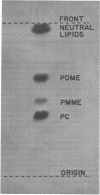
Abstract
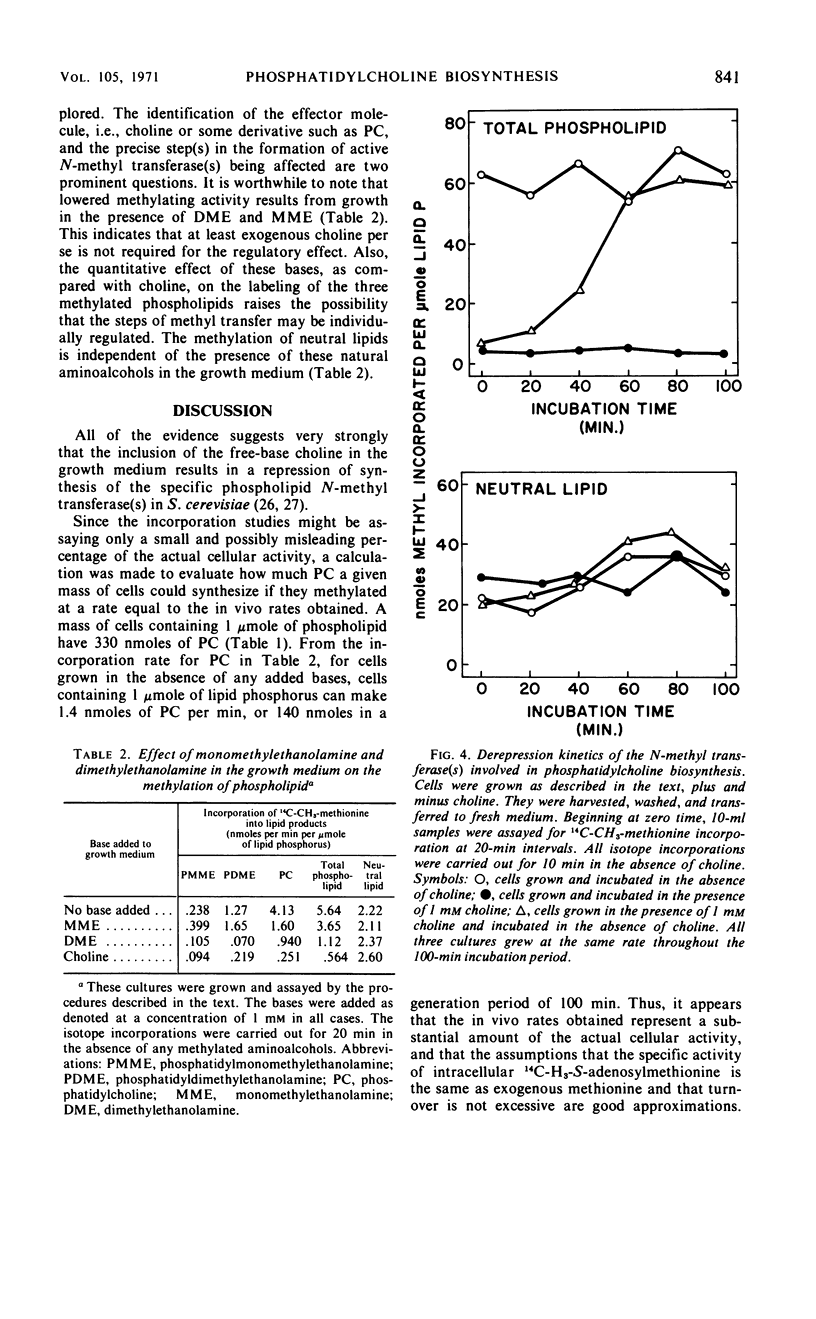
Evidence is presented which indicates that the biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine by the methylation pathway in growing cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is repressed by the presence of choline in the growth medium. This result, obtained previously for glucose-grown cells, was also observed for lactate-grown cells, of which half of the phosphatidylcholine is mitochondrial. A respiration-deficient mutant of the parent wild-type strain has been studied, and its inability to form functional mitochondria cannot be due to an impaired methylation pathway, as it has been shown to incorporate 14C-CH3-methionine into all of the methylated glycerophosphatides. The incorporation rate is depressed by the inclusion of 1 mm choline in the growth medium, suggesting a regulatory effect similar to that demonstrated for the wild-type strain. The effects of choline on the glycerophospholipid composition of lactate and glucose-grown cells is presented. The repressive effects of the two related bases, mono- and dimethylethanolamine, were examined, and reduced levels of 14C-CH3-methionine incorporation were found for cells grown in the presence of these bases. The effect of choline on the methylation rates is reversible and glucosegrown cells regain the nonrepressed level of methylation activity in 60 to 80 min after removal of choline from the growth medium.
