Abstract
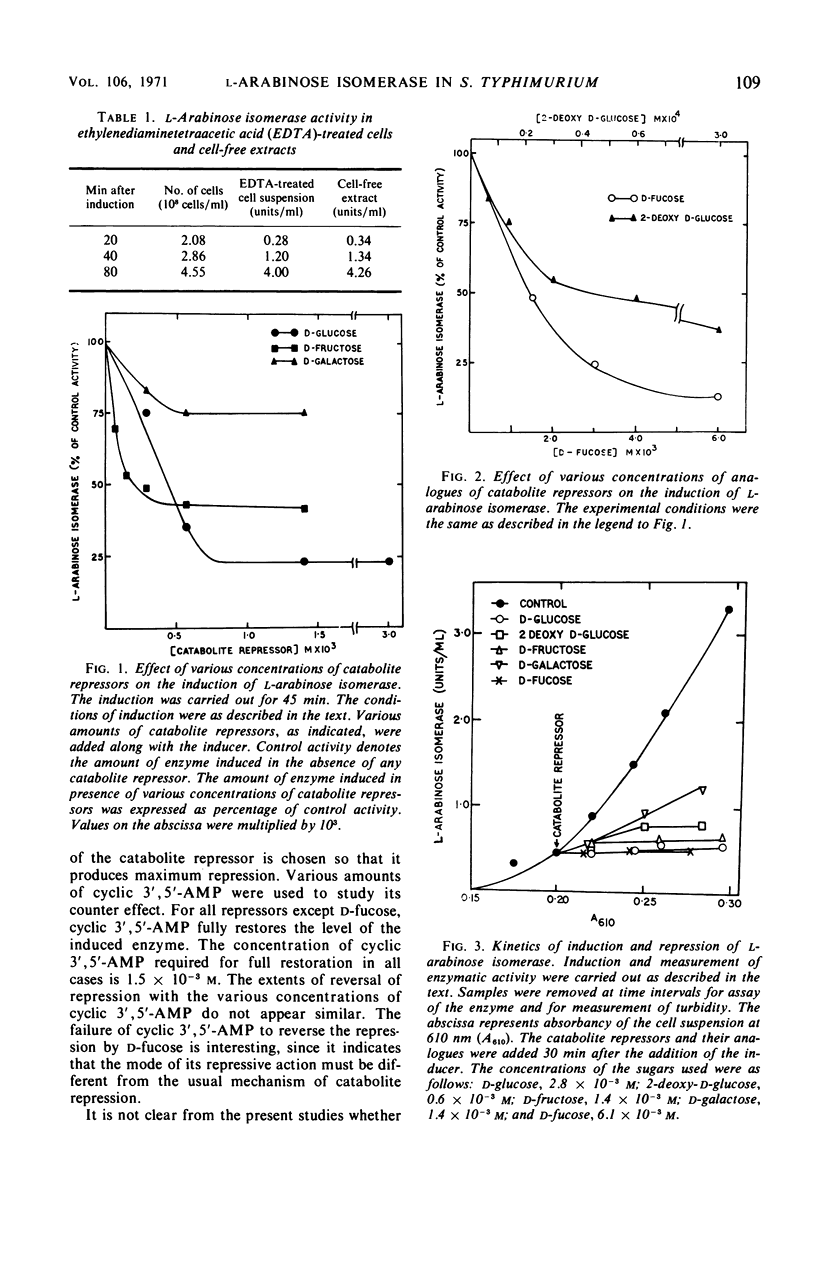
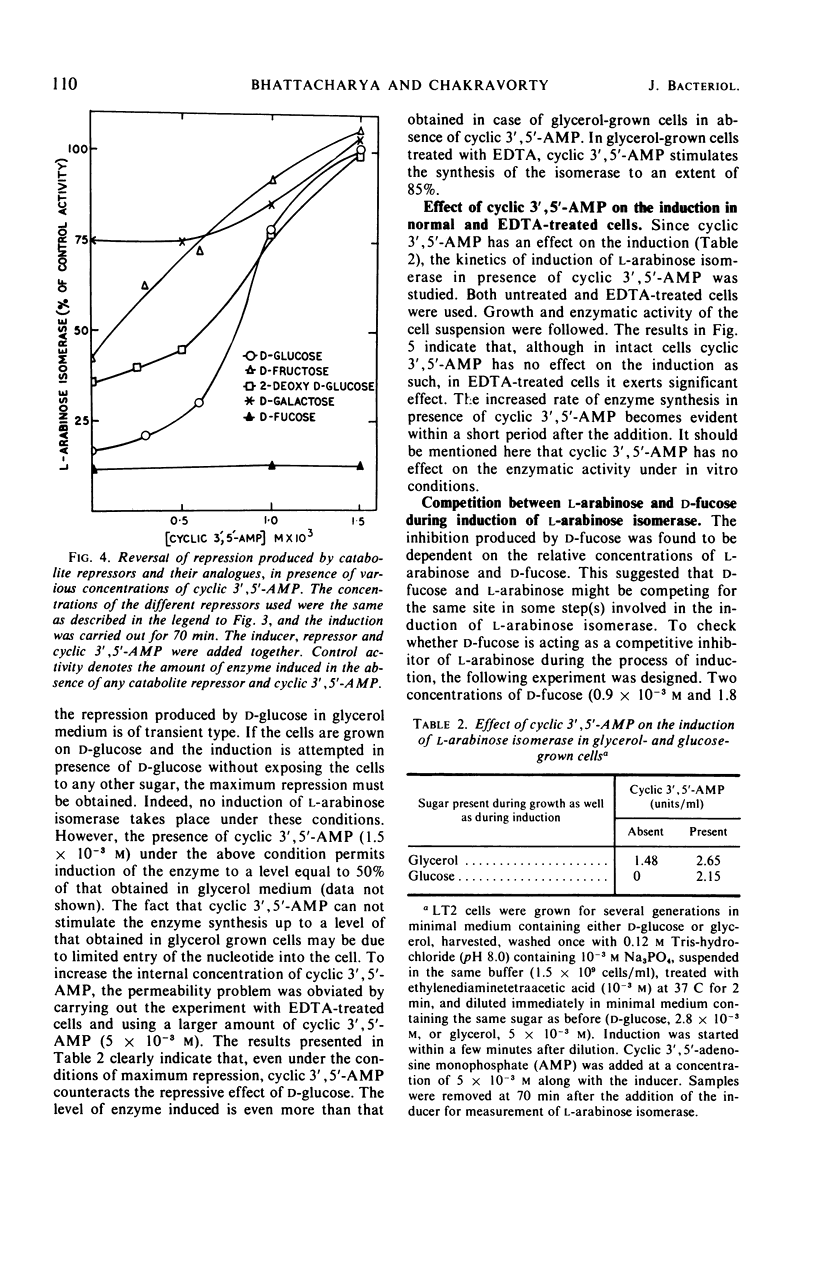
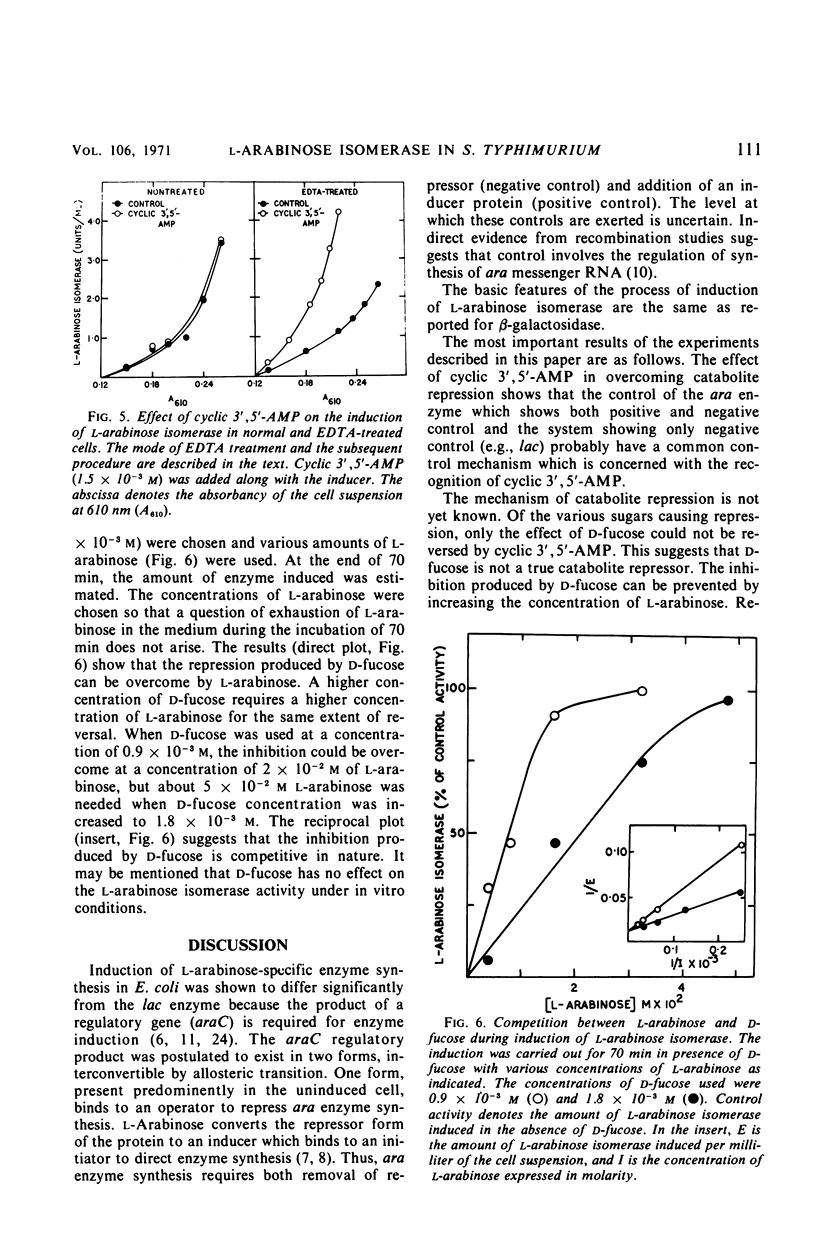
As with other inducible enzymes, the induced synthesis of l-arabinose isomerase (l-arabinose ketol isomerase, EC 5.3.1.4) in Salmonella typhimurium is subject to catabolite repression. Of the three catabolite repressors tested, glucose produces maximum repression. Analogues of catabolite repressors like 2-deoxy-d-glucose and d-fucose also inhibit the synthesis of the enzyme. The catabolite repression is completely reversed in the presence of 1.5 × 10−3m cyclic 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate (AMP). The maximum repression is produced in glucose-grown cells in glucose-containing induction medium. Cyclic 3′,5-AMP reverses this repression provided that the cells are treated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). In normal cells, cyclic 3′,5′-AMP has no effect on the induction but in EDTA-treated cells the cyclic nucleotide enhances synthesis of the enzyme. The inhibition produced by d-fucose cannot be reversed by cyclic 3′,5′-AMP. d-Fucose competes with the inducer l-arabinose in some step(s) involved in the process of induction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAKRAVORTY M. INDUCTION AND REPRESSION OF L-ARABINOSE ISOMERASE IN LACTOBACILLUS PLANTARUM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 6;85:152–161. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravorty M. Induction and repression of L-arabinose isomerase in bacteriophage-infected Salmonella typhimurium. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):541–547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.541-547.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z., BORENFREUND E. A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J Biol Chem. 1951 Oct;192(2):583–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOBROGOSZ W. J., DEMOSS R. D. INDUCTION AND REPRESSION OF L-ARABINOSE ISOMERASE IN PEDIOCOCCUS PENTOSACEUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1350–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1350-1355.