Abstract
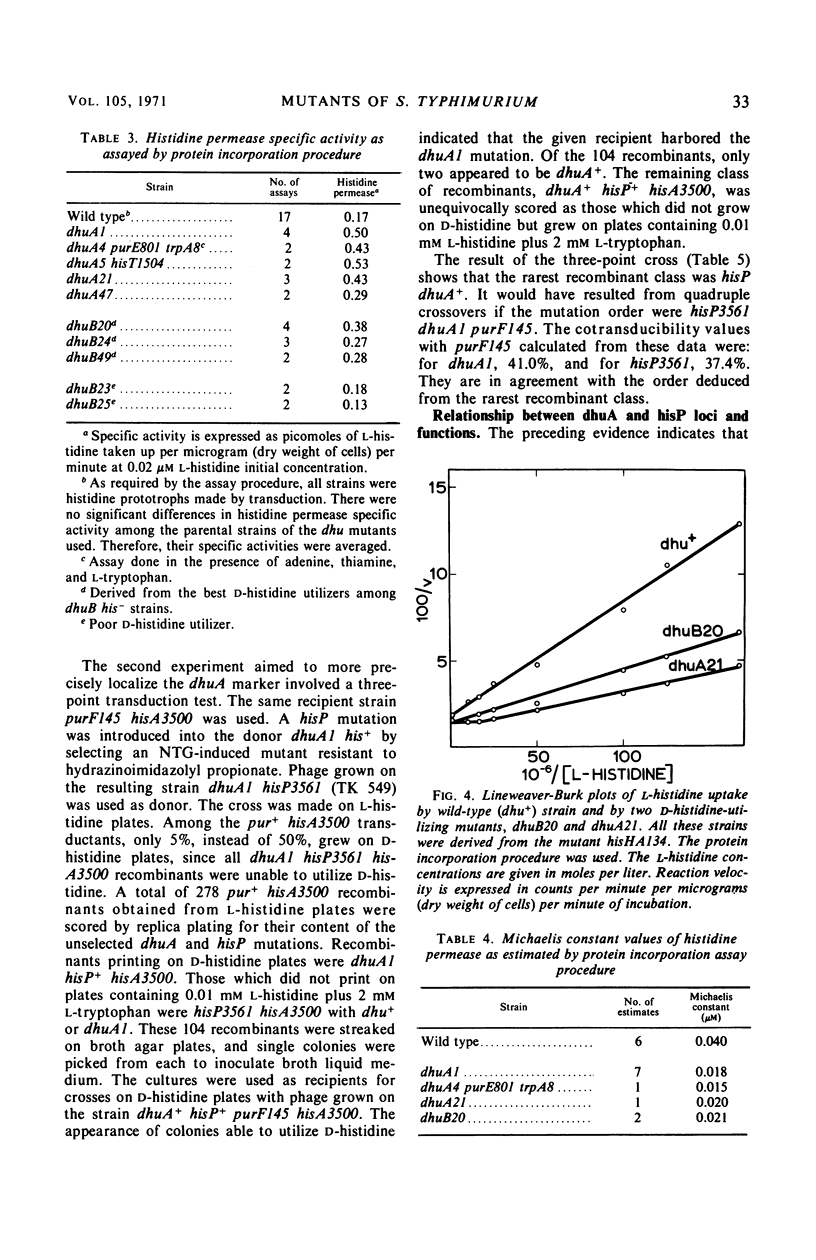
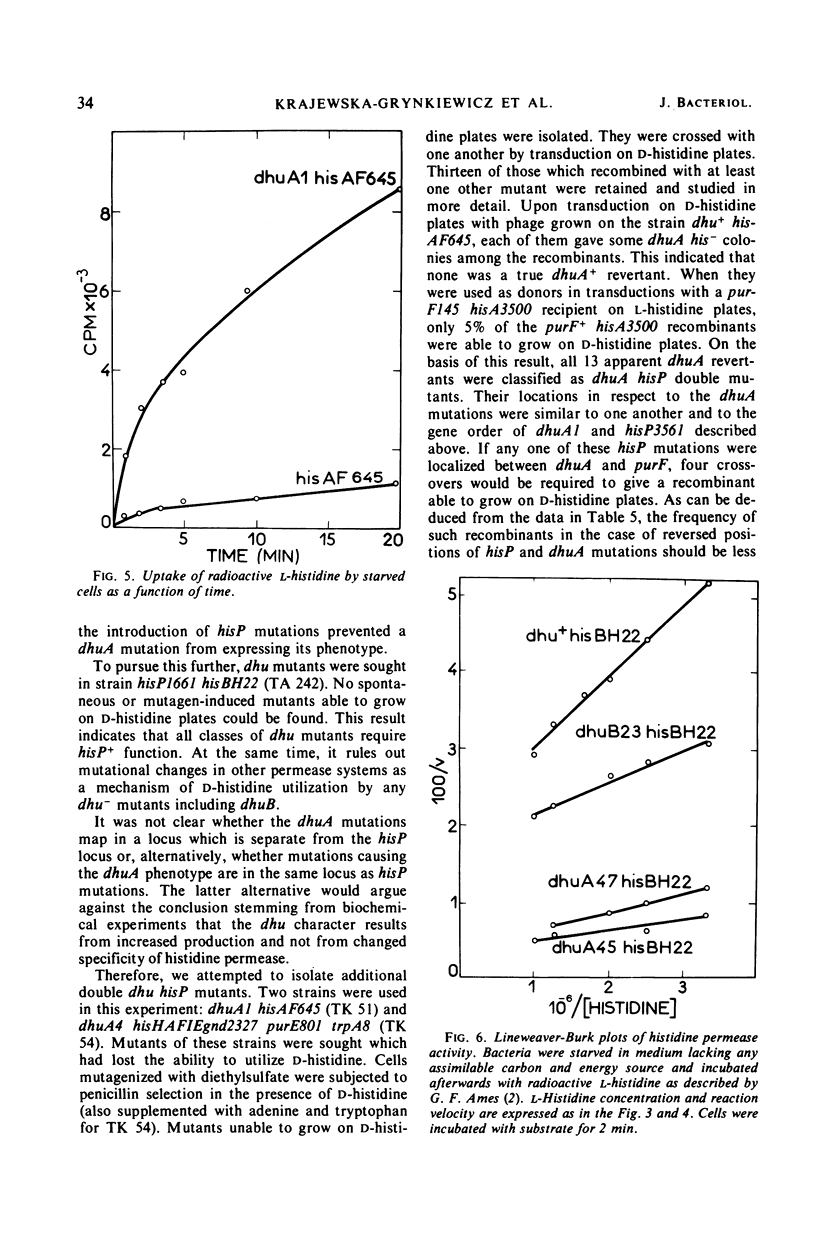
Secondary mutants able to utilize d-histidine, dhu, were isolated in histidine auxotrophs of Salmonella typhimurium. Mutations of one class (dhuA) are closely linked with the hisP locus which codes for a component of histidine permease. The specific activity of l-histidine permeation was estimated as increased two- to seven-fold in dhuA mutants. The dhuB mutants which have not been mapped also had elevated specific activity of l-histidine permeation. The uptake of d-histidine, barely detectable in the parental strains, was prominent in dhuA mutants and showed an apparent Michaelis constant about 1,000-fold higher than that observed with l-histidine. No change was detected in the kinetics of l-histidine permeation. d- and l-histidine competed in the uptake process. Tertiary mutants which lost the ability to grow on d-histidine were isolated by ampicillin counter-selection in dhuA his− strains. All of them mapped in the dhuA hisP region. Most of them had all known properties of hisP mutants. It is inferred from these data that the dhuA mutations increase synthesis of components critical to d- and l-histidine permeation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES G. F. UPTAKE OF AMINO ACIDS BY SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Lever J. Components of histidine transport: histidine-binding proteins and hisP protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1096–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Roth J. R. Histidine and aromatic permeases of Salmonella typhimurim. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1742–1749. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1742-1749.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern Y. S., Lupo M. Glutamate transport in wild-type and mutant strains of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1288–1295. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1288-1295.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M., Halpern Y. S. Genetic analysis of the glutamate permease in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1118–1128. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1118-1128.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penrose W. R., Nichoalds G. E., Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Purification and properties of a leucine-binding protein from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5921–5928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. R., Ames B. N. Histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium II. Histidine regulatory mutants having altered histidyl-tRNA synthetase. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shifrin S., Ames B. N., FerroLuzzi-Ames G. Effect of the alpha-hydrazino analogue of histidine on histidine transport and arginine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3424–3429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O. Defective phage formation by lysogens of integration deficient phage P22 mutants. Virology. 1968 Feb;34(2):203–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]