Full text
PDF
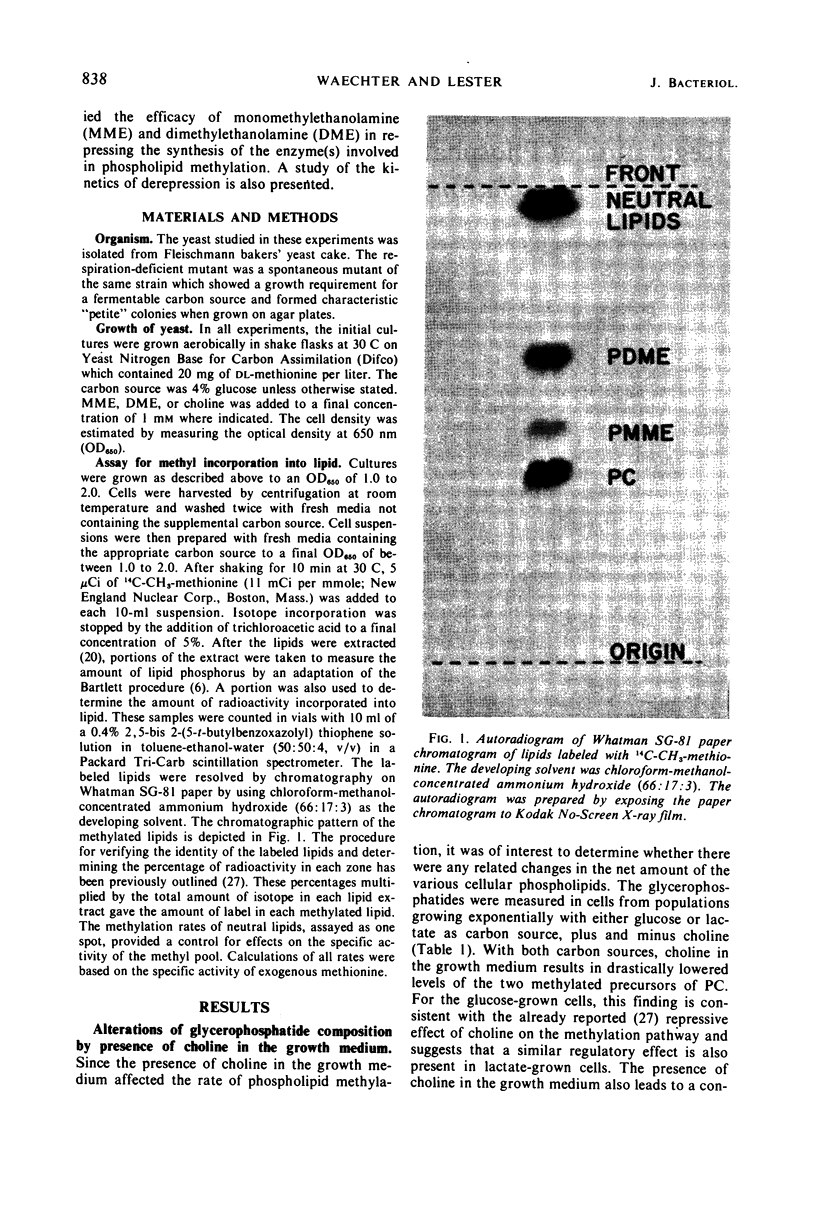
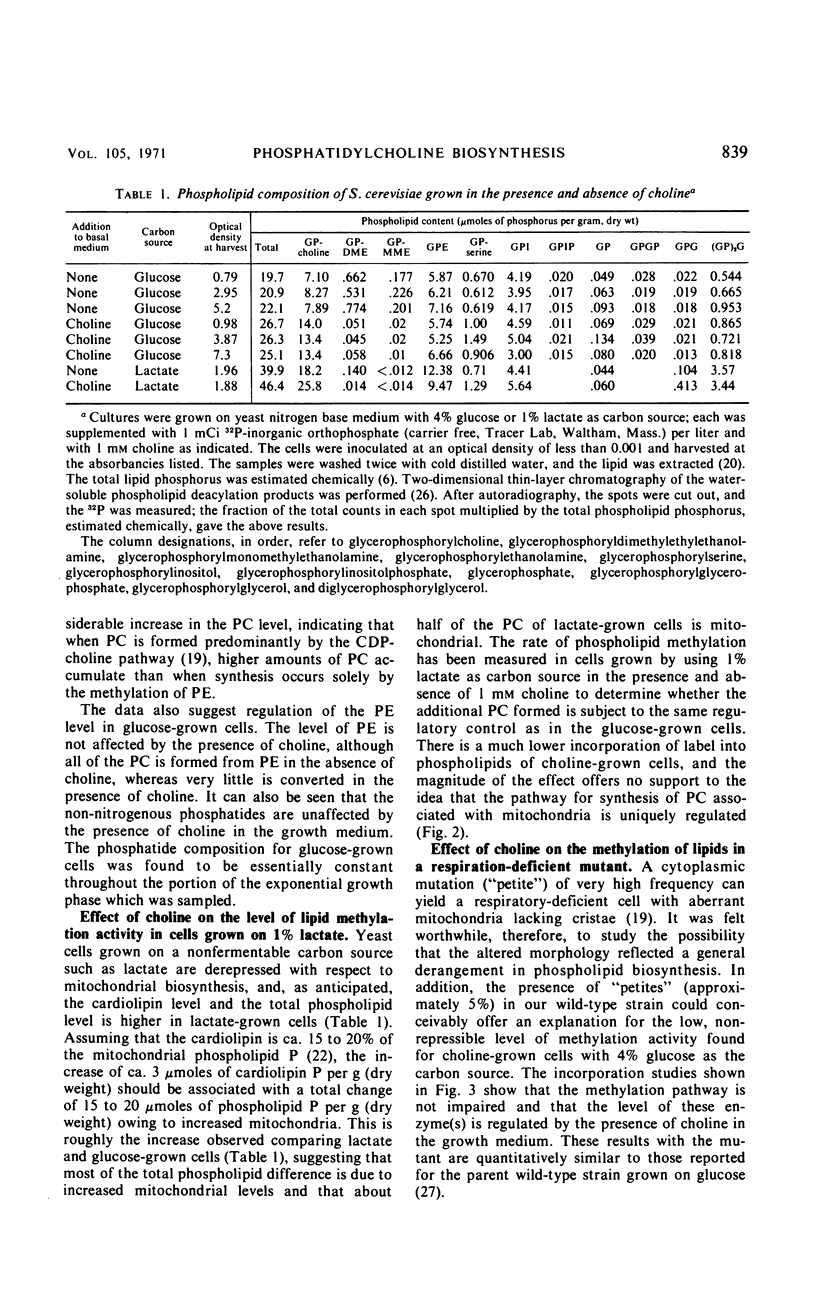
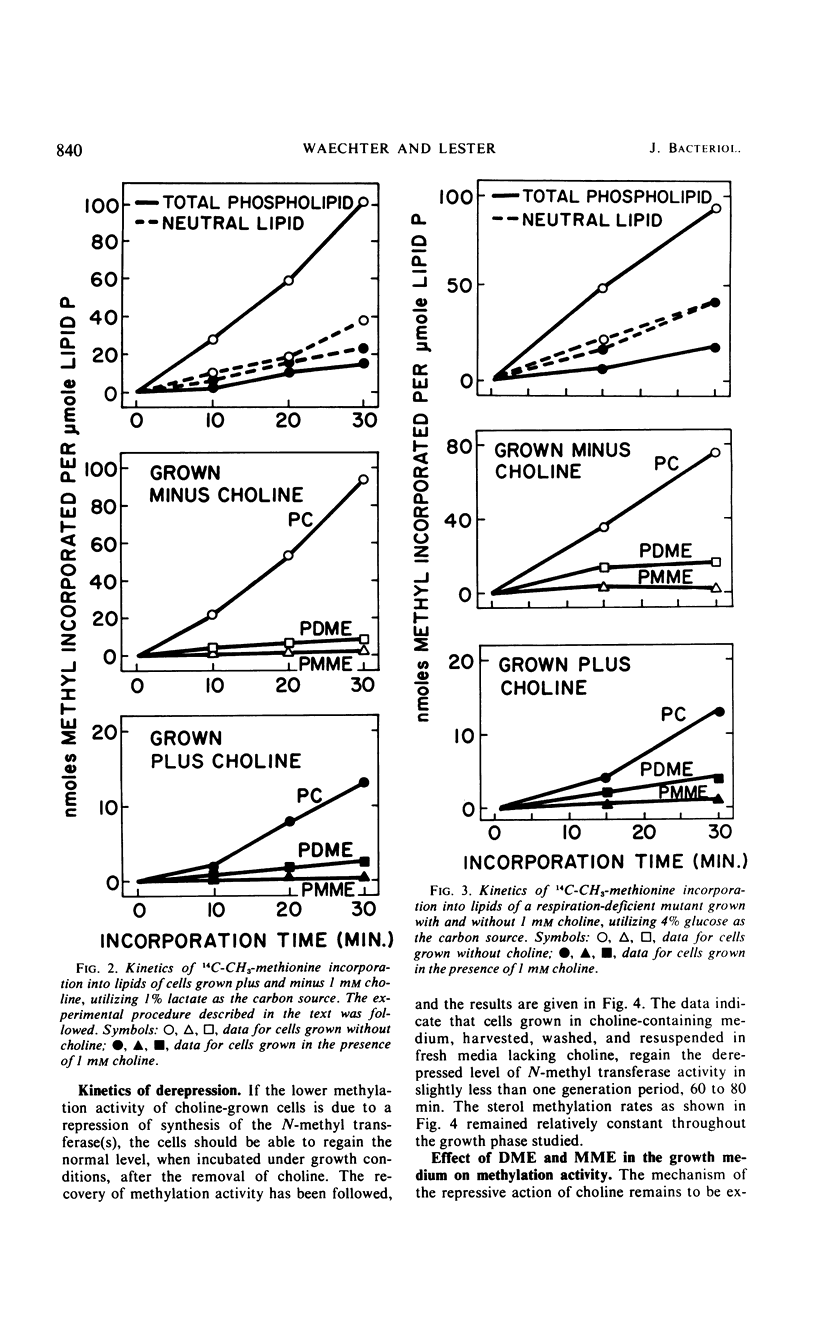


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER G. J., GOLD A. M., SCHWENK E. Biogenesis of yeast sterols. III. The origin of carbon 28 of ergosterol. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):599–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALEXANDER G. J., SCHWENK E. Biogenesis of yeast sterols. IV. Transmethylation in ergosterol synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARTOM C., LOFLAND H. B., Jr Lecithin formation by methylation of intactphosphatidyl dimethylethanolamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Sep;3:244–247. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansell G. B., Chojnacki T. The incorporation of the phosphate esters of N-substituted aminoethanols into the phospholipids of brain and liver. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):303–310. doi: 10.1042/bj0980303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvidson G. A. Biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholines in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Aug;5(3):415–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREMER J., GREENBERG D. M. Biosynthesis of choline in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jan 1;37:173–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREMER J., GREENBERG D. M. Mono- and dimethylethanolamine