Abstract
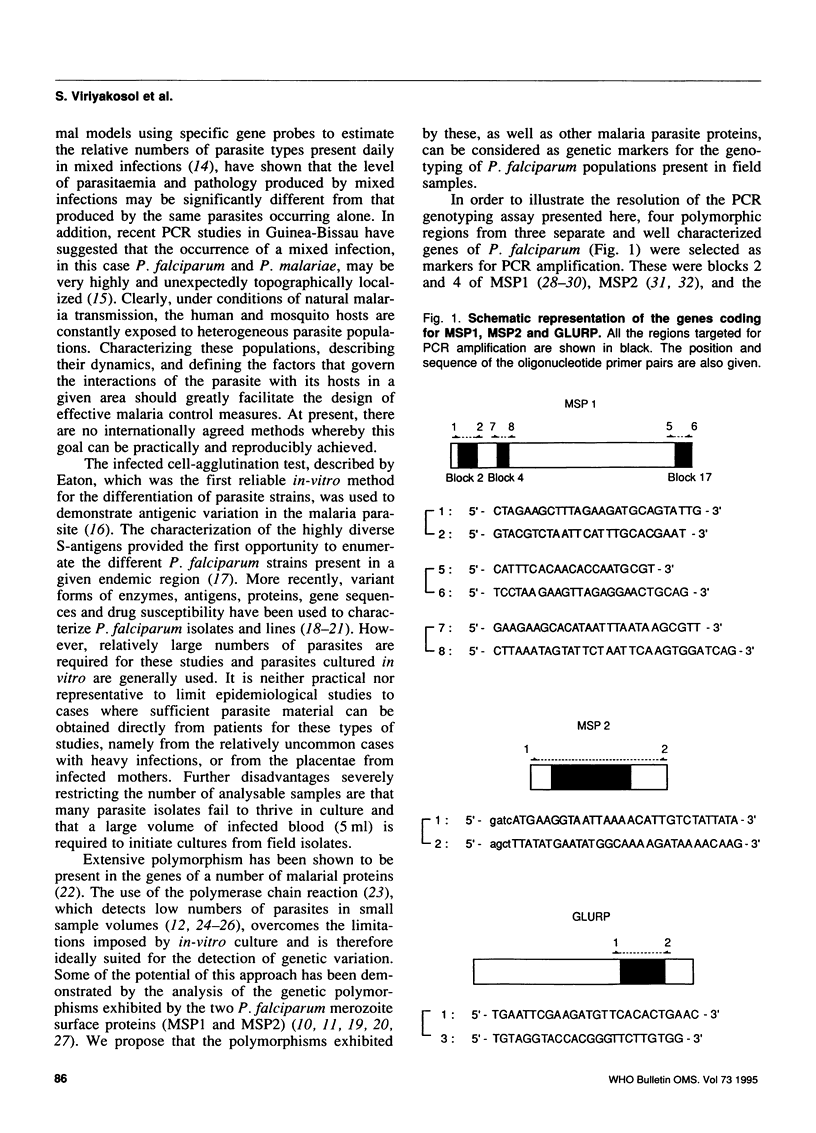
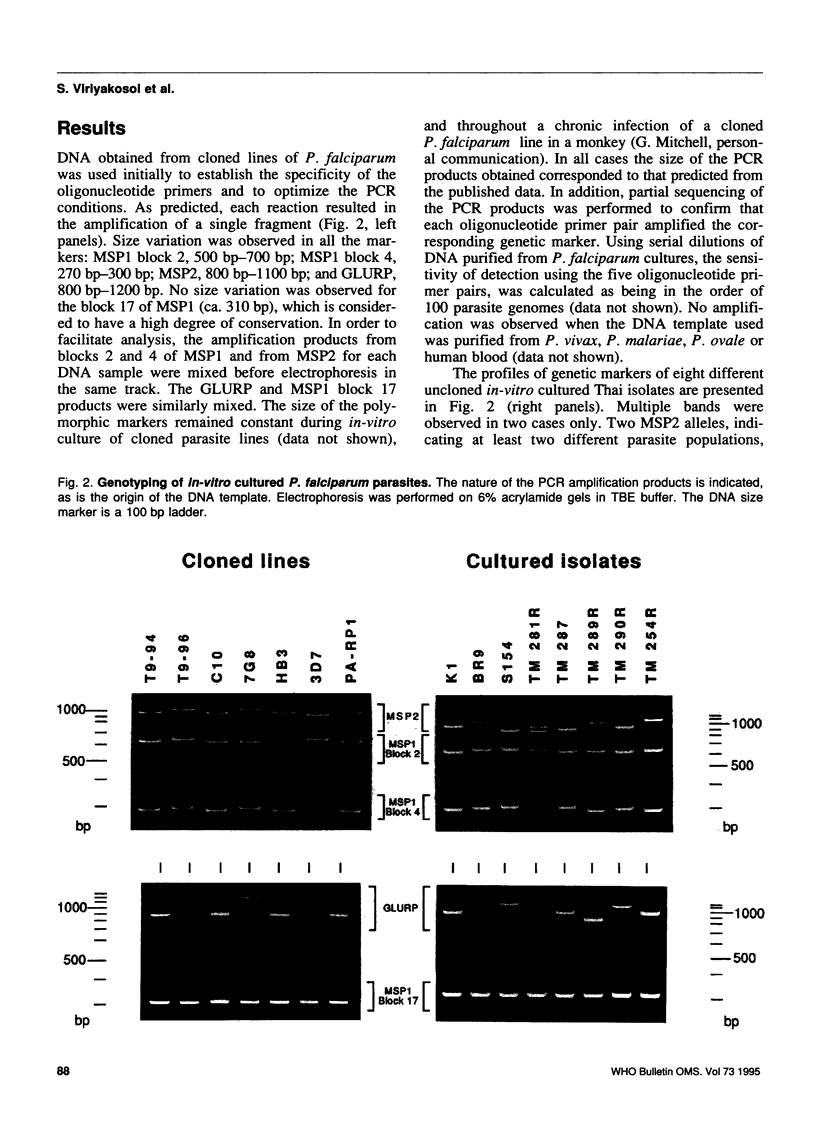
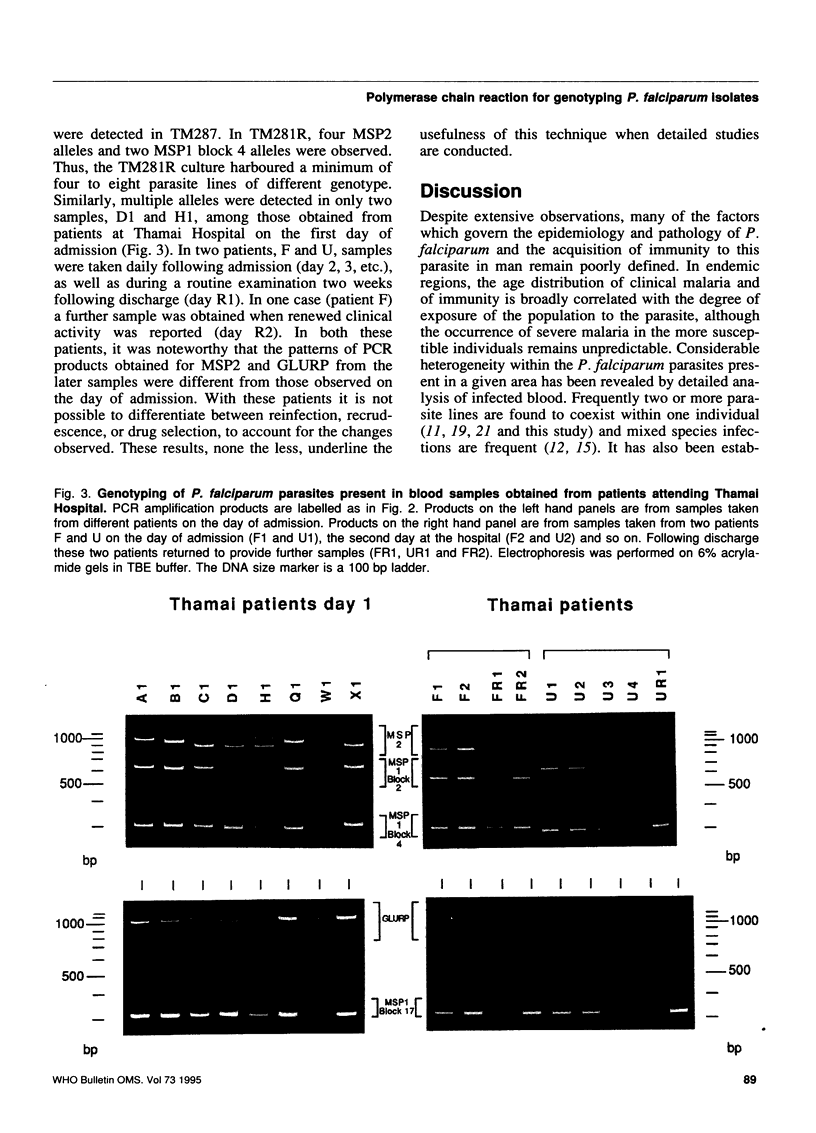
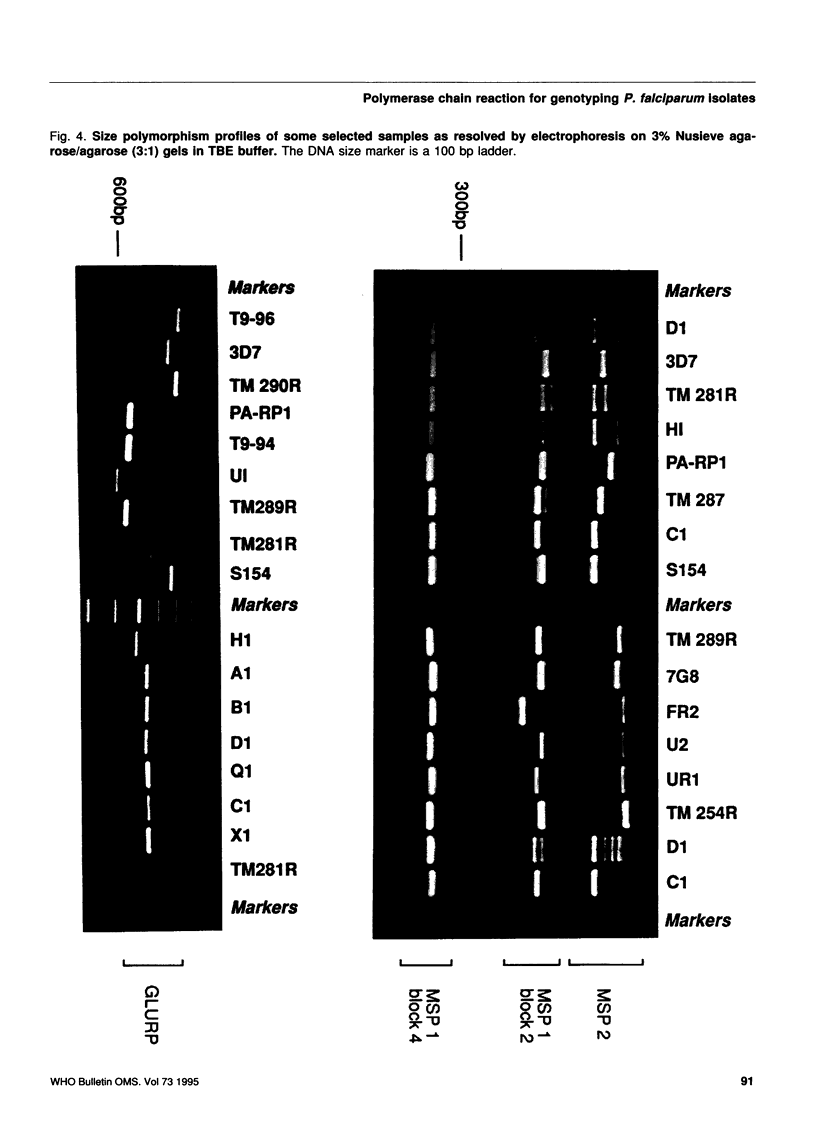
The epidemiology of malaria results from the interactions of three gene pools--parasite, human, and mosquito vector--with one another and with their environment. Methods are being developed for characterizing the genetics of human populations at risk and of potential vectors. The characterization of natural populations of Plasmodium and knowledge of their distribution within the human and insect hosts in any given area under study would also greatly enhance understanding of the epidemiology, pathology and biology of this parasite, particularly when combined with simultaneous human and vector studies. This paper describes a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based assay which provides a sensitive, reproducible and practical method by which parasite populations within species can be characterized. In order to illustrate the suitability of the PCR assay, four polymorphic domains on the genes of three P. falciparum proteins (MSP1 blocks 2 and 4, MSP2, and GLURP) and one largely conserved region (MSP1 block 17) were chosen for amplification by PCR. DNA derived from 15 in-vitro cultured lines of P. falciparum (7 of which were cloned) and from blood samples obtained from infected patients in Thailand were used as templates for PCR amplification. The amplification products were analysed by gel electrophoresis for length polymorphisms. Seven allelic variants of GLURP, five of MSP1 block 2, three of MSP1 block 4, and nine of MSP2 were detected. This high degree of polymorphism can be used to characterize the genetic composition of any parasite population, at a given time. The paper discusses the applicability of this type of genotyping to epidemiology and urges the adoption of international standards for its use so that data from different areas and different times can be compared.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders R. F., Smythe J. A. Polymorphic antigens in Plasmodium falciparum. Blood. 