Abstract
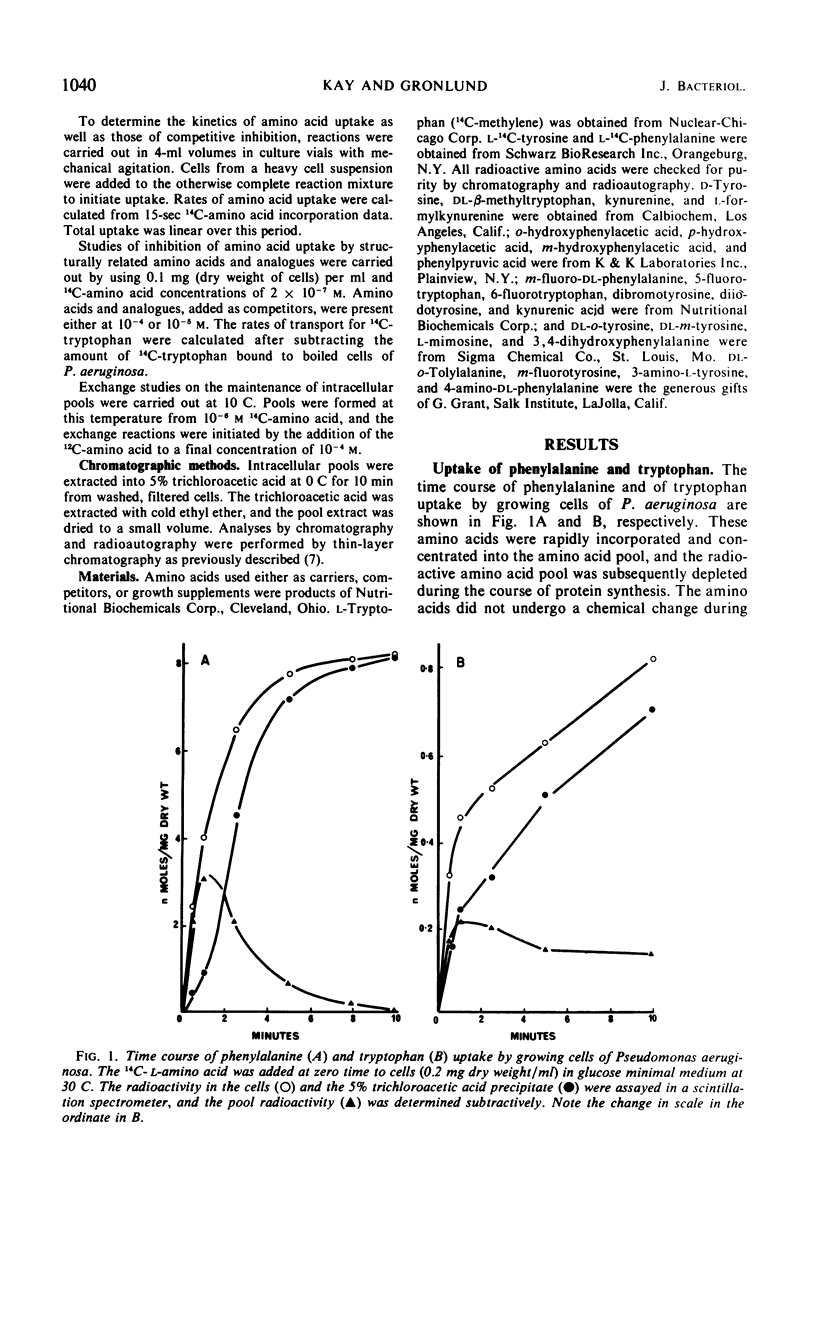
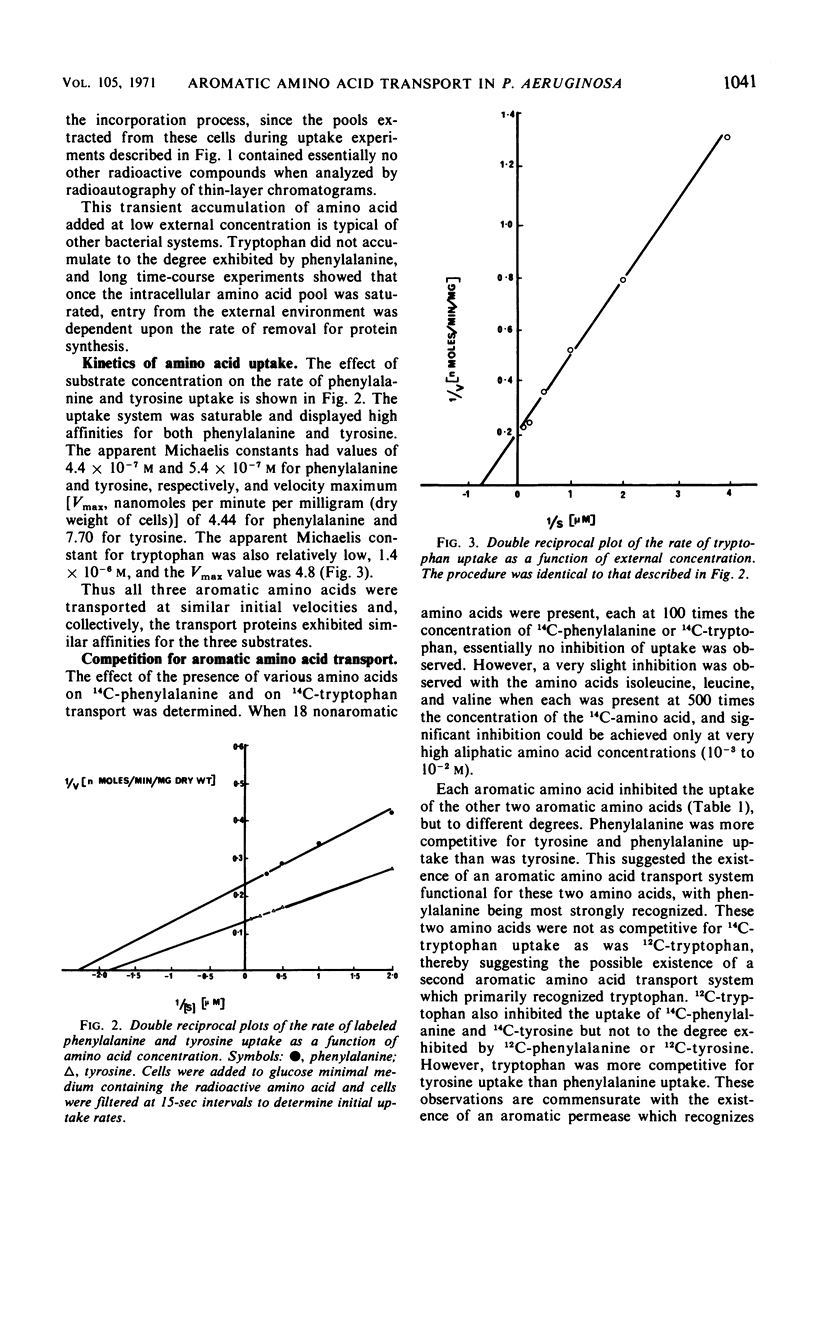
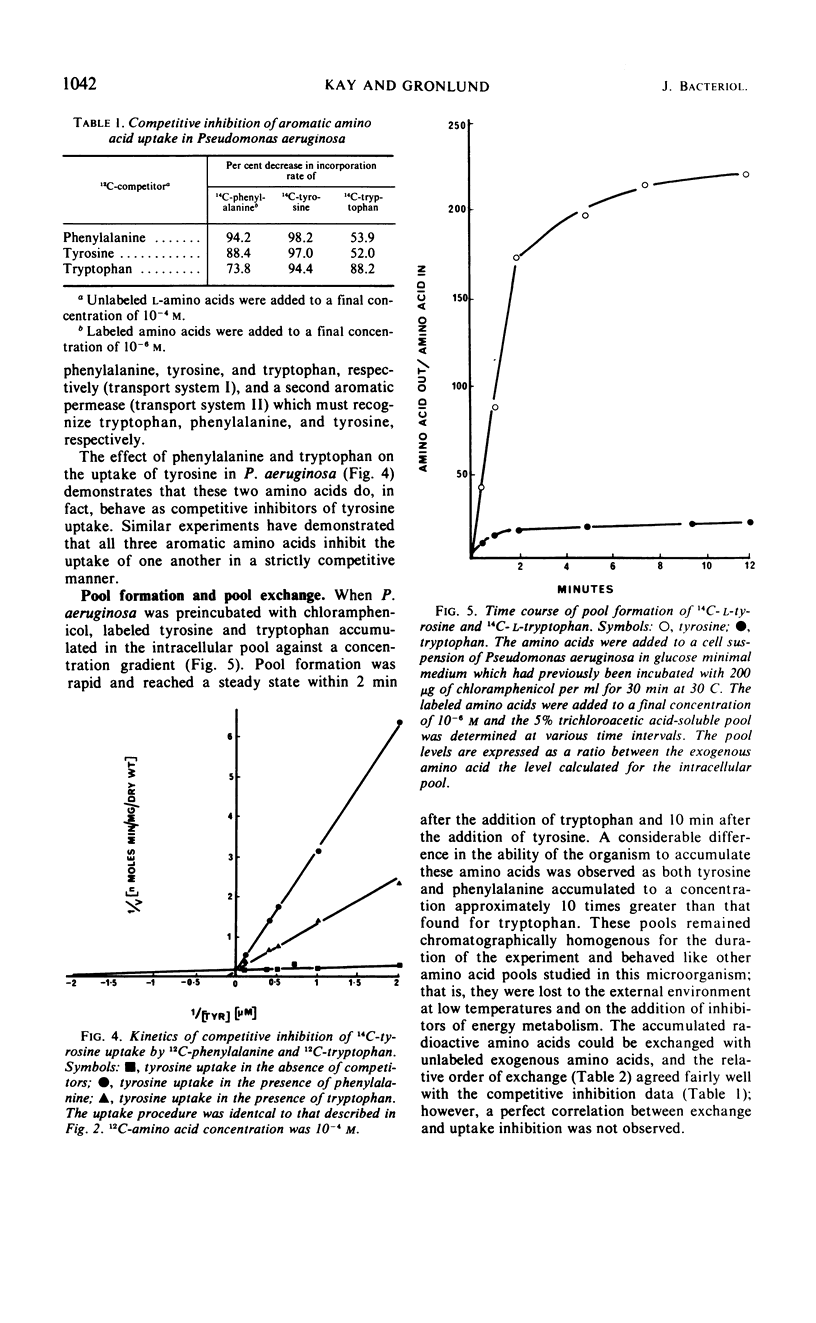
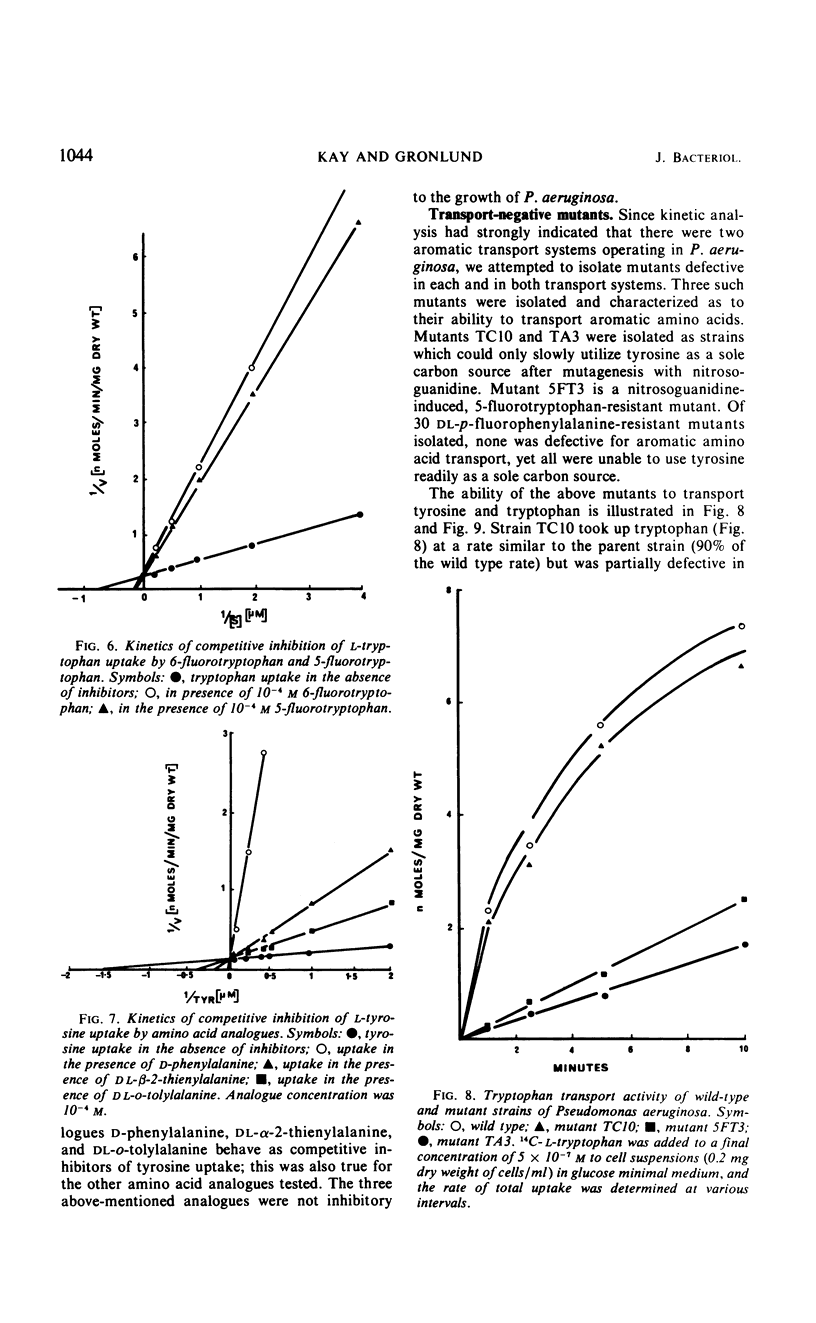
Kinetic studies of the transport of aromatic amino acids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa revealed the existence of two high-affinity transport systems which recognized the three aromatic amino acids. From competition data and studies on the exchange of preformed aromatic amino acid pools, the first transport system was found to be functional with phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan (in order of decreasing activity), whereas the second system was active with tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine. The two systems also transported a number of aromatic amino acid analogues but not other amino acids. Mutants defective in each of