococcal spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):734–737. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.734-737.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PELZER H. BAGSHAPED MACROMOLECULES--A NEW OUTLOOK ON BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1964;26:193–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122716.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C., Goldberg L. M., Carleton J., Hamburger M. Staphylococcal spheroplasts and L-colonies. 3. Induction by lysostaphin. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jan;119(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