isolated from rat-liver phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Sep;35:287–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90375-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone H. D. The calcium-stimulated incorporation of ethanolamine and serine into the phospholipids of the housefly Musca domestica. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):695–704. doi: 10.1042/bj1040695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON K. D., WILSON J. D., UDENFRIEND S. The enzymatic conversion of phospholipid ethanolamine to phospholipid choline in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:673–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBSCHER G. Metabolism of phospholipids. VI. The effect of metal ions on the incorporation of L-serine into phosphatidylserine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 12;57:555–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANESHIRO T., LAW J. H. PHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE SYNTHESIS IN AGROBACTERIUM TUMEFACIENS. I. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF A PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE N-METHYLTRANSFERASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1705–1713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY E. P., WEISS S. B. The function of cytidine coenzymes in the biosynthesis of phospholipides. J Biol Chem. 1956 Sep;222(1):193–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoh H. Biosynthesis of molecular species of phosphatidyl choline and phosphatidyl ethanolamine from radioactive precursors in rat liver slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 10;176(4):756–763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. L., Steiner M. R. The occurrence of diphosphoinositide and triphosphoinositide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4889–4893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytter D., Miller J. E., Cornatzer W. E. Specificity for incorporation of choline and ethanolamine into rat-liver microsomal lecithins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 4;152(2):418–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough G. A., Nyc J. F. Methylation of ethanolamine phosphatides by microsomes from normal and mutant strains of Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):238–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner M. R., Lester R. L. In vitro study of the methylation pathway of phosphatidylcholine synthesis and the regulation of this pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 6;9(1):63–69. doi: 10.1021/bi00803a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waechter C. J., Steiner M. R., Lester R. L. Regulation of phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis by the methylation pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3419–3422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]