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Crombrugghe B., Perlman R. L., Varmus H. E., Pastan I. Regulation of inducible enzyme synthesis in Escherichia coli by cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5828–5835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Irr J., Power J., Lee N. Positive control of enzyme synthesis by gene C in the L-arabinose system. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):946–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.946-957.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Sheppard D., Squires C., Meronk F., Jr An analysis of "revertants" of a deletion mutant in the C gene of the L-arabinose gene complex in Escherichia coli B-r: isolation of initiator constitutive mutants (Ic). J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 28;43(2):281–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Squires C., Meronk F., Jr The L-arabinose operon in Escherichia coli B-r: a genetic demonstration of two functional states of the product of a regulator gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1100–1107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATH E. C., HORECKER B. L., SMYRNIOTIS P. Z., TAKAGI Y. Pentose fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum. II. L-arabinose isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):1031–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLING R. B., WEINBERG R. COMPLEMENTATION STUDIES OF ARABINOSE GENES IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Genetics. 1963 Oct;48:1397–1410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.10.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B. The effect of arabinose-specific enzyme synthesis on recombination in the arabinose genes of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1967 Nov;57(3):665–675. doi: 10.1093/genetics/57.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet M., Kepes A. The step sensitive to catabolite repression and its reversal by 3'-5' cyclic AMP during induced synthesis of beta-galactosidase in E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 7;36(1):84–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90653-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamatu T., Yamanaka K. Crystallization and properties of L-arabinose isomerase from Lactobacillus gayonii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;178(1):156–165. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny C. P., Englesberg E. The L-arabinose permease system in Escherichia coli B/r. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):217–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen K. Phenomenon of transient repression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1201–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1201-1209.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. L. Stimulation of tryptophanase synthesis in Escherichia coli by cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2226–2232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. L. The role of the lac promotor locus in the regulation of beta-galactosidase synthesis by cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1336–1342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J. W., Lee N. Purification and properties of an L-arabinose isomerase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4312–4318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R. L., De Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Cyclic AMP regulates catabolite and transient repression in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Aug 23;223(5208):810–812. doi: 10.1038/223810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R. L., Pastan I. Regulation of beta-galactosidase synthesis in Escherichia coli by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5420–5427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R., Pastan I. Cyclic 3'5-AMP: stimulation of beta-galactosidase and tryptophanase induction in E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Mar 27;30(6):656–664. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90563-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard D. E., Englesberg E. Further evidence for positive control of the L-arabinose system by gene araC. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Loomis W. F., Jr, Magasanik B. Transient repression of the lac operon. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):2001–2011. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.2001-2011.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A., Monod J. Cyclic AMP as an antagonist of catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1968 Nov;2(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