1989 Nov 1;74(6):1865–1875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. H., Jr, Banchongaksorn T., Courval J. M., Suwonkerd W., Rimwungtragoon K., Wirth D. F. A simple method to detect Plasmodium falciparum directly from blood samples using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Apr;46(4):416–426. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.46.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickle Q., Coppel R. L. A fourth family of the Plasmodium falciparum S-antigen. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Nov;56(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90161-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borre M. B., Dziegiel M., Høgh B., Petersen E., Rieneck K., Riley E., Meis J. F., Aikawa M., Nakamura K., Harada M. Primary structure and localization of a conserved immunogenic Plasmodium falciparum glutamate rich protein (GLURP) expressed in both the preerythrocytic and erythrocytic stages of the vertebrate life cycle. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Nov;49(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90135-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N. Immunity to malaria: antigenic variation in chronic infections of Plasmodium knowlesi. Nature. 1965 Dec 25;208(5017):1286–1288. doi: 10.1038/2081286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway D. J., McBride J. S. Population genetics of Plasmodium falciparum within a malaria hyperendemic area. Parasitology. 1991 Aug;103(Pt 1):7–16. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000059229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton B., Clark J. T., Khan C. M., Robinson J. V., Walliker D., Ridley R., Scaife J. G., McBride J. S. Structural and antigenic polymorphism of the 35- to 48-kilodalton merozoite surface antigen (MSA-2) of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):963–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley M., Ranford-Cartwright L. C., Babiker H. A. Rapid and simple method for isolating malaria DNA from fingerprick samples of blood. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jul;53(1-2):241–244. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90026-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V., Allsopp C. E., Kwiatkowski D., Anstey N. M., Twumasi P., Rowe P. A., Bennett S., Brewster D., McMichael A. J., Greenwood B. M. Common west African HLA antigens are associated with protection from severe malaria. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):595–600. doi: 10.1038/352595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. M., Urwin R., Crampton J. M. A comparison of non-radioactive labeling and detection systems with synthetic oligonucleotide probes for the species identification of mosquitoes in the Anopheles gambiae complex. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Jun;44(6):609–622. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1991.44.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongwutiwes S., Tanabe K., Nakazawa S., Uemura H., Kanbara H. Coexistence of GP195 alleles of Plasmodium falciparum in a small endemic area. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Mar;44(3):299–305. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1991.44.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kain K. C., Lanar D. E. Determination of genetic variation within Plasmodium falciparum by using enzymatically amplified DNA from filter paper disks impregnated with whole blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1171–1174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1171-1174.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura E., Mattei D., di Santi S. M., Scherf A. Genetic diversity in the major merozoite surface antigen of Plasmodium falciparum: high prevalence of a third polymorphic form detected in strains derived from malaria patients. Gene. 1990 Jul 2;91(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90162-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyes S., Craig A. G., Marsh K., Newbold C. I. Plasmodium falciparum: a method for the amplification of S antigens and its application to laboratory and field samples. Exp Parasitol. 1993 Dec;77(4):473–483. doi: 10.1006/expr.1993.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall V. M., Coppel R. L., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Two novel alleles within subfamilies of the merozoite surface antigen 2 (MSA-2) of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jan;50(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90255-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranford-Cartwright L. C., Balfe P., Carter R., Walliker D. Genetic hybrids of Plasmodium falciparum identified by amplification of genomic DNA from single oocysts. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Dec;49(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90067-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherf A., Mattei D., Sarthou J. L. Multiple infections and unusual distribution of block 2 of the MSA1 gene of Plasmodium falciparum detected in west African clinical isolates by polymerase chain reaction analysis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Feb;44(2):297–299. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90016-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snewin V. A., Herrera M., Sanchez G., Scherf A., Langsley G., Herrera S. Polymorphism of the alleles of the merozoite surface antigens MSA1 and MSA2 in Plasmodium falciparum wild isolates from Colombia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Dec;49(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90070-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snounou G., Bourne T., Jarra W., Viriyakosol S., Wood J. C., Brown K. N. Assessment of parasite population dynamics in mixed infections of rodent plasmodia. Parasitology. 1992 Dec;105(Pt 3):363–374. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000074539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snounou G., Pinheiro L., Gonçalves A., Fonseca L., Dias F., Brown K. N., do Rosario V. E. The importance of sensitive detection of malaria parasites in the human and insect hosts in epidemiological studies, as shown by the analysis of field samples from Guinea Bissau. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1993 Nov-Dec;87(6):649–653. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(93)90274-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snounou G., Viriyakosol S., Zhu X. P., Jarra W., Pinheiro L., do Rosario V. E., Thaithong S., Brown K. N. High sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Oct;61(2):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90077-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe K., Mackay M., Goman M., Scaife J. G. Allelic dimorphism in a surface antigen gene of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):273–287. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90649-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaithong S., Beale G. H., Fenton B., McBride J., Rosario V., Walker A., Walliker D. Clonal diversity in a single isolate of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(2):242–245. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. W., Carr D. A., Carter J. M., Lyon J. A. Sequence comparison of allelic forms of the Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface antigen MSA2. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Dec;43(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90146-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibayrenc M., Ayala F. J. Towards a population genetics of microorganisms: The clonal theory of parasitic protozoa. Parasitol Today. 1991 Sep;7(9):228–232. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90234-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirasophon W., Ponglikitmongkol M., Wilairat P., Boonsaeng V., Panyim S. A novel detection of a single Plasmodium falciparum in infected blood. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):179–184. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walliker D., Quakyi I. A., Wellems T. E., McCutchan T. F., Szarfman A., London W. T., Corcoran L. M., Burkot T. R., Carter R. Genetic analysis of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1661–1666. doi: 10.1126/science.3299700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., McGregor I. A., Hall P., Williams K., Bartholomew R. Antigens associated with Plasmodium falciparum infections in man. Lancet. 1969 Jul 26;2(7613):201–205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91437-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooden J., Gould E. E., Paull A. T., Sibley C. H. Plasmodium falciparum: a simple polymerase chain reaction method for differentiating strains. Exp Parasitol. 1992 Sep;75(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(92)90180-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooden J., Kyes S., Sibley C. H. PCR and strain identification in Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitol Today. 1993 Aug;9(8):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(93)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]