Abstract
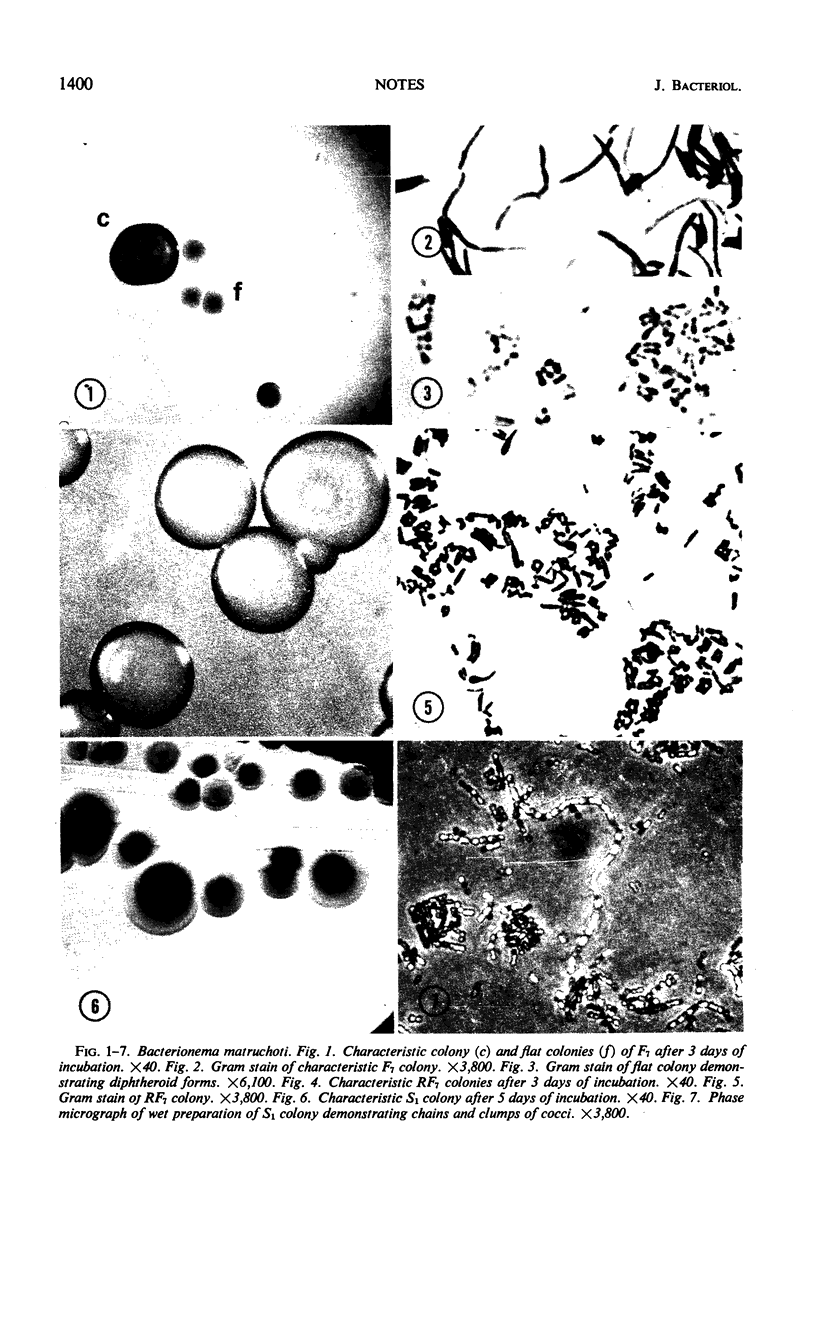
Bacterionema matruchotii, an oral filamentous organism, dissociated to form unusual flat colonies. Subculture of the flat colonies, composed of diphtheroids, yielded pure cultures of bacillary and streptococcal variants.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GILMOUR M. N., HOWELL A., Jr, BIBBY B. G. The classification of organisms termed Leptotrichia (Leptothrix) buccalis. I. Review of the literature and proposed separation into Leptotrichia buccalis Trevisan, 1879 and Bacterionema gen. nov., B. matruchotti (Mendel, 1919) comb. nov. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Jun;25:131–141. doi: 10.1128/br.25.2.131-141.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILMOUR M. N. The classification of organisms termed Leptotrichia (Leptothrix) buccalis. II. Reproduction of Bacterionema matruchotii. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Jun;25:142–151. doi: 10.1128/br.25.2.142-151.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL A., Jr, STEPHAN R. M., PAUL F. Prevalence of Actin-omyces israelii, A. naeslundii, Bacterionema matruchotii, and Candida albicans in selected areas of the oral cavity and saliva. J Dent Res. 1962 Sep-Oct;41:1050–1059. doi: 10.1177/00220345620410050701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. L., Bullock W. W., Parker R. B. Morphology of gram-positive filamentous bacteria identified in dental plaque by fluorescent antibody technique. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Nov;12(11):1269–1273. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]