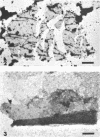
Abstract
Sulfur particles were isolated from the purple sulfur photosynthetic bacterium, Chromatium vinosum strain D. The composition of these particles was determined to be 93% sulfur, 5% protein, and 0.6% lipid. Gel electrophoresis indicated the presence of a single protein species with a molecular weight of 13,500 daltons. From these results, the sulfur particle is postulated to be bounded by a membrane consisting entirely of protein.
Full text
PDF
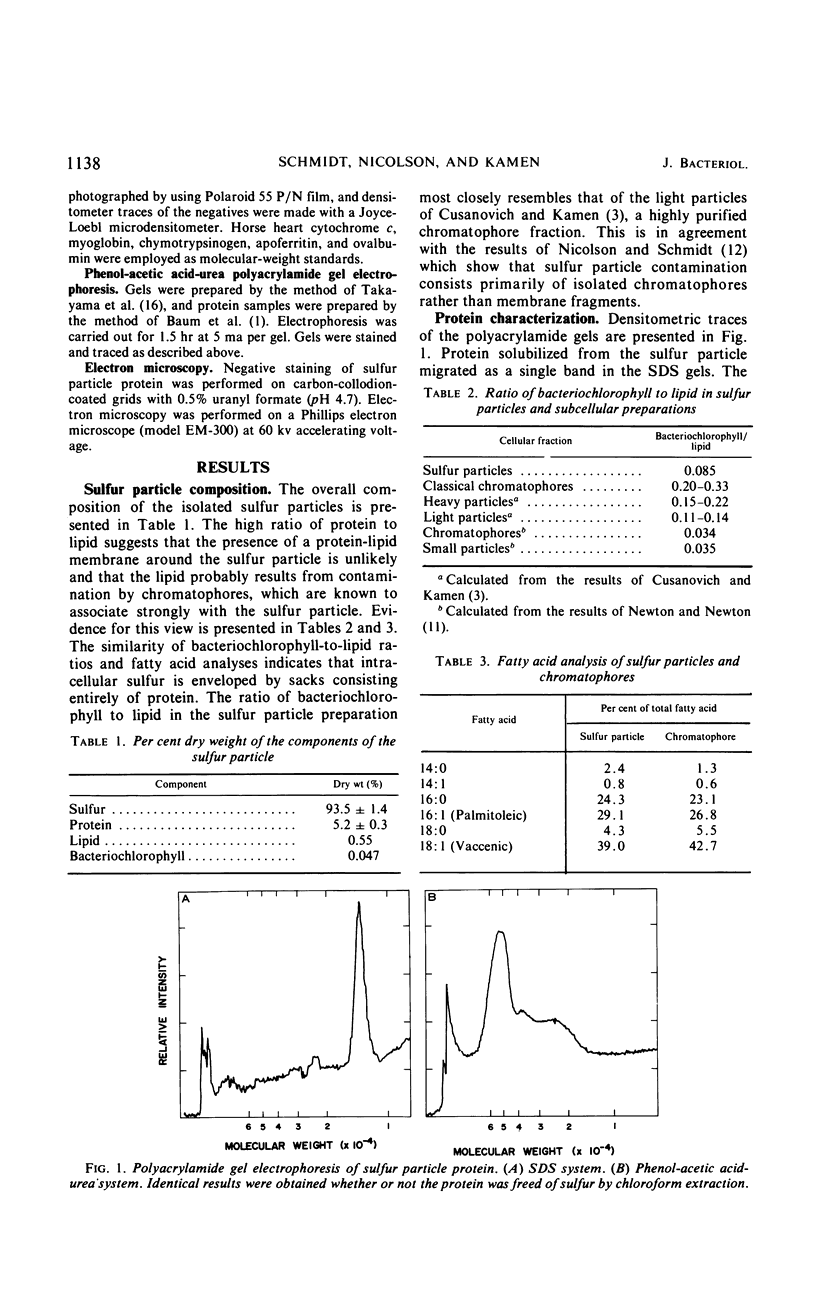



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum H., Silman H. I., Rieske H. S., Lipton S. H. On the composition and structural organization of complex 3 of the mitochondrial electron transfer chain. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):4876–4887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusanovich M. A., Kamen M. D. Light-induced electron transport in Chromatium strain D. I. Isolation and characterization of Chromatium chromatophores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 12;153(2):376–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90082-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageage G. J., Jr, Eanes E. D., Gherna R. L. X-ray diffraction studies of the sulfur globules accumulated by Chromatium species. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):464–469. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.464-469.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRICK J. M., DOUDOROFF M. DEPOLYMERIZATION OF POLY-BETA-HYDROXYBUTYRATE BY INTRACELLULAR ENZYME SYSTEM. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:60–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.60-71.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON J. W., NEWTON G. A. Composition of the photoactive subcellular particles from Chromatium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Sep;71(1):250–265. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Schmidt G. L. Structure of the Chromatium sulfur particle and its protein membrane. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1142–1148. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1142-1148.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. L., Kamen M. D. Variable cellular composition of Chromatium in browing cultures. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;73(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00409947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. V., Peat A., Bailey C. J. The isolation and characterisation of gas-cylinder membranes and alpha-granules from Anabaena flos-aquae D 124. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;65(2):87–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00693312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., MacLennan D. H., Tzagoloff A., Stoner C. D. Studies on the electron transfer system. LXVII. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the mitochondrial electron transfer complexes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toeckenius W., Kunau W. H. Further characterization of particulate fractions from lysed cell envelopes of Halobacterium halobium and isolation of gas vacuole membranes. J Cell Biol. 1968 Aug;38(2):337–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]