Abstract
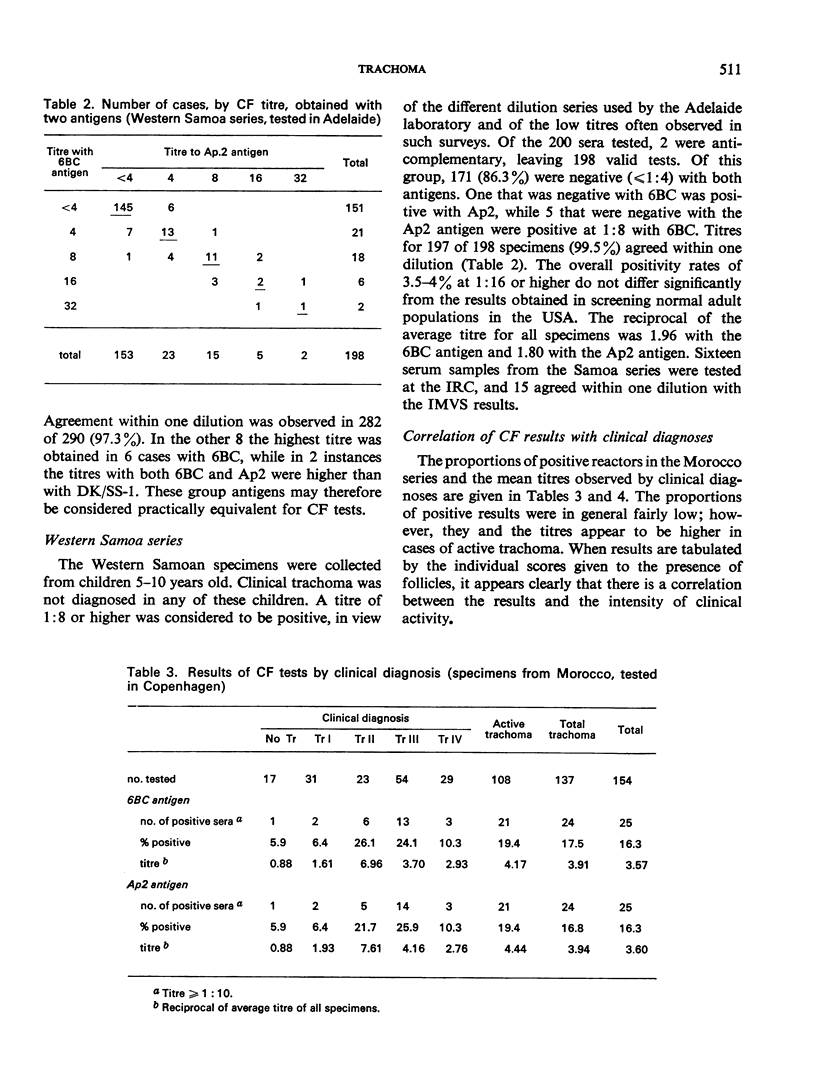
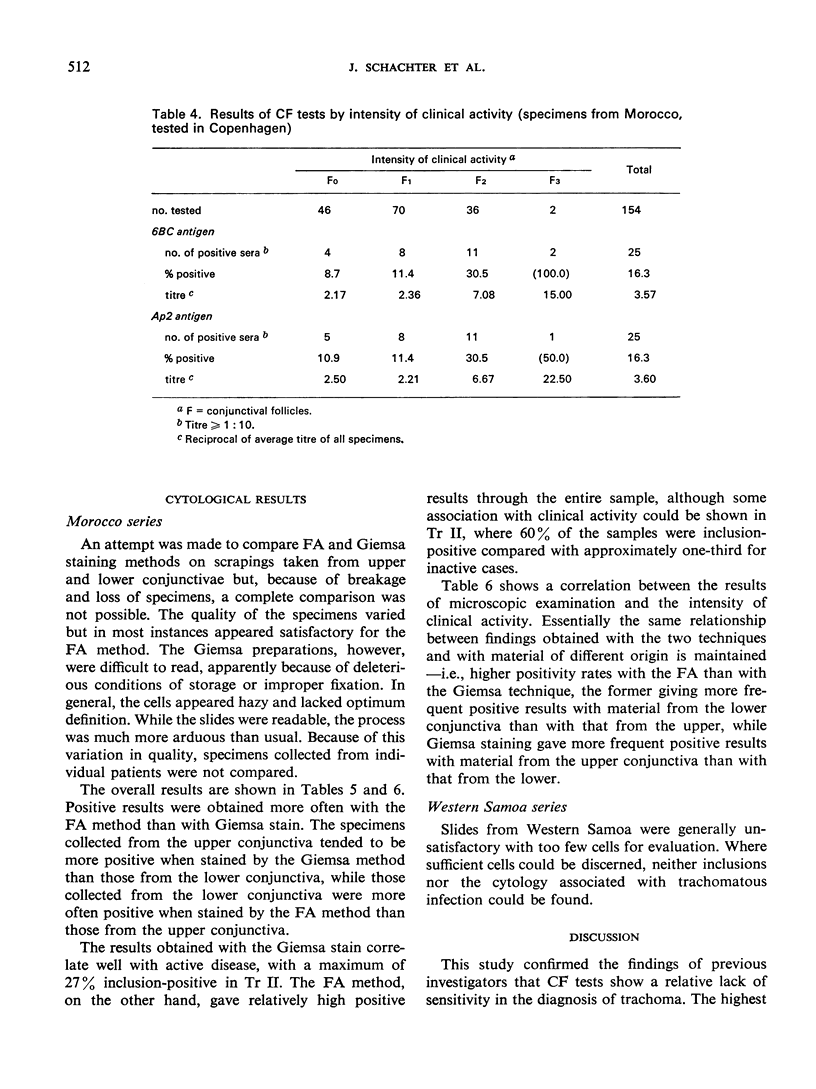
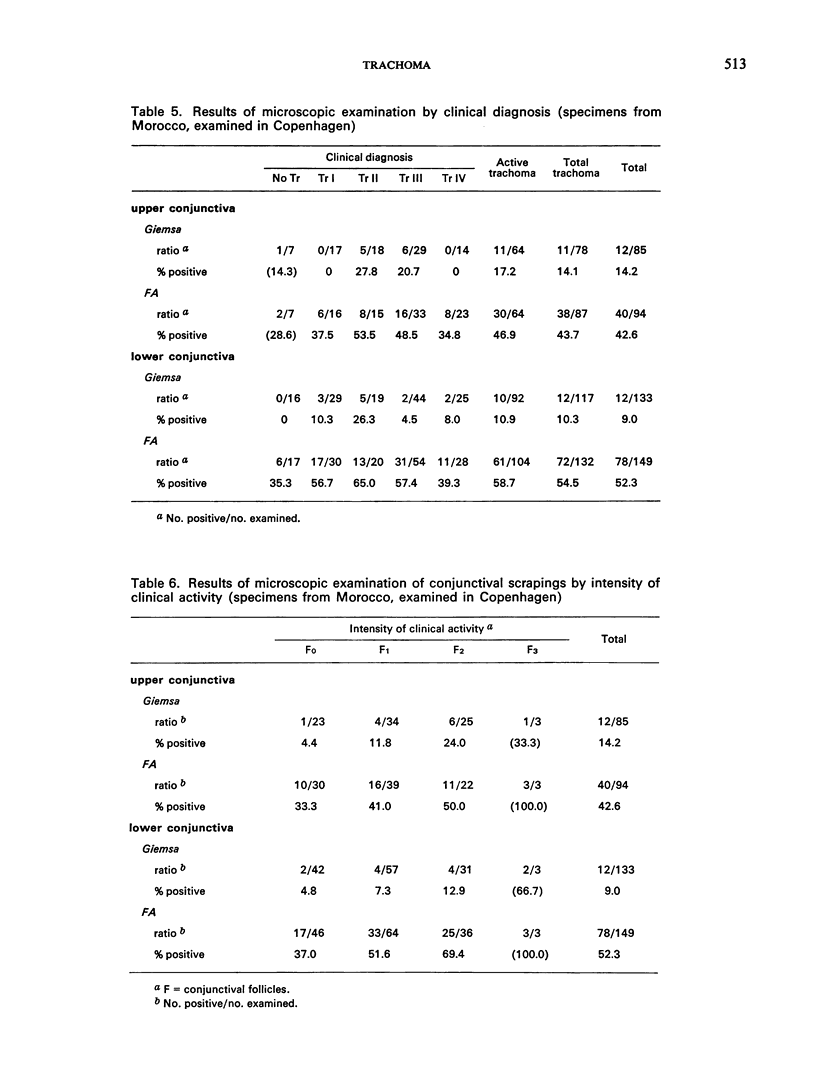
A collaborative study on the laboratory diagnosis of trachoma was carried out in three laboratories. A standardized complement fixation (CF) test with chlamydial (bedsonial) group antigen was found to be highly reproducible. The results obtained by different laboratories using the method and reagents suggested by the WHO International Reference Centre for Trachoma and other Chlamydial Infections agreed in more than 95% of the tests. Similar agreement was observed between the results obtained with these reagents and those routinely used in one of these laboratories. In confirmation of previous studies, the CF test was found to give positive results in only a limited proportion of trachoma cases. However, in an area where the disease is hyperendemic the rates showed good correlation with the intensity of clinical signs. A comparison was also made between Giemsa staining and a fluorescent antibody (FA) technique for the cytological examination of conjunctival scrapings. The results obtained with the former method correlated well with clinical activity but the positivity rate was lower than that obtained by the FA technique. The FA results, however, were not an accurate indicator of clinical intensity. These results suggest that the Giemsa method may detect only the most heavily infected individuals.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Schachter J., Dawson C. R., Balas S., Jones P. Evaluation of laboratory methods for detecting acute TRIC agent infection. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970 Sep;70(3):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(70)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarizzo M. L., Nabli B., Labonne J. Studies on trachoma. 11. Evaluation of laboratory diagnostic methods under field conditions. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(6):897–905. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKERT M., CHRISTENSEN P. M. Two ornithosis complement-fixing antigens from infected yolk sacs. I. The phosphatide antigen, the virus antigen and methods for their preparation. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1955;37(2):211–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Immunologic relationship between genital TRIC, lymphogranuloma venereum, and related organisms in a new microtiter indirect immunofluorescence test. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970 Sep;70(3):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(70)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