the two and in both transport systems were isolated and described. When the amino acids were added at low external concentrations to cells growing logarithmically in glucose minimal medium, the tryptophan pool very quickly became saturated. Under identical conditions, phenylalanine and tyrosine each accumulated in the intracellular pool of P. aeruginosa at a concentration which was 10 times greater than that of tryptophan.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES G. F. UPTAKE OF AMINO ACIDS BY SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Roth J. R. Histidine and aromatic permeases of Salmonella typhimurim. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1742–1749. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1742-1749.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Existence d'accepteurs spécifiques pour les aminoacides chez Escherichia coli. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1955 May 23;240(21):2086–2088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Gronlund A. F. Amino acid pool formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):282–291. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.282-291.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Gronlund A. F. Amino acid transport in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):273–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.273-281.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Gronlund A. F. Isolation of amino acid transport-negative mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cells with repressed transport activity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):116–123. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.116-123.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Gronlund A. F. Proline transport by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):444–455. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Amino acid transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5914–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld H., Feigelson P. Product induction in Pseudomonas acidovorans of a permease system which transports L-tryptophan. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):705–714. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.705-714.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shifrin S., Ames B. N., FerroLuzzi-Ames G. Effect of the alpha-hydrazino analogue of histidine on histidine transport and arginine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3424–3429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


